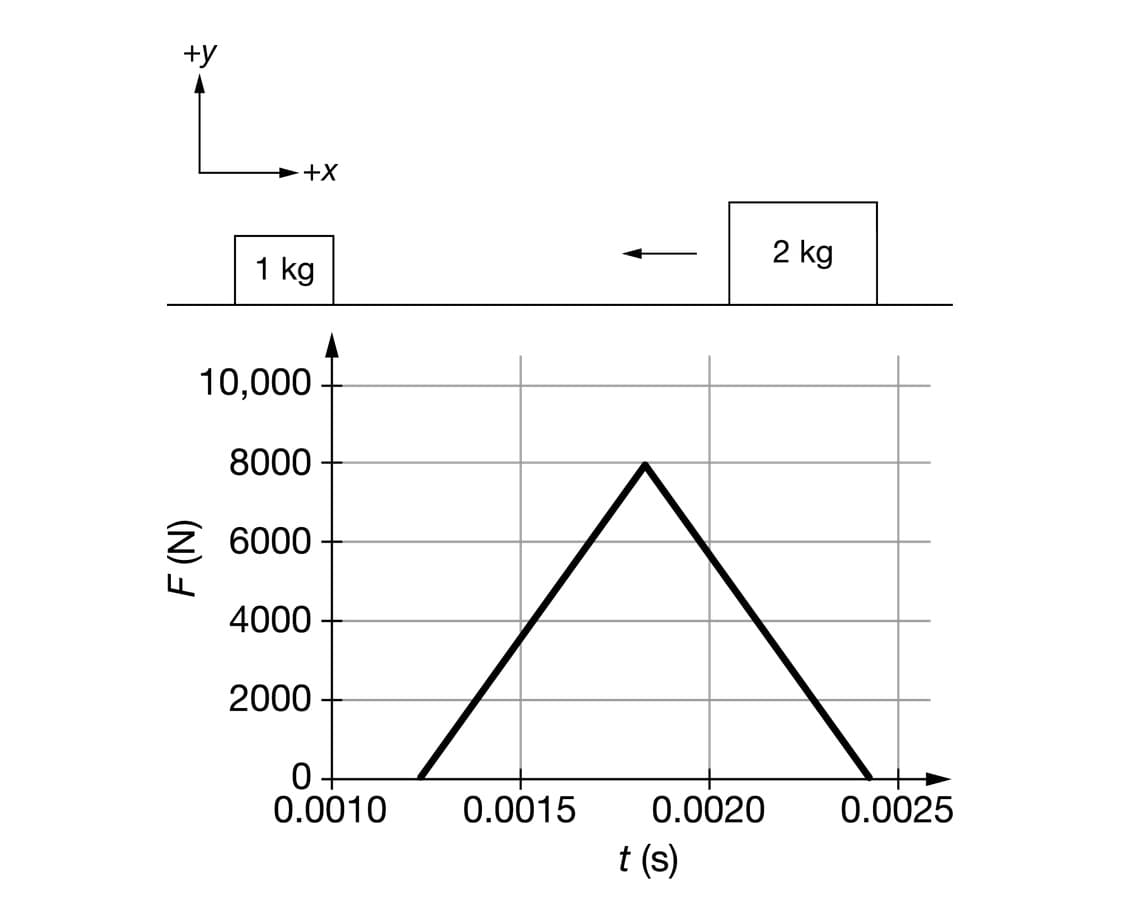
An object of mass 2 kg collides with an object of mass 1 kg that is at rest, as shown in the figure. A graph of the force as a function of time that the 1 kg object exerts on the 2 kg object is shown. After the collision, the 2 kg object has a speed of 2 , and the 1 kg object has a speed of 8 . A student must determine the initial speed vo of the 2 kg object. Which of the following options shows the correct substitutions into the equation Ap = FAt so that the initial speed of the unknown object can be determined? (2 kg)(2 - vo) = (8000 N)(0.00125 s), because the maximum force exerted on the 2 kg object must be considered. (2 kg)(2 – vo) = ÷(8000 N)(0.00125 s), because the average force exerted on the 2 kg object must be considered. (2 kg – 1 kg)(2 -vo) = (8000 N)(0.00125 s), because the difference in mass and the maximum force exerted on the 2 kg object must be considered. (2 kg – 1 kg)(2 m/s – vo) = (8000 N)(0.00125 s), because the difference in mass and the average force exerted on the 2 kg object must be considered.
An object of mass 2 kg collides with an object of mass 1 kg that is at rest, as shown in the figure. A graph of the force as a function of time that the 1 kg object exerts on the 2 kg object is shown. After the collision, the 2 kg object has a speed of 2 , and the 1 kg object has a speed of 8 . A student must determine the initial speed vo of the 2 kg object. Which of the following options shows the correct substitutions into the equation Ap = FAt so that the initial speed of the unknown object can be determined? (2 kg)(2 - vo) = (8000 N)(0.00125 s), because the maximum force exerted on the 2 kg object must be considered. (2 kg)(2 – vo) = ÷(8000 N)(0.00125 s), because the average force exerted on the 2 kg object must be considered. (2 kg – 1 kg)(2 -vo) = (8000 N)(0.00125 s), because the difference in mass and the maximum force exerted on the 2 kg object must be considered. (2 kg – 1 kg)(2 m/s – vo) = (8000 N)(0.00125 s), because the difference in mass and the average force exerted on the 2 kg object must be considered.
Astronomy
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168284
Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. Wolff
Publisher:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. Wolff
Chapter19: Celestial Distances
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7E: While a meter is the fundamental unit of length, most distances traveled by humans are measured in...
Related questions
Question
q9

Transcribed Image Text:An object of mass 2 kg collides with an object of mass 1 kg that is at rest, as shown in the figure. A graph
of the force as a function of time that the 1 kg object exerts on the 2 kg object is shown. After the
collision, the 2 kg object has a speed of 2 m, and the 1 kg object has a speed of 8 m. A student must
determine the initial speed vo of the 2 kg object. Which of the following options shows the correct
substitutions into the equation Ap = FAt so that the initial speed of the unknown object can be
determined?
(2 kg)(2 m – vo) = (8000 N)(0.00125 s), because the maximum force exerted on
the 2 kg object must be considered.
(2 kg)(2 - vo)
(8000 N)(0.00125 s), because the average force exerted on
m
S
the 2 kg object must be considered.
(2 kg – 1 kg)(2 -vo)
(8000 N)(0.00125 s), because the difference in mass
and the maximum force exerted on the 2 kg object must be considered.
(2 kg – 1 kg)(2 m/s – vo) = ;(8000 N)(0.00125 s), because the difference in
mass and the average force exerted on the 2 kg object must be considered.
Transcribed Image Text:+y
>+X
2 kg
1 kg
10,000
8000
2 6000
4000
2000
0 -
0.0010
0.0015
0.0020
0.0025
t (s)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168284
Author:
Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. Wolff
Publisher:
OpenStax

Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305960961
Author:
Michael A. Seeds, Dana Backman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168284
Author:
Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. Wolff
Publisher:
OpenStax

Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305960961
Author:
Michael A. Seeds, Dana Backman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College