As a collusive monopsony, NCAA hires less labor (Student- athletes) for a lower wage (student compensation is restricted to tuition, books, travel, meals etc). Microeconomic theory tells us that when input prices go down, the supply goes up, and equilibrium price charged to consumers is lower. Since NCAA pays lower wages, will consumers going to the game see lower prices on tickets? O Yes, since input prices (wage) went down O No, in a collusive monopsony, price charged to consumers will actually increase O No, the price charged to consumers will stay the same Yes, NCAA will profit from reduced price and higher attendance
As a collusive monopsony, NCAA hires less labor (Student- athletes) for a lower wage (student compensation is restricted to tuition, books, travel, meals etc). Microeconomic theory tells us that when input prices go down, the supply goes up, and equilibrium price charged to consumers is lower. Since NCAA pays lower wages, will consumers going to the game see lower prices on tickets? O Yes, since input prices (wage) went down O No, in a collusive monopsony, price charged to consumers will actually increase O No, the price charged to consumers will stay the same Yes, NCAA will profit from reduced price and higher attendance
Chapter16: Labor Markets
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 16.5P
Related questions
Question
8
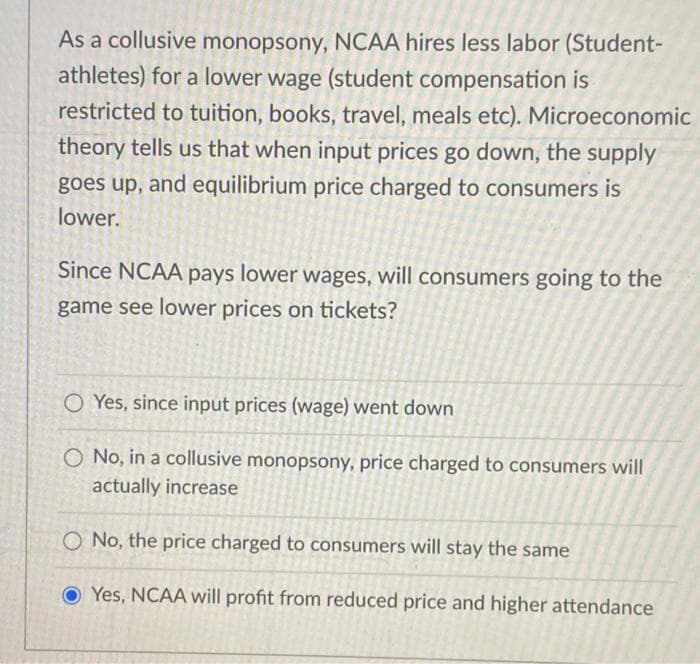
Transcribed Image Text:As a collusive monopsony, NCAA hires less labor (Student-
athletes) for a lower wage (student compensation is
restricted to tuition, books, travel, meals etc). Microeconomic
theory tells us that when input prices go down, the supply
goes up, and equilibrium price charged to consumers is
lower.
Since NCAA pays lower wages, will consumers going to the
game see lower prices on tickets?
O Yes, since input prices (wage) went down
O No, in a collusive monopsony, price charged to consumers will
actually increase
No, the price charged to consumers will stay the same
Yes, NCAA will profit from reduced price and higher attendance

Transcribed Image Text:Your answer to the previous question can be explained by the differences in the Marginal Cost and
Average Total Cost faced by a monopsony vs a perfectly competitive firm.
A monopsony's Marginal Cost curve shifts upward, compared to a perfectly competitive firm.
A monopsony's ATC curve shifts down and left, compared to a perfectly competitive firm.
Why is that the case?
O Higher MC curve: A perfectly competitive firm faces an increasing wage. A monopsonist faces a decreasing wage
as labor increases
Lower ATC curve: By restricting the quantity of labor employed, a monopsonist can lower its average total cost,
and earn positive profits
O Higher MC curve: A perfectly competitive firm faces a constant wage. A monopsonist has to pay a higher wage as
it hires less labor
Lower ATC curve: By increasing the quantity of labor employed, a monopsonist can lower its average total cost,
and earn positive profits
Higher MC curve: A perfectly competitive firm faces a higher price on inputs, and a monopsonist can pay lower
price for inputs
Lower ATC curve: By restricting the quantity of labor employed, a monopsonist can increase its average total cost,
thus increasing profits
Higher MC curve: A perfectly competitive firm faces a constant wage. A monopsonist has to pay a higher
wage as it hires more labor
Lower ATC curve: By restricting the quantity of labor employed, a monopsonist can lower its average total
cost, and earn positive profits
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning