Assume a population of 46, 51, 53, and 59. Assume that samples of sizen=2 are randomly selected with replacement from the population. Listed below are the sixteen different samples. Complete parts (a) through (c). 51,59 46,46 46,51 46,53 46,59 51,46 51,51 51,53 53,46 53,51 53,53 53,59 59,46 59,51 59,53 59,59 a. Find the median of each of the sixteen samples, then summarize the sampling distribution of the medians in the format of a table representing the probability distribution of the distinct median values. Use ascending order of the samp medians. Sample Median Probability Sample Median Probability (Type integers or simplified fractions. Use ascending order of the sample medians.) b. Compare the population median to the mean of the sample medians. Choose the correct answer below. O A. The population median is equal to half of the mean of the sample medians. O B. The population median is equal to the mean of the sample medians. O C. The population median is equal to double the mean of the sample medians. O D. The population median is not equal to the mean of the sample medians (it is also not half or double the mean of the sample medians). c. Do the sample medians target the value of the population median? In general, do sample medians make unbiased estimators of population medians? Why or why not? O A. The sample medians target the population median, so sample medians are biased estimators, because the mean of the sample medians equals the population median. O B. The sample medians target the population median, so sample medians are unbiased estimators, because the mean of the sample medians equals the population median. OC. The sample medians do not target the population median, so sample medians are biased estimators, because the mean of the sample medians does not equal the population median. O D. The sample medians do not target the population median, so sample medians are unbiased estimators, because the mean of the sample medians does not equal the population median. Click to select your answer(s).
Assume a population of 46, 51, 53, and 59. Assume that samples of sizen=2 are randomly selected with replacement from the population. Listed below are the sixteen different samples. Complete parts (a) through (c). 51,59 46,46 46,51 46,53 46,59 51,46 51,51 51,53 53,46 53,51 53,53 53,59 59,46 59,51 59,53 59,59 a. Find the median of each of the sixteen samples, then summarize the sampling distribution of the medians in the format of a table representing the probability distribution of the distinct median values. Use ascending order of the samp medians. Sample Median Probability Sample Median Probability (Type integers or simplified fractions. Use ascending order of the sample medians.) b. Compare the population median to the mean of the sample medians. Choose the correct answer below. O A. The population median is equal to half of the mean of the sample medians. O B. The population median is equal to the mean of the sample medians. O C. The population median is equal to double the mean of the sample medians. O D. The population median is not equal to the mean of the sample medians (it is also not half or double the mean of the sample medians). c. Do the sample medians target the value of the population median? In general, do sample medians make unbiased estimators of population medians? Why or why not? O A. The sample medians target the population median, so sample medians are biased estimators, because the mean of the sample medians equals the population median. O B. The sample medians target the population median, so sample medians are unbiased estimators, because the mean of the sample medians equals the population median. OC. The sample medians do not target the population median, so sample medians are biased estimators, because the mean of the sample medians does not equal the population median. O D. The sample medians do not target the population median, so sample medians are unbiased estimators, because the mean of the sample medians does not equal the population median. Click to select your answer(s).
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8CR
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
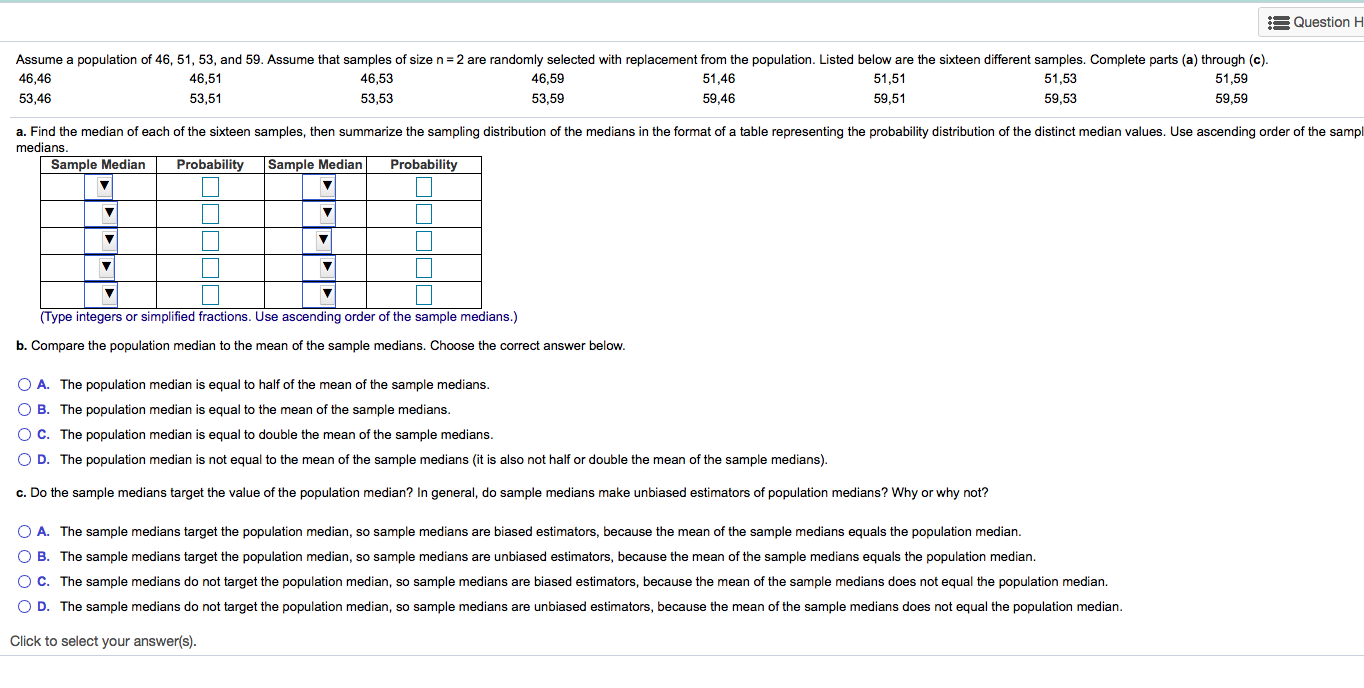
Transcribed Image Text:Assume a population of 46, 51, 53, and 59. Assume that samples of sizen=2 are randomly selected with replacement from the population. Listed below are the sixteen different samples. Complete parts (a) through (c).
51,59
46,46
46,51
46,53
46,59
51,46
51,51
51,53
53,46
53,51
53,53
53,59
59,46
59,51
59,53
59,59
a. Find the median of each of the sixteen samples, then summarize the sampling distribution of the medians in the format of a table representing the probability distribution of the distinct median values. Use ascending order of the samp
medians.
Sample Median
Probability
Sample Median
Probability
(Type integers or simplified fractions. Use ascending order of the sample medians.)
b. Compare the population median to the mean of the sample medians. Choose the correct answer below.
O A. The population median is equal to half of the mean of the sample medians.
O B. The population median is equal to the mean of the sample medians.
O C. The population median is equal to double the mean of the sample medians.
O D. The population median is not equal to the mean of the sample medians (it is also not half or double the mean of the sample medians).
c. Do the sample medians target the value of the population median? In general, do sample medians make unbiased estimators of population medians? Why or why not?
O A. The sample medians target the population median, so sample medians are biased estimators, because the mean of the sample medians equals the population median.
O B. The sample medians target the population median, so sample medians are unbiased estimators, because the mean of the sample medians equals the population median.
OC. The sample medians do not target the population median, so sample medians are biased estimators, because the mean of the sample medians does not equal the population median.
O D. The sample medians do not target the population median, so sample medians are unbiased estimators, because the mean of the sample medians does not equal the population median.
Click to select your answer(s).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning