Attempts Keep the Highest /3 7. Correcting for negative externalities - Taxes versus tradable permits Paper factories emit chemicals as a waste product. This generates a cost to society that is not paid for by the firm; therefore, pollution is a negative externality of paper production. Suppose the U.S. government wants to correct this market failure by getting firms to internalize the cost of pollution. To do this, the government can charge firms for pollution rights (the right to emit a given quantity of chemicals). The following graph shows the daily demand for pollution rights. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. Graph Input Tool Daily Demand for Pollution Rights 90 81 I Price (Dollars per ton) 9 72 Quantity Demanded 450 E 63 (Millions of tons) 54 45 36 27 Demand 18 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 QUANTITY (Millions of tons) Suppose the government has determined that the socially optimal quantity of chemical pollution is 350 million tons per day. One way governments can charge firms for pollution rights is by imposing a per-unit tax on emissions. A tax (or price in this case) of $ per ton of chemicals emitted will achieve the desired level of pollution. Now su ppose the IIS govern ment does pot know the demand cunve for pollution and therefore cannot determine the ontimal tay to achieve the PRICE (Dollars per ton)
Attempts Keep the Highest /3 7. Correcting for negative externalities - Taxes versus tradable permits Paper factories emit chemicals as a waste product. This generates a cost to society that is not paid for by the firm; therefore, pollution is a negative externality of paper production. Suppose the U.S. government wants to correct this market failure by getting firms to internalize the cost of pollution. To do this, the government can charge firms for pollution rights (the right to emit a given quantity of chemicals). The following graph shows the daily demand for pollution rights. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. Graph Input Tool Daily Demand for Pollution Rights 90 81 I Price (Dollars per ton) 9 72 Quantity Demanded 450 E 63 (Millions of tons) 54 45 36 27 Demand 18 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 QUANTITY (Millions of tons) Suppose the government has determined that the socially optimal quantity of chemical pollution is 350 million tons per day. One way governments can charge firms for pollution rights is by imposing a per-unit tax on emissions. A tax (or price in this case) of $ per ton of chemicals emitted will achieve the desired level of pollution. Now su ppose the IIS govern ment does pot know the demand cunve for pollution and therefore cannot determine the ontimal tay to achieve the PRICE (Dollars per ton)
Chapter8: Market Failure
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2P: Draw a standard supply and demand diagram for televisions, and indicate the equilibrium price and...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Back to Assignment
Attempts
Keep the Highest / 3
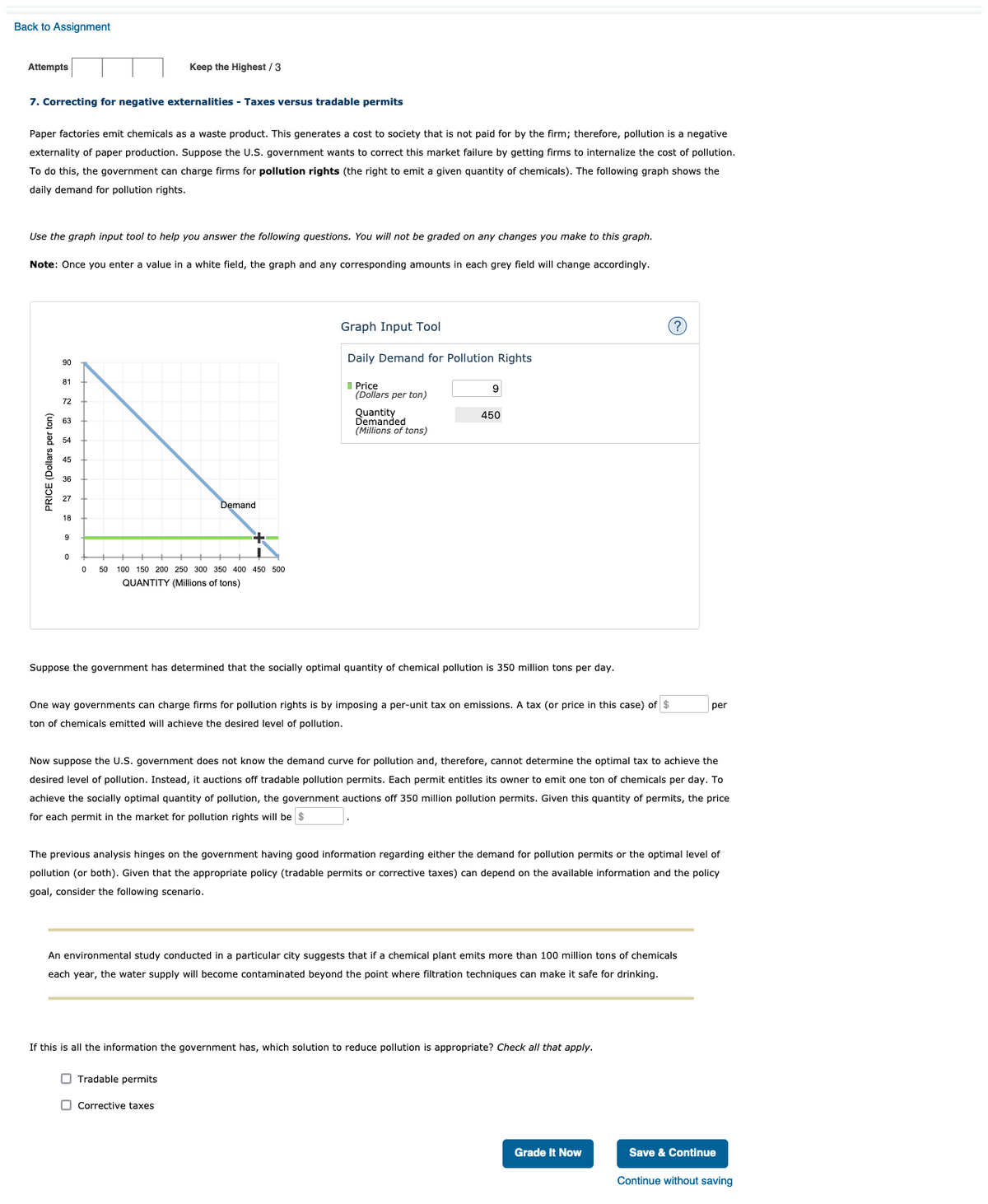
7. Correcting for negative externalities - Taxes versus tradable permits
Paper factories emit chemicals as a waste product. This generates a cost to society that is not paid for by the firm; therefore, pollution is a negative
externality of paper production. Suppose the U.S. government wants to correct this market failure by getting firms to internalize the cost of pollution.
To do this, the government can charge firms for pollution rights (the right to emit a given quantity of chemicals). The following graph shows the
daily demand for pollution rights.
Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph.
Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly.
Graph Input Tool
(?
Daily Demand for Pollution Rights
90
81
I Price
(Dollars per ton)
72
Quantity
Demanded
(Millions of tons)
450
63
54
45
36
27
Demand
18
50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
QUANTITY (Millions of tons)
Suppose the government has determined that the socially optimal quantity of chemical pollution is 350 million tons per day.
One way governments can charge firms for pollution rights is by imposing a per-unit tax on emissions. A tax (or price in this case) of $
per
ton of chemicals emitted will achieve the desired level of pollution.
Now suppose the U.S. government does not know the demand curve for pollution and, therefore, cannot determine the optimal tax to achieve the
desired level of pollution. Instead, it auctions off tradable pollution permits. Each permit entitles its owner to emit one ton of chemicals per day. To
achieve the socially optimal quantity of pollution, the government auctions off 350 million pollution permits. Given this quantity of permits, the price
for each permit in the market for pollution rights will be $
The previous analysis hinges on the government having good information regarding either the demand for pollution permits or the optimal level of
pollution (or both). Given that the appropriate policy (tradable permits or corrective taxes) can depend on the available information and the policy
goal, consider the following scenario.
An environmental study conducted in a particular city suggests that if a chemical plant emits more than 100 million tons of chemicals
each year, the water supply will become contaminated beyond the point where filtration techniques can make it safe for drinking.
If this is all the information the government has, which solution to reduce pollution is appropriate? Check all that apply.
O Tradable permits
O Corrective taxes
Grade It Now
Save & Continue
Continue without saving
PRICE (Dollars per ton)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning