B-1. Which is more desirable assuming data are COST Decertaine the course dagram. 90 60 (45) 45 99 so 50 30 20 /2 40 50 B-2. A firm must decide whether to construct a small, medium or large stamping plant. A consultant's report indicates a 0.20 probability that demand will be low and 0.80 that demand will be high. If the firm builds a small facility and demand turns out to be low, the Net Present Value (NPV) will be $42M. If demand turns out to be high, the firm can either subcontract and realize the NPV of $42M or expand greatly for a Net Present Value of $48M. The firm could build a medium size facility as a hedge: if demand turns out to be low, its NPV is estimated at $22M; if demand turns out to be high, the firm could do nothing and realize a NPV of $46M, or could expand and realize a NPV of $50OM. If the firm builds a large facility and demand is low, the NPV will be ($20M), whereas high demand will result in a NPV of $72M. a) Analyze and solve this problem using a decision tree b) What is the Maximin Alternative and c) Compute the EVPI
B-1. Which is more desirable assuming data are COST Decertaine the course dagram. 90 60 (45) 45 99 so 50 30 20 /2 40 50 B-2. A firm must decide whether to construct a small, medium or large stamping plant. A consultant's report indicates a 0.20 probability that demand will be low and 0.80 that demand will be high. If the firm builds a small facility and demand turns out to be low, the Net Present Value (NPV) will be $42M. If demand turns out to be high, the firm can either subcontract and realize the NPV of $42M or expand greatly for a Net Present Value of $48M. The firm could build a medium size facility as a hedge: if demand turns out to be low, its NPV is estimated at $22M; if demand turns out to be high, the firm could do nothing and realize a NPV of $46M, or could expand and realize a NPV of $50OM. If the firm builds a large facility and demand is low, the NPV will be ($20M), whereas high demand will result in a NPV of $72M. a) Analyze and solve this problem using a decision tree b) What is the Maximin Alternative and c) Compute the EVPI
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter11: Simulation Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 68P
Related questions
Question
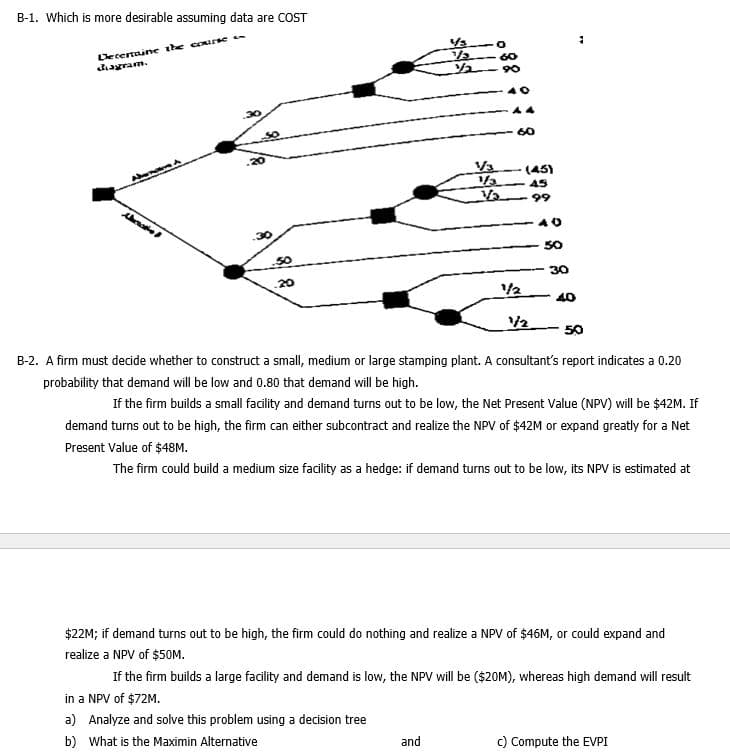
Transcribed Image Text:B-1. Which is more desirable assuming data are COST
Decenaine the cousen
dagram.
60
90
60
1/3
(45)
45
99
40
50
50
30
20
/2
40
50
B-2. A firm must decide whether to construct a small, medium or large stamping plant. A consultant's report indicates a 0.20
probability that demand will be low and 0.80 that demand will be high.
If the firm builds a small facility and demand turns out to be low, the Net Present Value (NPV) will be $42M. If
demand turns out to be high, the firm can either subcontract and realize the NPV of $42M or expand greatly for a Net
Present Value of $48M.
The firm could build a medium size facility as a hedge: if demand turns out to be low, its NPV is estimated at
$22M; if demand turns out to be high, the firm could do nothing and realize a NPV of $46M, or could expand and
realize a NPV of $50M.
If the firm builds a large facility and demand is low, the NPV will be ($20M), whereas high demand will result
in a NPV of $72M.
a) Analyze and solve this problem using a decision tree
b) What is the Maximin Alternative
and
c) Compute the EVPI
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,