b) In another experiment, the following equilibrium was established: 2 NO(g) + Cl₂(g) = 2 NOCI(g) 2.6 moles of NO(g) and 1.8 moles of Cl₂(g) were put in a sealed container and allowed to reach equilibrium. At equilibrium, there were 1.8 moles of NO(g) and the total pressure was 125 kPa. By constructing an ICE table (or other method) to find mole fractions and partial pressures at equilibrium, determine the equilibrium constant Kp for this reaction and give its units.
b) In another experiment, the following equilibrium was established: 2 NO(g) + Cl₂(g) = 2 NOCI(g) 2.6 moles of NO(g) and 1.8 moles of Cl₂(g) were put in a sealed container and allowed to reach equilibrium. At equilibrium, there were 1.8 moles of NO(g) and the total pressure was 125 kPa. By constructing an ICE table (or other method) to find mole fractions and partial pressures at equilibrium, determine the equilibrium constant Kp for this reaction and give its units.
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter12: Chemical Equilibrium
Section12.2: The Equilibrium Constant
Problem 12.3CE: After a mixture of cis-2-butene and trans-2-butene has reached equilibrium at 600 K, where Kc =...
Related questions
Question
Could you help me answer "part b" of this question please. Thank You
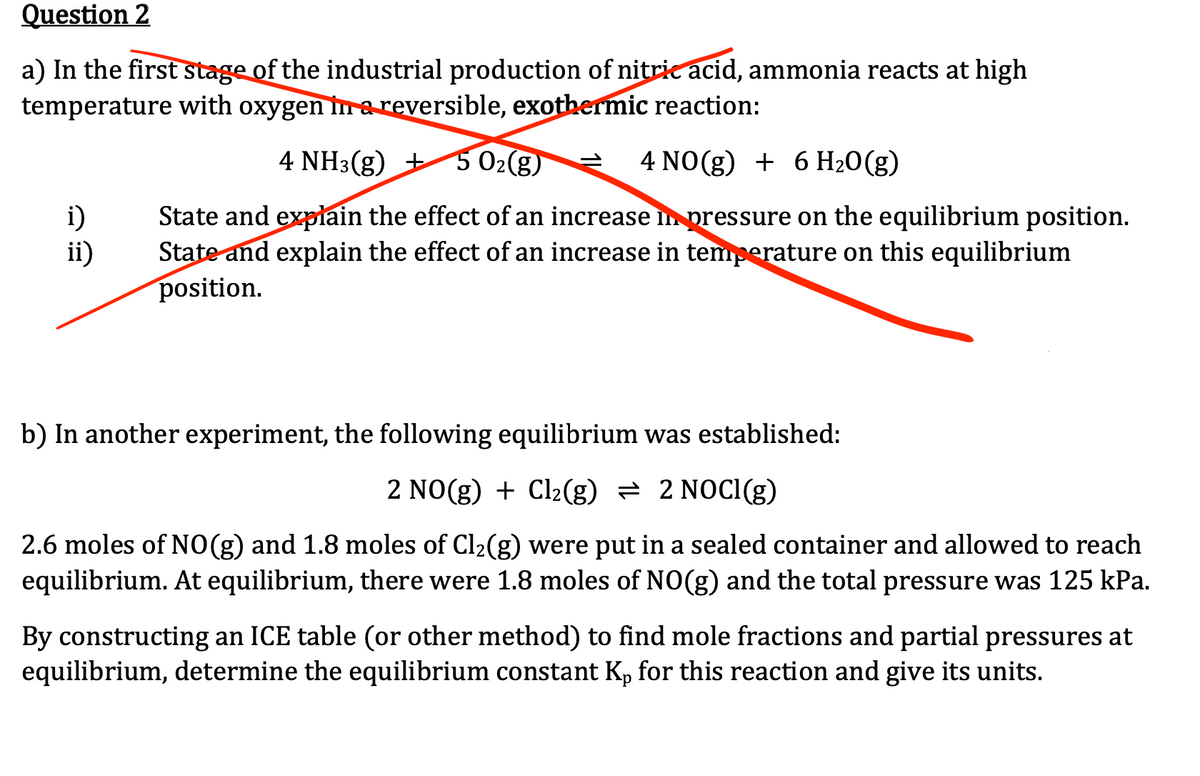
Transcribed Image Text:Question 2
a) In the first stage of the industrial production of nitric acid, ammonia reacts at high
temperature with oxygen in a reversible, exothermic reaction:
4 NH3(g) + 5 0₂(g)
4 NO(g) + 6 H₂O(g)
State and explain the effect of an increase in pressure on the equilibrium position.
State and explain the effect of an increase in temperature on this equilibrium
position.
i)
ii)
b) In another experiment, the following equilibrium was established:
2 NO(g) + Cl₂(g) = 2 NOCI(g)
2.6 moles of NO(g) and 1.8 moles of Cl₂(g) were put in a sealed container and allowed to reach
equilibrium. At equilibrium, there were 1.8 moles of NO(g) and the total pressure was 125 kPa.
By constructing an ICE table (or other method) to find mole fractions and partial pressures at
equilibrium, determine the equilibrium constant Kp for this reaction and give its units.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning