(b) What is the probability that a random sample of n = 40 oil changes results in a sample mean time less than 20 minutes? The probability is approximately 0.0467. (Round to four decimal places as needed.) (c) Suppose the manager agrees to pay each employee a $50 bonus if they meet a certain goal. On a typical Saturday, the oil-change facility will perform 40 oil changes between 10 A.M. and 12 P.M. Treating this as a random sample, at what mean oil-change time would there be a 10% chance of being at or below? This will be the goal established by the manager. There would be a 10% chance of being at or below minutes. (Round to one decimal place as needed.)
(b) What is the probability that a random sample of n = 40 oil changes results in a sample mean time less than 20 minutes? The probability is approximately 0.0467. (Round to four decimal places as needed.) (c) Suppose the manager agrees to pay each employee a $50 bonus if they meet a certain goal. On a typical Saturday, the oil-change facility will perform 40 oil changes between 10 A.M. and 12 P.M. Treating this as a random sample, at what mean oil-change time would there be a 10% chance of being at or below? This will be the goal established by the manager. There would be a 10% chance of being at or below minutes. (Round to one decimal place as needed.)
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.4: Distributions Of Data
Problem 19PFA
Related questions
Question
Pls answer both
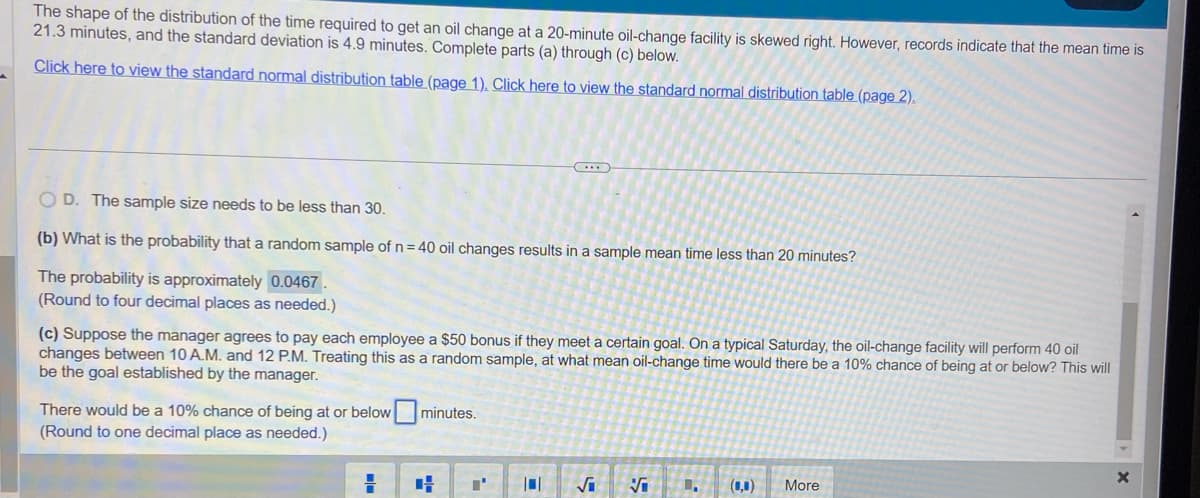
Transcribed Image Text:The shape of the distribution of the time required to get an oil change at a 20-minute oil-change facility is skewed right. However, records indicate that the mean time is
21.3 minutes, and the standard deviation is 4.9 minutes. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1). Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2).
OD. The sample size needs to be less than 30.
(b) What is the probability that a random sample of n = 40 oil changes results in a sample mean time less than 20 minutes?
The probability is approximately 0.0467.
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
(c) Suppose the manager agrees to pay each employee a $50 bonus if they meet a certain goal. On a typical Saturday, the oil-change facility will perform 40 oil
changes between 10 A.M. and 12 P.M. Treating this as a random sample, at what mean oil-change time would there be a 10% chance of being at or below? This will
be the goal established by the manager.
There would be a 10% chance of being at or below minutes.
(Round to one decimal place as needed.)
H
I'
101
√₁
Vi
1.
(0,0) More
X
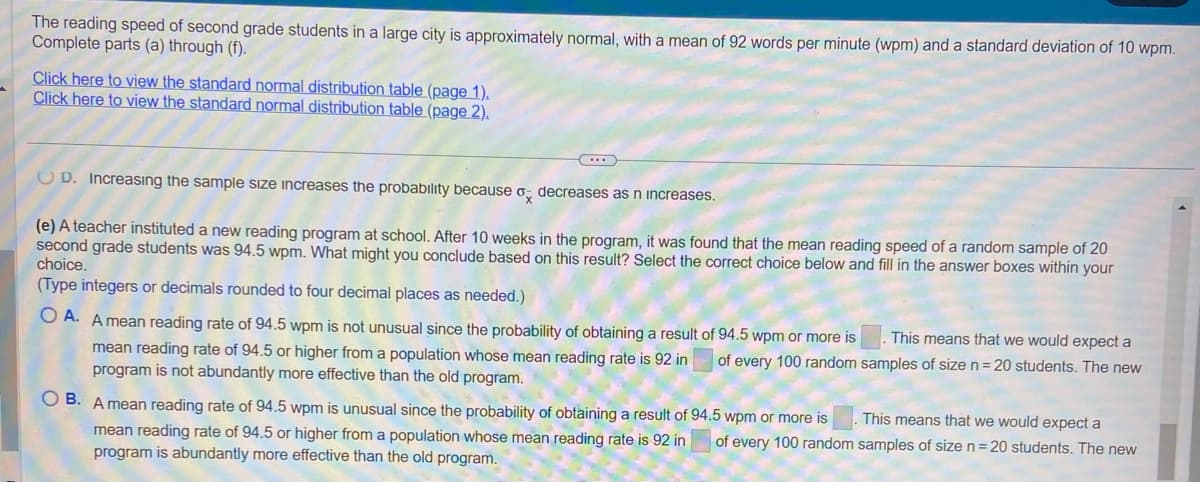
Transcribed Image Text:The reading speed of second grade students in a large city is approximately normal, with a mean of 92 words per minute (wpm) and a standard deviation of 10 wpm.
Complete parts (a) through (f).
Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1).
Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2).
(...)
UD. Increasing the sample size increases the probability because o decreases as n increases.
(e) A teacher instituted a new reading program at school. After 10 weeks in the program, it was found that the mean reading speed of a random sample of 20
second grade students was 94.5 wpm. What might you conclude based on this result? Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer boxes within your
choice.
(Type integers or decimals rounded to four decimal places as needed.)
OA. A mean reading rate of 94.5 wpm is not unusual since the probability of obtaining a result of 94.5 wpm or more is This means that we would expect a
mean reading rate of 94.5 or higher from a population whose mean reading rate is 92 in of every 100 random samples of size n = 20 students. The new
program is not abundantly more effective than the old program.
OB. A mean reading rate of 94.5 wpm is unusual since the probability of obtaining a result of
mean reading rate of 94.5 or higher from a population whose mean reading rate is 92 in
program is abundantly more effective than the old program.
94.5 wpm or more is
This means that we would expect a
of every 100 random samples of size n = 20 students. The new
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill