Based on what you have learned so far, provide your response to cach item below. 1. Refer to the figure as you answer the following questions: E D 1 2 4 5 cheeseburgers a. Bundle C is preferred to Bundle A because Bundle C represents a more balanced Bundle. Do you agree or disagree with this statement and why? b. Calculate the MRSXY between points A and B, and between points C and D. Interpret your computed values. C. What assumption about preferences would allow you to say that Bundle E is preferred to Bundle B? Briefly explain. d. Bundle E has one less cheeseburger than Bundle D. What assumption(s) would still allow you to say that Bundle E is preferred to Bundle D? Briefly explain. pearl shakes
Based on what you have learned so far, provide your response to cach item below. 1. Refer to the figure as you answer the following questions: E D 1 2 4 5 cheeseburgers a. Bundle C is preferred to Bundle A because Bundle C represents a more balanced Bundle. Do you agree or disagree with this statement and why? b. Calculate the MRSXY between points A and B, and between points C and D. Interpret your computed values. C. What assumption about preferences would allow you to say that Bundle E is preferred to Bundle B? Briefly explain. d. Bundle E has one less cheeseburger than Bundle D. What assumption(s) would still allow you to say that Bundle E is preferred to Bundle D? Briefly explain. pearl shakes
Chapter1: Making Economics Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1QTC
Related questions
Question
(1e)
Hello! I just want to ask for help whether the answers in the given pictures are correct. If it's not, please help me recheck and resolve it. Please refer to the given pictures below for the answers and questions.
After verifying the given answers shown in the subsequent picture, PLEASE ANSWER LETTER — D. Bundle E has one less cheeseburger than Bundle D. What assumption(s) would still allow you to say that Bundle E is preferred to Bundle D? Briefly explain.
NOTE: Type only your answers. Please do not handwritten your answers.
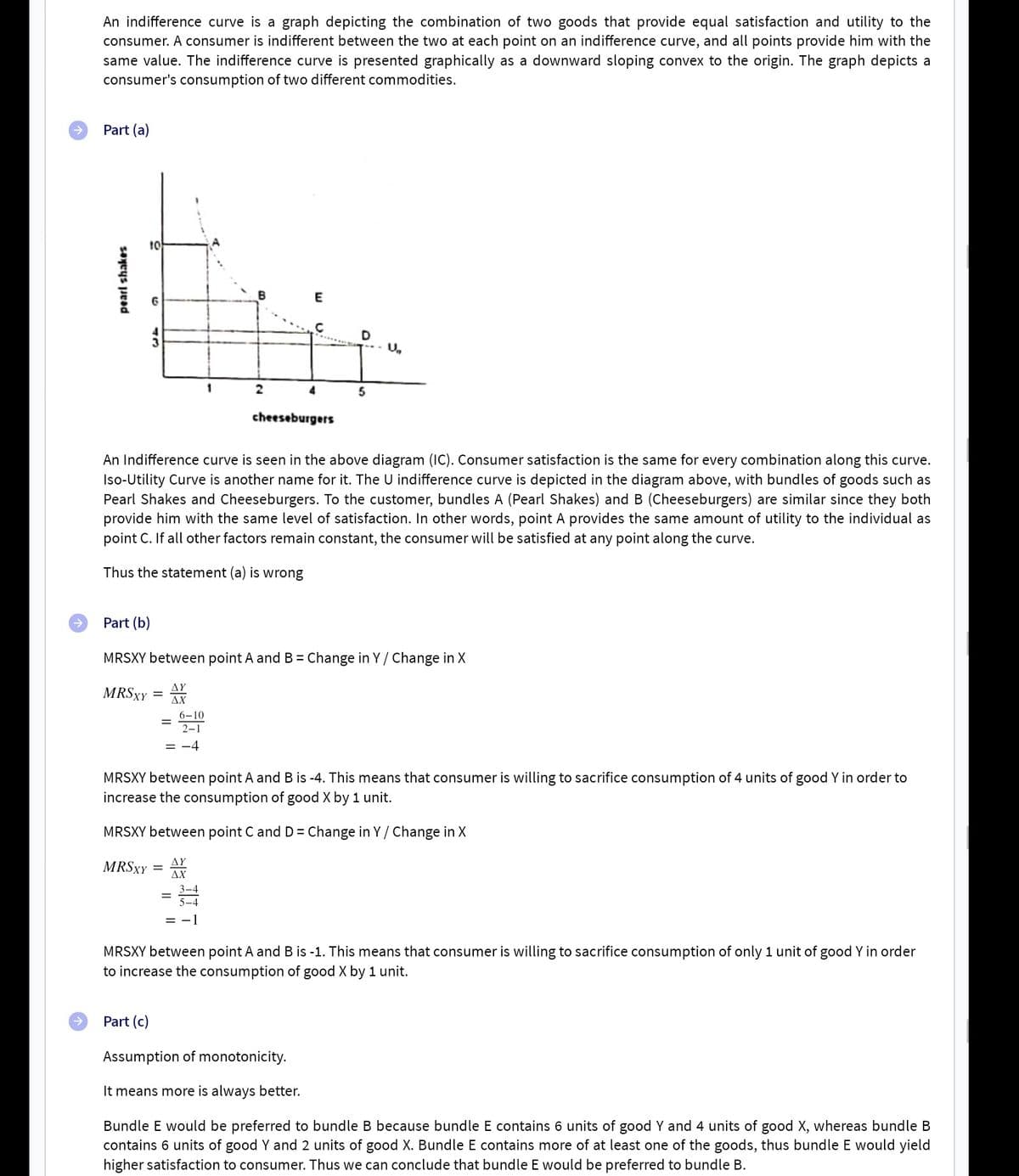
Transcribed Image Text:An indifference curve is a graph depicting the combination of two goods that provide equal satisfaction and utility to the
consumer. A consumer is indifferent between the two at each point on an indifference curve, and all points provide him with the
same value. The indifference curve is presented graphically as a downward sloping convex to the origin. The graph depicts a
consumer's consumption of two different commodities.
Part (a)
E
D
U,
2
cheeseburgers
An Indifference curve is seen in the above diagram (IC). Consumer satisfaction is the same for every combination along this curve.
Iso-Utility Curve is another name for it. The U indifference curve is depicted in the diagram above, with bundles of goods such as
Pearl Shakes and Cheeseburgers. To the customer, bundles A (Pearl Shakes) and B (Cheeseburgers) are similar since they both
provide him with the same level of satisfaction. In other words, point A provides the same amount of utility to the individual as
point C. If all other factors remain constant, the consumer will be satisfied at any point along the curve.
Thus the statement (a) is wrong
Part (b)
MRSXY between point A and B = Change in Y/ Change in X
ΔΥ
MRSXY
AX
6-10
2-1
= -4
MRSXY between point A and B is -4. This means that consumer is willing to sacrifice consumption of 4 units of good Y in order to
increase the consumption of good X by 1 unit.
MRSXY between point C and D= Change in Y/ Change in X
AY
MRSXY
AX
3-4
5-4
= -1
MRSXY between point A and B is -1. This means that consumer is willing to sacrifice consumption of only 1 unit of good Y in order
to increase the consumption of good X by 1 unit.
Part (c)
Assumption of monotonicity.
It means more is always better.
Bundle E would be preferred to bundle B because bundle E contains 6 units of good Y and 4 units of good X, whereas bundle B
contains 6 units of good Y and 2 units of good X. Bundle E contains more of at least one of the goods, thus bundle E would yield
higher satisfaction to consumer. Thus we can conclude that bundle E would be preferred to bundle B.
pearl shakes
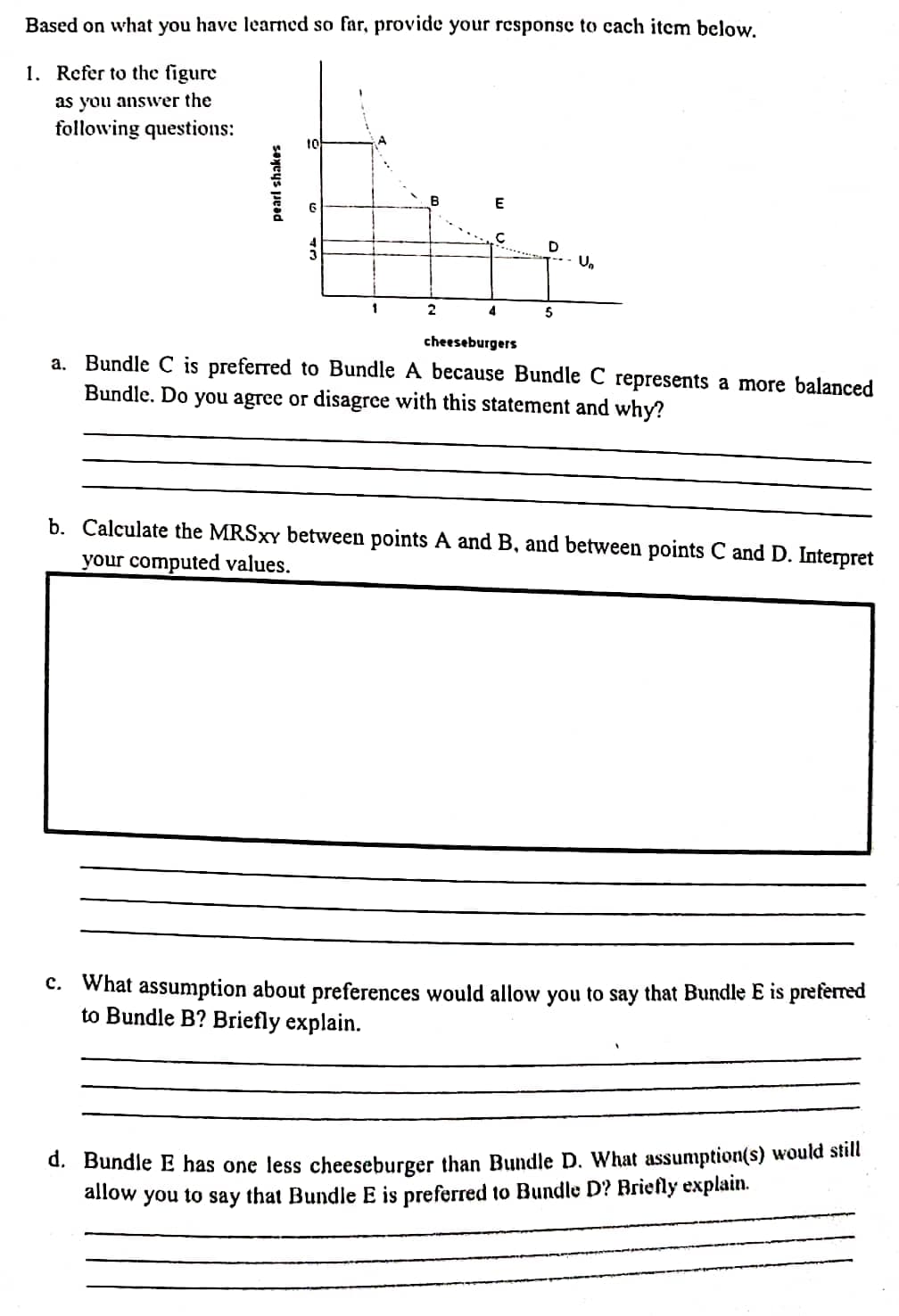
Transcribed Image Text:Based on what you have learned so far, provide your response to cach item below.
1. Refer to the figure
as you ansver the
following questions:
E
D
1
2
4
5
cheeseburgers
a. Bundle C is preferred to Bundle A because Bundle C represents a more balanced
Bundle. Do you agree or disagree with this statement and why?
b. Calculate the MRSXY between points A and B, and between points C and D. Interpret
your computed values.
C. What assumption about preferences would allow you to say that Bundle E is preferred
to Bundle B? Briefly explain.
d. Bundle E has one less cheeseburger than Bundle D. What assumption(s) would still
allow
to
that Bundle E is preferred to Bundle D? Briefly explain.
you
say
pearl shakes
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-…
Economics
ISBN:
9781259290619
Author:
Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education