5. pH Optimum of Lysozyme The enzymatic activity of lysozyme is optimal at pH 5.2. The active site of lysozyme contains two amino acid residues essential for catalysis, Glu³* and Asp². The pK, values of the carboxyl side chains of these two residues are 5.9 and 4.5, respectively. (a) What is the ionization state (protonated or deprotonated) of each residue at the pH optimum of lysozyme? (b) How can the ionization states of these two amino acid residues explain the pH-activity profile of lysozyme shown below? (c) Lysozyme destroys bacterial cell walls by hydrolyzing a glycosidic linkage between two sugars moieties. Based on your answers to parts (a) and (b), predict the possible catalytic roles of Glu³5 and Asp". 100 50 4 6 10 pH Activity (% of maximal)
5. pH Optimum of Lysozyme The enzymatic activity of lysozyme is optimal at pH 5.2. The active site of lysozyme contains two amino acid residues essential for catalysis, Glu³* and Asp². The pK, values of the carboxyl side chains of these two residues are 5.9 and 4.5, respectively. (a) What is the ionization state (protonated or deprotonated) of each residue at the pH optimum of lysozyme? (b) How can the ionization states of these two amino acid residues explain the pH-activity profile of lysozyme shown below? (c) Lysozyme destroys bacterial cell walls by hydrolyzing a glycosidic linkage between two sugars moieties. Based on your answers to parts (a) and (b), predict the possible catalytic roles of Glu³5 and Asp". 100 50 4 6 10 pH Activity (% of maximal)
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Chapter26: Synthesis And Degradation Of Nucleotides
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 16P
Related questions
Question
Help with enzyme catalysts #5 please
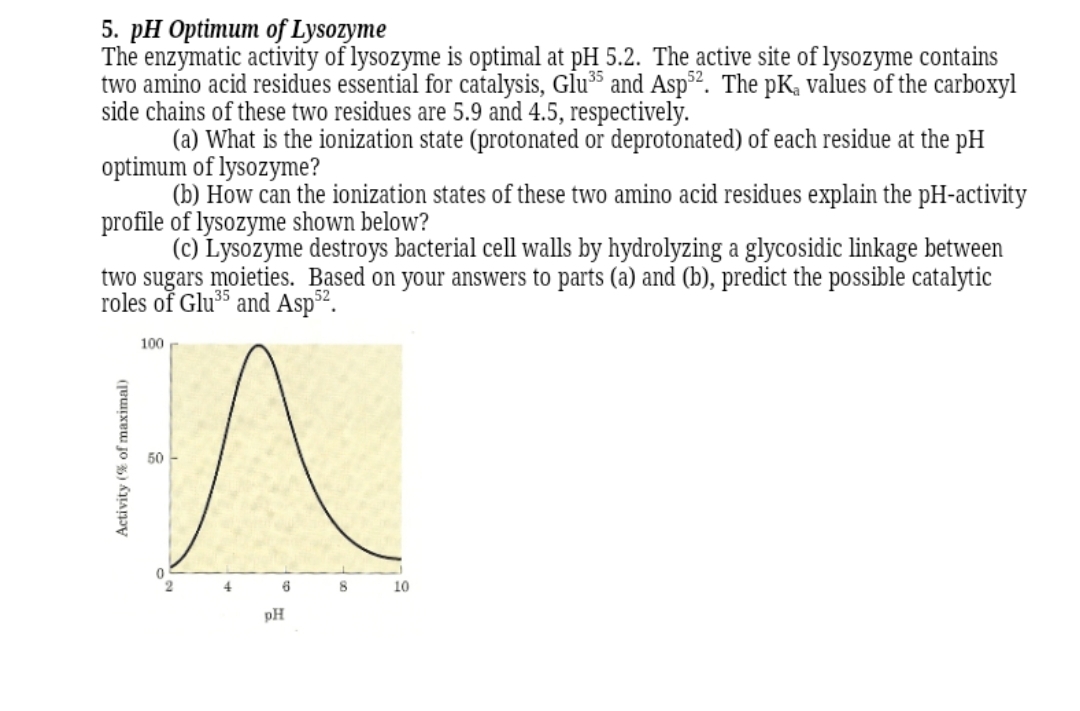
Transcribed Image Text:5. pH Optimum of Lysozyme
The enzymatic activity of lysozyme is optimal at pH 5.2. The active site of lysozyme contains
two amino acid residues essential for catalysis, Glu³* and Asp². The pK, values of the carboxyl
side chains of these two residues are 5.9 and 4.5, respectively.
(a) What is the ionization state (protonated or deprotonated) of each residue at the pH
optimum of lysozyme?
(b) How can the ionization states of these two amino acid residues explain the pH-activity
profile of lysozyme shown below?
(c) Lysozyme destroys bacterial cell walls by hydrolyzing a glycosidic linkage between
two sugars moieties. Based on your answers to parts (a) and (b), predict the possible catalytic
roles of Glu³5 and Asp".
100
50
4
6
10
pH
Activity (% of maximal)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning