BYOB is a monopolist in beer production and distribution in the imaginary economy of Hopsville. Suppose that BYOB cannot price discriminate; that is, it sells its beer at the same price per can to all customers. The following graph shows the marginal cost (MCMC), marginal revenue (MRMR), average total cost (ATCATC), and demand (D�) for beer in this market. On the following graph, place the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity for BYOB. If BYOB is making a profit, use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade in the area representing its profit. If BYOB is suffering a loss, use the purple rectangle (diamond symbols) to shade in the area representing its loss. Suppose that BYOB charges
BYOB is a monopolist in beer production and distribution in the imaginary economy of Hopsville. Suppose that BYOB cannot price discriminate; that is, it sells its beer at the same price per can to all customers. The following graph shows the marginal cost (MCMC), marginal revenue (MRMR), average total cost (ATCATC), and demand (D�) for beer in this market. On the following graph, place the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity for BYOB. If BYOB is making a profit, use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade in the area representing its profit. If BYOB is suffering a loss, use the purple rectangle (diamond symbols) to shade in the area representing its loss. Suppose that BYOB charges
Chapter14: Monopoly
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 14.5P
Related questions
Question
100%
BYOB is a monopolist in beer production and distribution in the imaginary economy of Hopsville. Suppose that BYOB cannot price discriminate ; that is, it sells its beer at the same price per can to all customers. The following graph shows the marginal cost (MCMC), marginal revenue (MRMR), average total cost (ATCATC), and demand (D�) for beer in this market.
On the following graph, place the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity for BYOB. If BYOB is making a profit, use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade in the area representing its profit. If BYOB is suffering a loss, use the purple rectangle (diamond symbols) to shade in the area representing its loss.
Suppose that BYOB charges $2.50 per can. Your friend Felix says that since BYOB is a monopoly with market power, it should charge a higher price of $3.00 per can because this will increase BYOB's profit.
Complete the following table to determine whether Felix is correct. (Hint: If BYOB is suffering a loss, enter a negative value for profit.)
|
Price
|
Quantity Demanded
|
Total Revenue
|
Total Cost
|
Profit
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
(Dollars per can)
|
(Cans)
|
(Dollars)
|
(Dollars)
|
(Dollars)
|
| 2.50 |
|
|
||
| 3.00 |
|
|
Given the earlier information, Felix correct in his assertion that BYOB should charge $3.00 per can.
Suppose that a technological innovation decreases BYOB’s costs so that it now faces the marginal cost (MCMC) and average total cost (ATCATC) given on the following graph. Specifically, the technological innovation causes a decrease in average fixed costs, thereby lowering the ATCATC curve and moving the MCMC curve.
On the following graph, place the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity for BYOB. If BYOB is making a profit, use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade in the area representing its profit. If BYOB is suffering a loss, use the purple rectangle (diamond symbols) to shade in the area representing the loss.
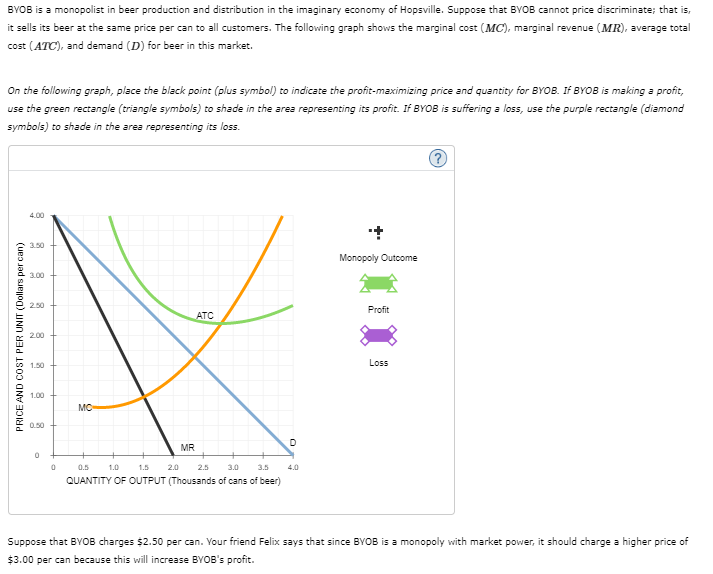
Transcribed Image Text:BYOB is a monopolist in beer production and distribution in the imaginary economy of Hopsville. Suppose that BYOB cannot price discriminate; that is,
it sells its beer at the same price per can to all customers. The following graph shows the marginal cost (MC), marginal revenue (MR), average total
cost (ATC), and demand (D) for beer in this market.
On the following graph, place the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity for BYOB. If BYOB is making a profit,
use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade in the area representing its profit. If BYOB is suffering a loss, use the purple rectangle (diamond
symbols) to shade in the area representing its loss.
4.00
PRICE AND COST PER UNIT (Dollars per can)
2.50
ATC
2.00
X
1.50
1.00
MC
MR
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0 3.5
QUANTITY OF OUTPUT (Thousands of cans of beer)
3.50
3.00
0.50
0
D
4.0
Monopoly Outcome
Profit
Loss
Suppose that BYOB charges $2.50 per can. Your friend Felix says that since BYOB is a monopoly with market power, it should charge a higher price of
$3.00 per can because this will increase BYOB's profit.
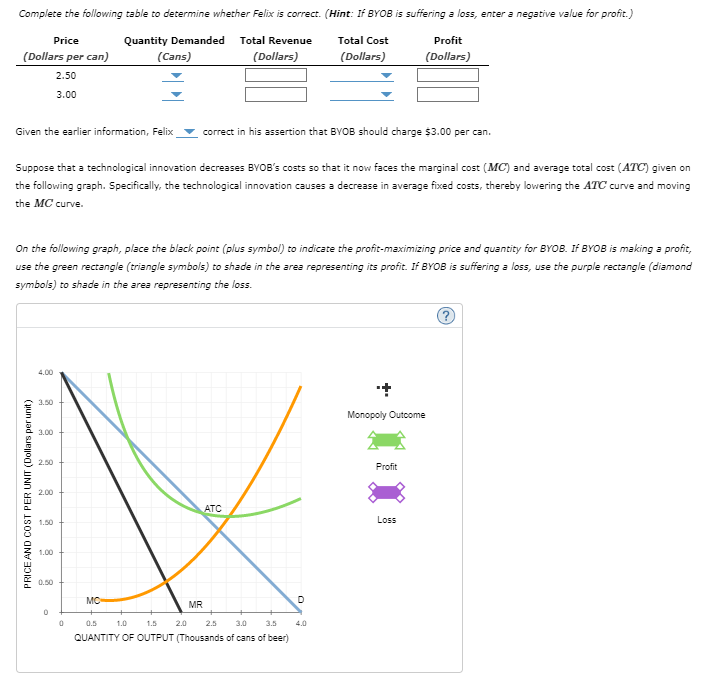
Transcribed Image Text:Complete the following table to determine whether Felix is correct. (Hint: If BYOB is suffering a loss, enter a negative value for profit.)
Total Cost
Profit
Quantity Demanded Total Revenue
(Cans)
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
Price
(Dollars per can)
2.50
3.00
Given the earlier information, Felix
Suppose that a technological innovation decreases BYOB's costs so that it now faces the marginal cost (MC) and average total cost (ATC) given on
the following graph. Specifically, the technological innovation causes a decrease in average fixed costs, thereby lowering the ATC curve and moving
the MC curve.
On the following graph, place the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity for BYOB. If BYOB is making a profit,
use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade in the area representing its profit. If BYOB is suffering a loss, use the purple rectangle (diamond
symbols) to shade in the area representing the loss.
PRICE AND COST PER UNIT (Dollars per unit)
4.00
3.50
3.00
2.50
2.00
1.50
1.00
0.50
0
0
correct in his assertion that BYOB should charge $3.00 per can.
MO
MR
ATC
3.0 3.5
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
QUANTITY OF OUTPUT (Thousands of cans of beer)
D
4.0
Monopoly Outcome
Profit
Loss
Expert Solution
Step 1
As per economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of the aggregate quantity produced. In a free market economy, productively efficient business optimize their production process by minimizing costs consistent with every possible level of production, and the outcome is a cost curve.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you








Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning