II AM Lab data percent yield carbon dioxide.pdf Name Sect Percent Yield of Carbon Dioxide To predict the amount of carbon dioxide gas that should be produced in a Purpose: chemical reaction. Then calculate the amount of carbon dioxide actually produced and determine the percent yield. The reaction is represented in the equation below: CH,COOH + NaHCO, → NaCH,C00 + H20 + CO2 Materials: sodium bicarbonate (aka baking soda), acetic acid solution (aka vinegar), Erlenmeyer flasks, balance .Procedure: 1. Measure and record the mass of a 250-mL Erlenmeyer flask. Label it as flask A. 2. Add approximately 7.5 g of sodium bicarbonate to flask A. 3. Measure and record the mass of a second 250-ml Erlenmeyer flask. Call it flask B. 4. Add approximately 75 g of acetic acid solution to flask B. 5. Slowly add acetic acid to flask A until the reaction has stopped. Do not add all of the vinegar; just enough to complete the reaction. 6. After the reaction has stopped, measure and record the masses of both flasks. Actual Fietd Theoretiaal Feld Fercent Fietd - (Actrat YiGEd-Theoreticat Ftetd) Data: Data Units Mass of beaker A (empty) 76.56 2 Mass of Bealker A + Baking Soda 3 Mass of Baking Soda (2-1) 4. Mass of beaker B (empty) 131.62 Mass of Beaker B+ Vinegar 235.42 9. Mass of Beaker B+Vinegar after reaction 331.25 Mass of Vinegar added to Beaker A (5-6) 95.83 Mass of Bealker A after reaction 方 90'01 103.79 6. Mass of product after the reaction (8-1) Mass of Baking Soda + Vinegar (3+7) Mass of Carbon Dioxide lost (10-9) 4. 28 tv MacBook Pro LE Periods Discussion Questions: What are the reactants in this experiment? Which are the products in this experiment? 3, Identify the limiting reactanti 4. Identify the excess reactant: Using stoichiometry (ie. mass of Baking Soda) caleulate the theoretical yield of carbon dioxide: Show Work: m. 6.6 N Hc0 44.014107 » 3.65g What is the percent yield? Show Work: What is the percent error? Show Work: 8. Matter cannot be created nor destroyed during a reaction. Does this apply to this lab? (Yes or No) Explain your answer: Why NoT l60% yield? 4. étv 28 MacBook Pro
II AM Lab data percent yield carbon dioxide.pdf Name Sect Percent Yield of Carbon Dioxide To predict the amount of carbon dioxide gas that should be produced in a Purpose: chemical reaction. Then calculate the amount of carbon dioxide actually produced and determine the percent yield. The reaction is represented in the equation below: CH,COOH + NaHCO, → NaCH,C00 + H20 + CO2 Materials: sodium bicarbonate (aka baking soda), acetic acid solution (aka vinegar), Erlenmeyer flasks, balance .Procedure: 1. Measure and record the mass of a 250-mL Erlenmeyer flask. Label it as flask A. 2. Add approximately 7.5 g of sodium bicarbonate to flask A. 3. Measure and record the mass of a second 250-ml Erlenmeyer flask. Call it flask B. 4. Add approximately 75 g of acetic acid solution to flask B. 5. Slowly add acetic acid to flask A until the reaction has stopped. Do not add all of the vinegar; just enough to complete the reaction. 6. After the reaction has stopped, measure and record the masses of both flasks. Actual Fietd Theoretiaal Feld Fercent Fietd - (Actrat YiGEd-Theoreticat Ftetd) Data: Data Units Mass of beaker A (empty) 76.56 2 Mass of Bealker A + Baking Soda 3 Mass of Baking Soda (2-1) 4. Mass of beaker B (empty) 131.62 Mass of Beaker B+ Vinegar 235.42 9. Mass of Beaker B+Vinegar after reaction 331.25 Mass of Vinegar added to Beaker A (5-6) 95.83 Mass of Bealker A after reaction 方 90'01 103.79 6. Mass of product after the reaction (8-1) Mass of Baking Soda + Vinegar (3+7) Mass of Carbon Dioxide lost (10-9) 4. 28 tv MacBook Pro LE Periods Discussion Questions: What are the reactants in this experiment? Which are the products in this experiment? 3, Identify the limiting reactanti 4. Identify the excess reactant: Using stoichiometry (ie. mass of Baking Soda) caleulate the theoretical yield of carbon dioxide: Show Work: m. 6.6 N Hc0 44.014107 » 3.65g What is the percent yield? Show Work: What is the percent error? Show Work: 8. Matter cannot be created nor destroyed during a reaction. Does this apply to this lab? (Yes or No) Explain your answer: Why NoT l60% yield? 4. étv 28 MacBook Pro
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Chapter10: Quantity Relationships In Chemical Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 70E: Classify each of the following statements as true or false: a Coefficients in a chemical equation...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:II AM Lab data percent yield carbon dioxide.pdf
Name
Sect
Percent Yield of Carbon Dioxide
To predict the amount of carbon dioxide gas that should be produced in a
Purpose:
chemical reaction. Then calculate the amount of carbon dioxide actually produced and
determine the percent yield. The reaction is represented in the equation below:
CH,COOH + NaHCO, → NaCH,C00 + H20 + CO2
Materials:
sodium bicarbonate (aka baking soda), acetic acid solution (aka vinegar),
Erlenmeyer flasks, balance
.Procedure:
1. Measure and record the mass of a 250-mL Erlenmeyer flask. Label it as flask A.
2. Add approximately 7.5 g of sodium bicarbonate to flask A.
3. Measure and record the mass of a second 250-ml Erlenmeyer flask. Call it flask B.
4. Add approximately 75 g of acetic acid solution to flask B.
5. Slowly add acetic acid to flask A until the reaction has stopped. Do not add all of the
vinegar; just enough to complete the reaction.
6. After the reaction has stopped, measure and record the masses of both flasks.
Actual Fietd
Theoretiaal Feld
Fercent Fietd -
(Actrat YiGEd-Theoreticat Ftetd)
Data:
Data
Units
Mass of beaker A (empty)
76.56
2
Mass of Bealker A + Baking Soda
3
Mass of Baking Soda (2-1)
4.
Mass of beaker B (empty)
131.62
Mass of Beaker B+ Vinegar
235.42
9.
Mass of Beaker B+Vinegar after reaction
331.25
Mass of Vinegar added to Beaker A (5-6)
95.83
Mass of Bealker A after reaction
方
90'01
103.79
6.
Mass of product after the reaction (8-1)
Mass of Baking Soda + Vinegar (3+7)
Mass of Carbon Dioxide lost (10-9)
4.
28
tv
MacBook Pro
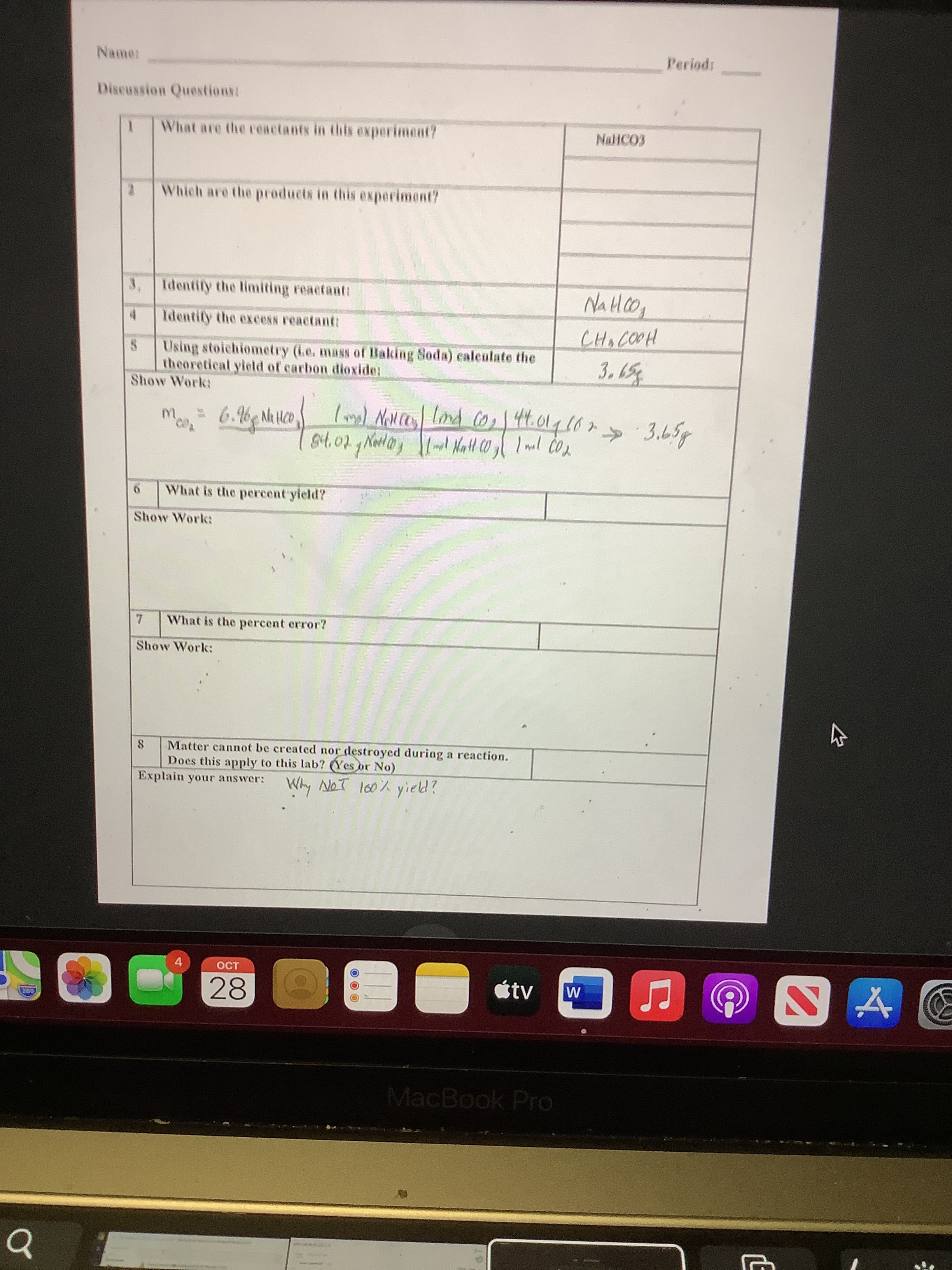
Transcribed Image Text:LE
Periods
Discussion Questions:
What are the reactants in this experiment?
Which are the products in this experiment?
3, Identify the limiting reactanti
4.
Identify the excess reactant:
Using stoichiometry (ie. mass of Baking Soda) caleulate the
theoretical yield of carbon dioxide:
Show Work:
m.
6.6 N Hc0
44.014107
» 3.65g
What is the percent yield?
Show Work:
What is the percent error?
Show Work:
8.
Matter cannot be created nor destroyed during a reaction.
Does this apply to this lab? (Yes or No)
Explain your answer:
Why NoT l60% yield?
4.
étv
28
MacBook Pro
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133109655
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax