122 CHAPTER 5ID 15. Which of the following best describes the particle-level bonding in a crystal of KBr? iupil doiw (A) alternating positive and negative metal ions in a crystal lattice framework. (B) positive and negative ions in fixed position in a crystal lattice framework. (C) mobile valence electrons shared between positive metal ions. (D) metallic and nonmetallic atoms covalently bonded in a 3-dimenional framework. () HO (C) CC (D) CH'OE Questions 16-17 use the following information. 6801 9010 oloegsini doidW8 H H H---H H H Ethane wolod a (B) но-с-Сн, — СH, — СH, — СH, ннн нннн H-C-C- C-C-C-C-C-H || | | I|| Η Η Η Η | H. нн Heptane Pentanoic Acid 10 Name Chemical Formula Molar Mass (g/mole) Boiling Point (°C) Ethane 30.07 -88.5 Heptane 16 100.20 98.1-98.7 Pentanoic Acid 102.13 186-187 16. Heptane and pentanoic acid have very similar molar masses, but pentanoic acid has a significantly higher boiling point. Which of the following statements best helps explain this observation? (A) The sum of the bond energies in heptane is lower than the sum of the bond energies in pentanoic acid. (B) There are more opportunities for London dispersion forces in heptane than in pentanoic acid. (C) There are more opportunities for hydrogen bonding in pentanoic acid than there are in heptane. (D) The carbon chains in heptane are farther apart than they are in heptane. quo
122 CHAPTER 5ID 15. Which of the following best describes the particle-level bonding in a crystal of KBr? iupil doiw (A) alternating positive and negative metal ions in a crystal lattice framework. (B) positive and negative ions in fixed position in a crystal lattice framework. (C) mobile valence electrons shared between positive metal ions. (D) metallic and nonmetallic atoms covalently bonded in a 3-dimenional framework. () HO (C) CC (D) CH'OE Questions 16-17 use the following information. 6801 9010 oloegsini doidW8 H H H---H H H Ethane wolod a (B) но-с-Сн, — СH, — СH, — СH, ннн нннн H-C-C- C-C-C-C-C-H || | | I|| Η Η Η Η | H. нн Heptane Pentanoic Acid 10 Name Chemical Formula Molar Mass (g/mole) Boiling Point (°C) Ethane 30.07 -88.5 Heptane 16 100.20 98.1-98.7 Pentanoic Acid 102.13 186-187 16. Heptane and pentanoic acid have very similar molar masses, but pentanoic acid has a significantly higher boiling point. Which of the following statements best helps explain this observation? (A) The sum of the bond energies in heptane is lower than the sum of the bond energies in pentanoic acid. (B) There are more opportunities for London dispersion forces in heptane than in pentanoic acid. (C) There are more opportunities for hydrogen bonding in pentanoic acid than there are in heptane. (D) The carbon chains in heptane are farther apart than they are in heptane. quo
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter6: Covalent Bonding
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6.ACP
Related questions
Question
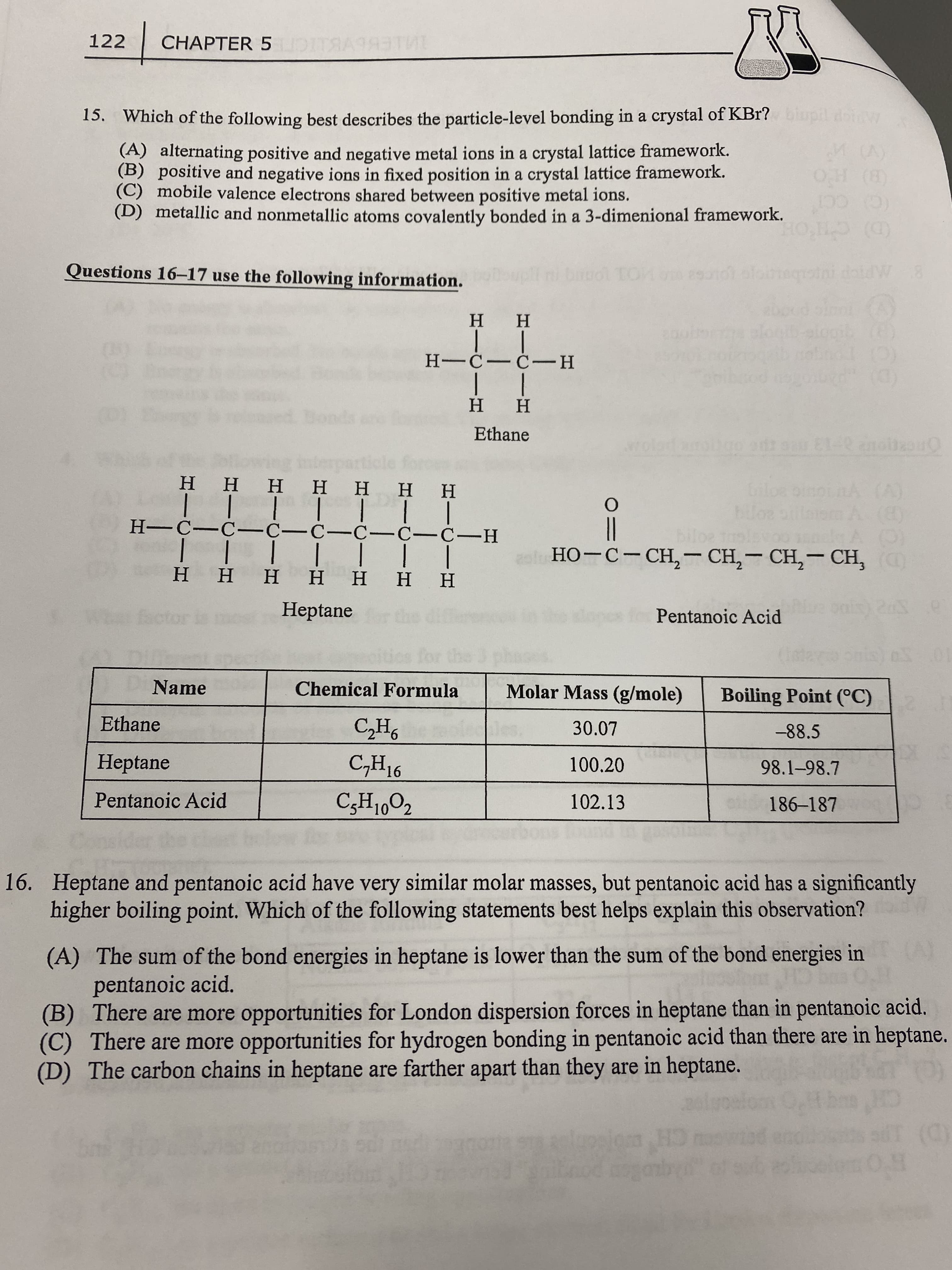
Transcribed Image Text:122
CHAPTER 5ID
15. Which of the following best describes the particle-level bonding in a crystal of KBr? iupil doiw
(A) alternating positive and negative metal ions in a crystal lattice framework.
(B) positive and negative ions in fixed position in a crystal lattice framework.
(C) mobile valence electrons shared between positive metal ions.
(D) metallic and nonmetallic atoms covalently bonded in a 3-dimenional framework.
() HO
(C) CC
(D) CH'OE
Questions 16-17 use the following information.
6801
9010 oloegsini doidW8
H H
H---H
H H
Ethane
wolod a
(B)
но-с-Сн, — СH, — СH, — СH,
ннн нннн
H-C-C- C-C-C-C-C-H
|| | | I||
Η Η Η Η
|
H.
нн
Heptane
Pentanoic Acid
10
Name
Chemical Formula
Molar Mass (g/mole)
Boiling Point (°C)
Ethane
30.07
-88.5
Heptane
16
100.20
98.1-98.7
Pentanoic Acid
102.13
186-187
16. Heptane and pentanoic acid have very similar molar masses, but pentanoic acid has a significantly
higher boiling point. Which of the following statements best helps explain this observation?
(A) The sum of the bond energies in heptane is lower than the sum of the bond energies in
pentanoic acid.
(B) There are more opportunities for London dispersion forces in heptane than in pentanoic acid.
(C) There are more opportunities for hydrogen bonding in pentanoic acid than there are in heptane.
(D) The carbon chains in heptane are farther apart than they are in heptane.
quo
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning