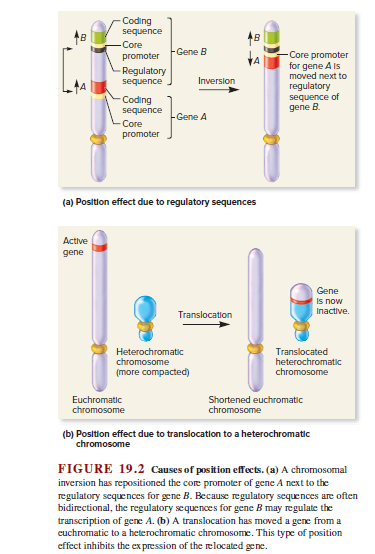
Coding sequence -Core promoter -Gene B Core promoter for gene A is moved next to regulatory sequence of депe B Regulatory sequence Inversion Coding sequence Gene A Core promoter (a) Postion effect due to regulatory sequences Active gene Gene Is now Inactive. Translocation Heterochromatic chromosome Translocated heterochromatic chromosome (more compacted) Euchromatic chromosome Shortened euchromatic chromosome (b) Position effect due to translocation to a heterochromatic chromosome FIGURE 19.2 Causes of position effects. (a) A chromosomal inversion has repositioned the core promoter of gene A next to the regulatory sequences for gene B. Because regulatory sequences are often bidirectional, the regulatory sequences for gene B may regulate the transcription of gene A. (b) A translocation has moved a gene from a cuchromatic to a heterochromatic chromosome. This type of position effect inhibits the ex pression of the relocated gene.
Coding sequence -Core promoter -Gene B Core promoter for gene A is moved next to regulatory sequence of депe B Regulatory sequence Inversion Coding sequence Gene A Core promoter (a) Postion effect due to regulatory sequences Active gene Gene Is now Inactive. Translocation Heterochromatic chromosome Translocated heterochromatic chromosome (more compacted) Euchromatic chromosome Shortened euchromatic chromosome (b) Position effect due to translocation to a heterochromatic chromosome FIGURE 19.2 Causes of position effects. (a) A chromosomal inversion has repositioned the core promoter of gene A next to the regulatory sequences for gene B. Because regulatory sequences are often bidirectional, the regulatory sequences for gene B may regulate the transcription of gene A. (b) A translocation has moved a gene from a cuchromatic to a heterochromatic chromosome. This type of position effect inhibits the ex pression of the relocated gene.
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Chapter29: Transcription And The Regulation Of Gene Expression
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
Explain what the term position effect means.
Transcribed Image Text:Coding
sequence
-Core
promoter
-Gene B
Core promoter
for gene A is
moved next to
regulatory
sequence of
депe B
Regulatory
sequence
Inversion
Coding
sequence
Gene A
Core
promoter
(a) Postion effect due to regulatory sequences
Active
gene
Gene
Is now
Inactive.
Translocation
Heterochromatic
chromosome
Translocated
heterochromatic
chromosome
(more compacted)
Euchromatic
chromosome
Shortened euchromatic
chromosome
(b) Position effect due to translocation to a heterochromatic
chromosome
FIGURE 19.2 Causes of position effects. (a) A chromosomal
inversion has repositioned the core promoter of gene A next to the
regulatory sequences for gene B. Because regulatory sequences are often
bidirectional, the regulatory sequences for gene B may regulate the
transcription of gene A. (b) A translocation has moved a gene from a
cuchromatic to a heterochromatic chromosome. This type of position
effect inhibits the ex pression of the relocated gene.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305073951
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305073951
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning