Collisions between gas particles or with the walls of the container are elastic, meaning no energy lost when it collides with another particle or with the walls of the container.
Collisions between gas particles or with the walls of the container are elastic, meaning no energy lost when it collides with another particle or with the walls of the container.
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter13: Gases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 140AP: he following demonstration takes place in a two-step process: rst, solid calcium carbide...
Related questions
Question
100%
Can you help me with the 5 row
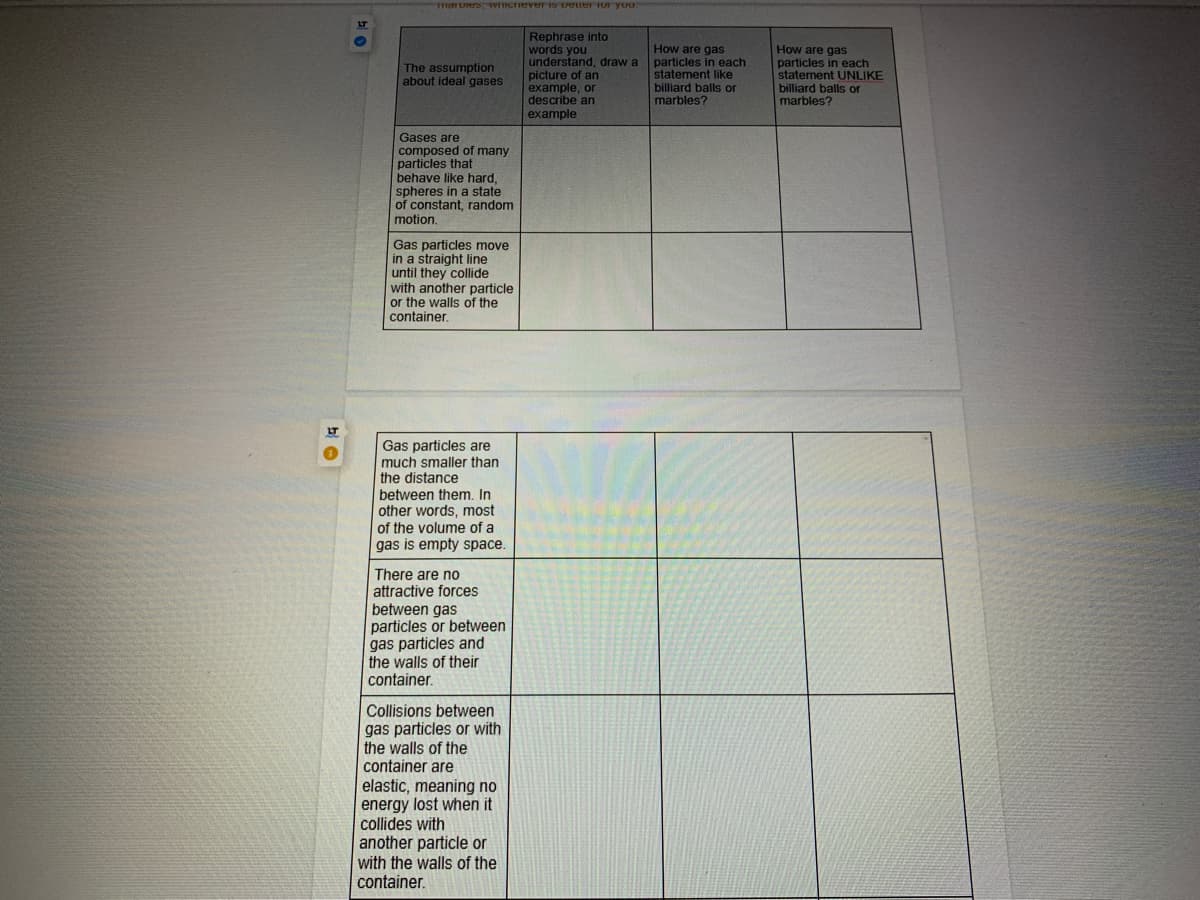
Transcribed Image Text:THar DES, ITICTIever s vener 1or you
Rephrase into
words you
understand, draw a
picture of an
example, or
describe an
example
How are gas
particles in each
statement like
billiard balls or
marbles?
How are gas
particles in each
statement UNLIKE
billiard balls or
marbles?
The assumption
about ideal gases
Gases are
composed of many
particles that
behave like hard,
spheres in a state
of constant, random
motion.
Gas particles move
in a straight line
until they collide
with another particle
or the walls of the
container.
LT
Gas particles are
much smaller than
the distance
between them, In
other words, most
of the volume of a
gas is empty space.
There are no
attractive forces
between gas
particles or between
gas particles and
the walls of their
container.
Collisions between
gas particles or with
the walls of the
container are
elastic, meaning no
energy lost when it
collides with
another particle or
with the walls of the
container.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199030
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning