Consider a utility function of two goods x and y: U (x,y) = A (ax +by') where A >0, a>0, b>0, r € (-∞,0)U(0, 1) are constants. This utility function is called a "constant elasticity of substitution (CES)" function and is frequently used in Macroeconom- ics. (a) Prove that when a+b = 1, this utility function converges to a Cobb-Douglas utility function as r→0. Hint: apply l'Hopital's rule to lim In ) = limm(ar +by') (b) Calculate the slope of the indifference curves of U. Based on your answer, are good x and y perfect/imperfect substitutes/complements when r → 1? When r → -0?
Consider a utility function of two goods x and y: U (x,y) = A (ax +by') where A >0, a>0, b>0, r € (-∞,0)U(0, 1) are constants. This utility function is called a "constant elasticity of substitution (CES)" function and is frequently used in Macroeconom- ics. (a) Prove that when a+b = 1, this utility function converges to a Cobb-Douglas utility function as r→0. Hint: apply l'Hopital's rule to lim In ) = limm(ar +by') (b) Calculate the slope of the indifference curves of U. Based on your answer, are good x and y perfect/imperfect substitutes/complements when r → 1? When r → -0?
Chapter4: Utility Maximization And Choice
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4.13P
Related questions
Question
11.) Answer only part B
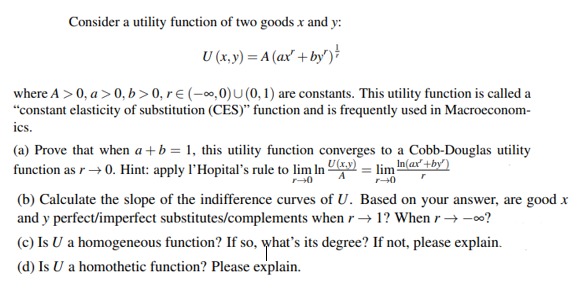
Transcribed Image Text:Consider a utility function of two goodsx and y:
U (x, y) = A (ax' +by')
where A > 0, a> 0, b>0, r € (-∞,0)U (0,1) are constants. This utility function is called a
"constant elasticity of substitution (CES)" function and is frequently used in Macroeconom-
ics.
(a) Prove that when a+b = 1, this utility function converges to a Cobb-Douglas utility
function as r→ 0. Hint: apply l'Hopital's rule to lim In U(x.y) = lim In(ax' +by')
(b) Calculate the slope of the indifference curves of U. Based on your answer, are good x
and y perfect/imperfect substitutes/complements when r → 1? When r → -00?
(c) Is U a homogeneous function? If so, what's its degree? If not, please explain.
(d) Is U a homothetic function? Please explain.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

