Consider an astronaut on a large planet in another galaxy. To learn more about the composition of this planet, the astronaut drops an electronic sensor into a deep trench. The sensor transmits its vertical position every second in relation to the astronaut's position. The summary of the falling sensor data is displayed in the following table. Time after Position (m) dropping (s) -1 -2 -4 4 -8 -14 (a) Using a calculator or computer program, find the best-fit quadratic curve to measure the position of the sensor (in m) as a function of t, the time (in s) after the sensor is dropped. (Round all numerical values to four decimal places.) p(t) =
Consider an astronaut on a large planet in another galaxy. To learn more about the composition of this planet, the astronaut drops an electronic sensor into a deep trench. The sensor transmits its vertical position every second in relation to the astronaut's position. The summary of the falling sensor data is displayed in the following table. Time after Position (m) dropping (s) -1 -2 -4 4 -8 -14 (a) Using a calculator or computer program, find the best-fit quadratic curve to measure the position of the sensor (in m) as a function of t, the time (in s) after the sensor is dropped. (Round all numerical values to four decimal places.) p(t) =
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Chapter5: A Survey Of Other Common Functions
Section5.4: Combining And Decomposing Functions
Problem 18E
Related questions
Question
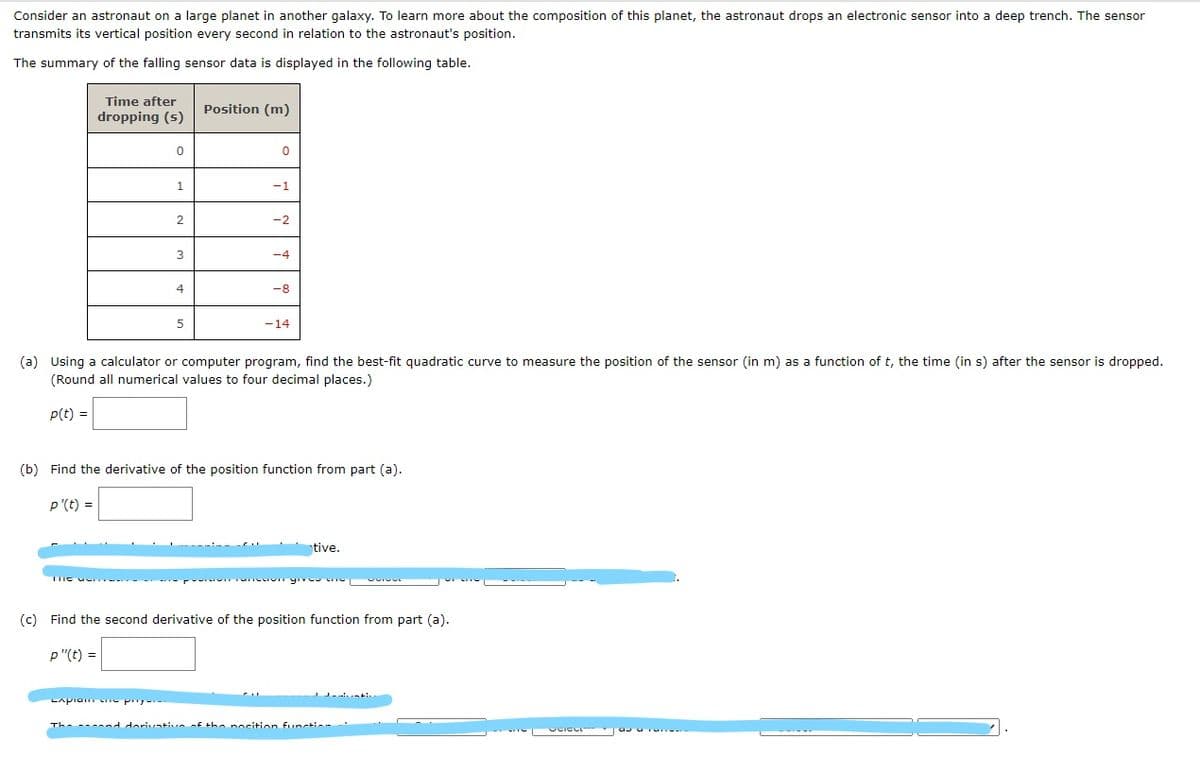
Transcribed Image Text:Consider an astronaut on a large planet in another galaxy. To learn more about the composition of this planet, the astronaut drops an electronic sensor into a deep trench. The sensor
transmits its vertical position every second in relation to the astronaut's position.
The summary of the falling sensor data is displayed in the following table.
Time after
Position (m)
dropping (s)
1.
-1
-2
3
-4
4
-8
5
-14
(a) Using a calculator or computer program, find the best-fit quadratic curve to measure the position of the sensor (in m) as a function of t, the time (in s) after the sensor is dropped.
(Round all numerical values to four decimal places.)
P(t) =
(b) Find the derivative of the position function from part (a).
p'(t) =
tive.
wncor yıve
(c) Find the second derivative of the position function from part (a).
p "(t) =
LApiam py
The ---nd dorivative f the nocition functio-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,