Consider the following air-conditioning system design which involves a refrigeration process ('cooling coil unit') and a mixing process ('mixing box'). Cooling Unit Mixing Box 4 NNN ma1 T, 01 w2 T2 02 T, Ø4 mcoolant Tcoolant.in 3 maa T3 03 Condensate Cooling Coil Coolant Return Air Given the properties in Table 1 only, solve for: 45. the relative humidity of the moist air at exit, 02, in %; a) 40 Table 1 b) 60 c) 80 0.5 kg/s d) 100 T 37°C e) none of the above 60% 46. the moist air temperature at exit, T2, in °C (assume p, = p); 0.0078 a) 13.1 b) 12.2 c) 10.3 d) 9.2 e) none of the above
Consider the following air-conditioning system design which involves a refrigeration process ('cooling coil unit') and a mixing process ('mixing box'). Cooling Unit Mixing Box 4 NNN ma1 T, 01 w2 T2 02 T, Ø4 mcoolant Tcoolant.in 3 maa T3 03 Condensate Cooling Coil Coolant Return Air Given the properties in Table 1 only, solve for: 45. the relative humidity of the moist air at exit, 02, in %; a) 40 Table 1 b) 60 c) 80 0.5 kg/s d) 100 T 37°C e) none of the above 60% 46. the moist air temperature at exit, T2, in °C (assume p, = p); 0.0078 a) 13.1 b) 12.2 c) 10.3 d) 9.2 e) none of the above
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter9: Heat Transfer With Phase Change
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9.34P
Related questions
Question
plz solve 20-30 mins. I'll give you multiple Upvote
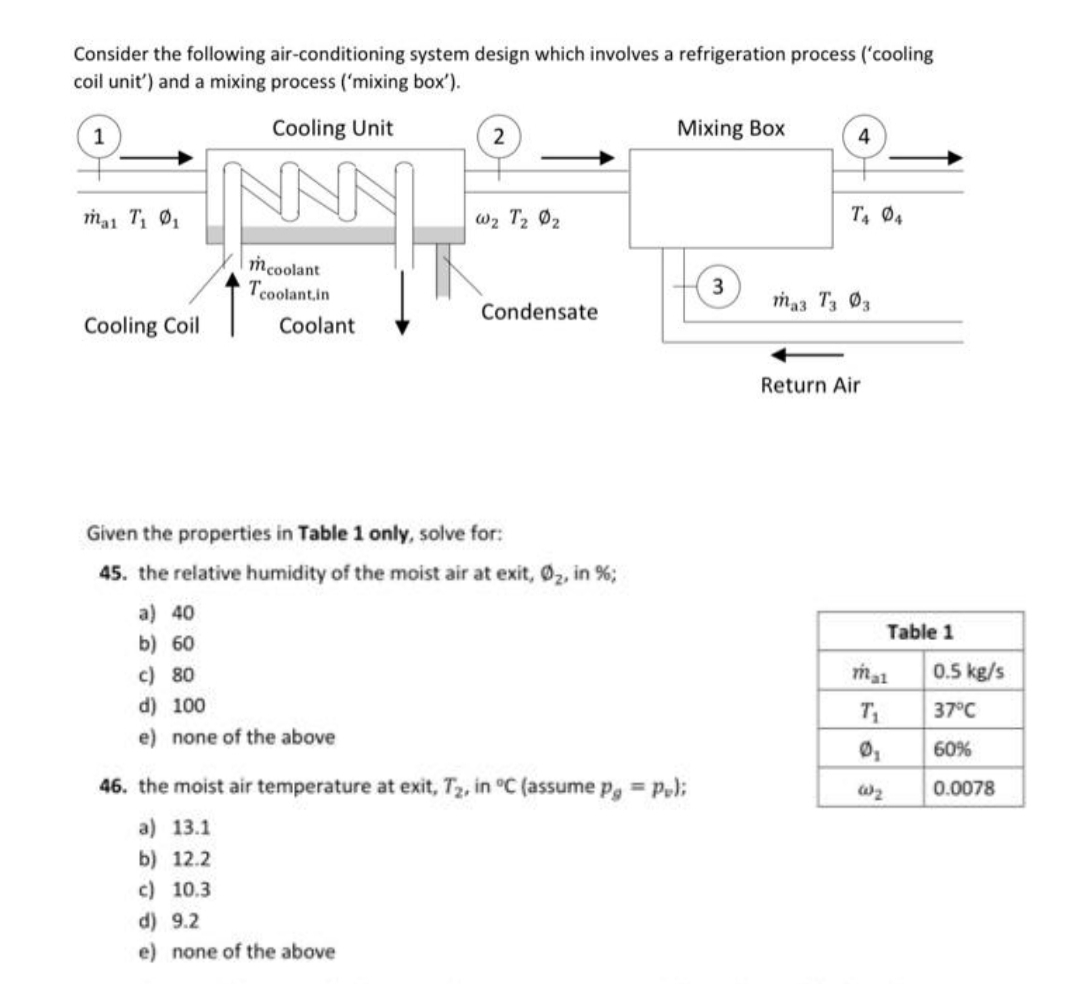
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following air-conditioning system design which involves a refrigeration process ('cooling
coil unit') and a mixing process ('mixing box').
Cooling Unit
2
Mixing Box
4
ma1 T 01
w2 T2 02
mcoolant
Tcoolant.in
3
ma3 T3 03
Condensate
Cooling Coil
Coolant
Return Air
Given the properties in Table 1 only, solve for:
45. the relative humidity of the moist air at exit, 02, in %;
a) 40
Table 1
b) 60
c) 80
d) 100
0.5 kg/s
T
37°C
e) none of the above
60%
46. the moist air temperature at exit, T2, in °C (assume p, = p,);
0.0078
a) 13.1
b) 12.2
c) 10.3
d) 9.2
e) none of the above
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning