Consider the following model of the Philips curve. In this model inflation is regressed upon unemployment using a sample of 56 observations, where INF denotes a measure of the inflation rate and UNEM denotes a measure of the unemployment rate. An initial analysis of this model produced the results reported in Tables Two and Three. Table Two Dependent Variable: INF Method: Least Squares Sample: 1948 2o03 Included observations: 56 Coeficient Std. Eror t-Statistic Variable Prob. 1.053565 1.547957 0.502378 0.265562 0.680617 1.891752 0.4990 0.0639 UNEM Akake info criterion 5.051084 Schwarz criterion 5.123418 Table Three
Consider the following model of the Philips curve. In this model inflation is regressed upon unemployment using a sample of 56 observations, where INF denotes a measure of the inflation rate and UNEM denotes a measure of the unemployment rate. An initial analysis of this model produced the results reported in Tables Two and Three. Table Two Dependent Variable: INF Method: Least Squares Sample: 1948 2o03 Included observations: 56 Coeficient Std. Eror t-Statistic Variable Prob. 1.053565 1.547957 0.502378 0.265562 0.680617 1.891752 0.4990 0.0639 UNEM Akake info criterion 5.051084 Schwarz criterion 5.123418 Table Three
College Algebra
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter1: Equations And Graphs
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10T: Olympic Pole Vault The graph in Figure 7 indicates that in recent years the winning Olympic men’s...
Related questions
Question
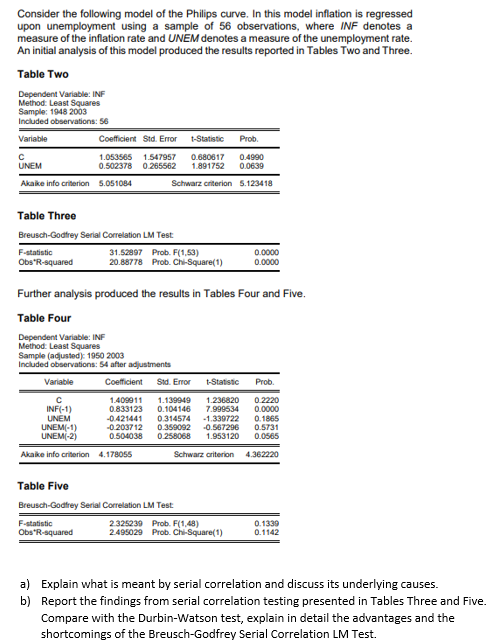
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following model of the Philips curve. In this model inflation is regressed
upon unemployment using a sample of 56 observations, where INF denotes a
measure of the inflation rate and UNEM denotes a measure of the unemployment rate.
An initial analysis of this model produced the results reported in Tables Two and Three.
Table Two
Dependent Variable: INF
Method: Least Squares
Sample: 1948 2003
Included observations: 56
Variable
Coefficient Std. Error
t-Statistic
Prob.
0.4990
0.0639
1.053565 1.547957
0.680617
1.891752
UNEM
0.502378 0.265562
Akaike info criterion 5.051084
Schwarz criterion 5.123418
Table Three
Breusch-Godtrey Serial Correlation LM Test
F-statistic
31.52897 Prob. F(1,53)
20.88778 Prob. Chi-Square(1)
0.0000
Obs'R-squared
0.0000
Further analysis produced the results in Tables Four and Five.
Table Four
Dependent Variable: INF
Method: Least Squares
Sample (adusted) 1950 2003
Included observations: 54 after adjustments
Variable
Coefficient
Std. Error
t-Statistic
Prob.
1.409911
0.833123
-0.421441
-0.2037 12
0.504038
1.139949
0.104146
0.314574
0.359092
0 258068
1.236820
INF(-1)
UNEM
UNEM(-1)
UNEMI-2)
7.999534
-1.339722
-0.567296
1.953120
0.2220
0.0000
0.1865
0.5731
0.0565
Akaike info criterion 4.178055
Schwarz ariterion
4.362220
Table Five
Breusch-Godfrey Serial Correlation LM Test
F-statistic
Obs'R-squared
2.325239 Prob. F(1,48)
2495029 Prob. Chi-Square(1)
0.1339
0.1142
a) Explain what is meant by serial correlation and discuss its underlying causes.
b) Report the findings from serial correlation testing presented in Tables Three and Five.
Compare with the Durbin-Watson test, explain in detail the advantages and the
shortcomings of the Breusch-Godfrey Serial Correlation LM Test.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage