Consider the reaction of CO2 and solid carbon described by the chemical reaction below. Determine the equilibrium constant for this reaction by constructing an ICE table, writing the equilibrium constant expression, and solving it. Complete Parts 1-2 before submitting your answer. C(s) + CO2(g) 2 CO(g) 1 2 NEXT > When 1.50 mol of CO2 and an 10.0 mol solid carbon are heated in a 20.0 L container at 1100 K, the equilibrium concentration of CO is 0.0700 M. Fill in the ICE table with the appropriate value for each involved species to determine concentrations of all reactants and products..
Consider the reaction of CO2 and solid carbon described by the chemical reaction below. Determine the equilibrium constant for this reaction by constructing an ICE table, writing the equilibrium constant expression, and solving it. Complete Parts 1-2 before submitting your answer. C(s) + CO2(g) 2 CO(g) 1 2 NEXT > When 1.50 mol of CO2 and an 10.0 mol solid carbon are heated in a 20.0 L container at 1100 K, the equilibrium concentration of CO is 0.0700 M. Fill in the ICE table with the appropriate value for each involved species to determine concentrations of all reactants and products..
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
11th Edition
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Chapter7: Reaction Rates And Chemical Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.64P: 7-64 As we shall see in Chapter 20, there are two forms of glucose, designated alpha and betawhich...
Related questions
Question
Can you answer correctly?
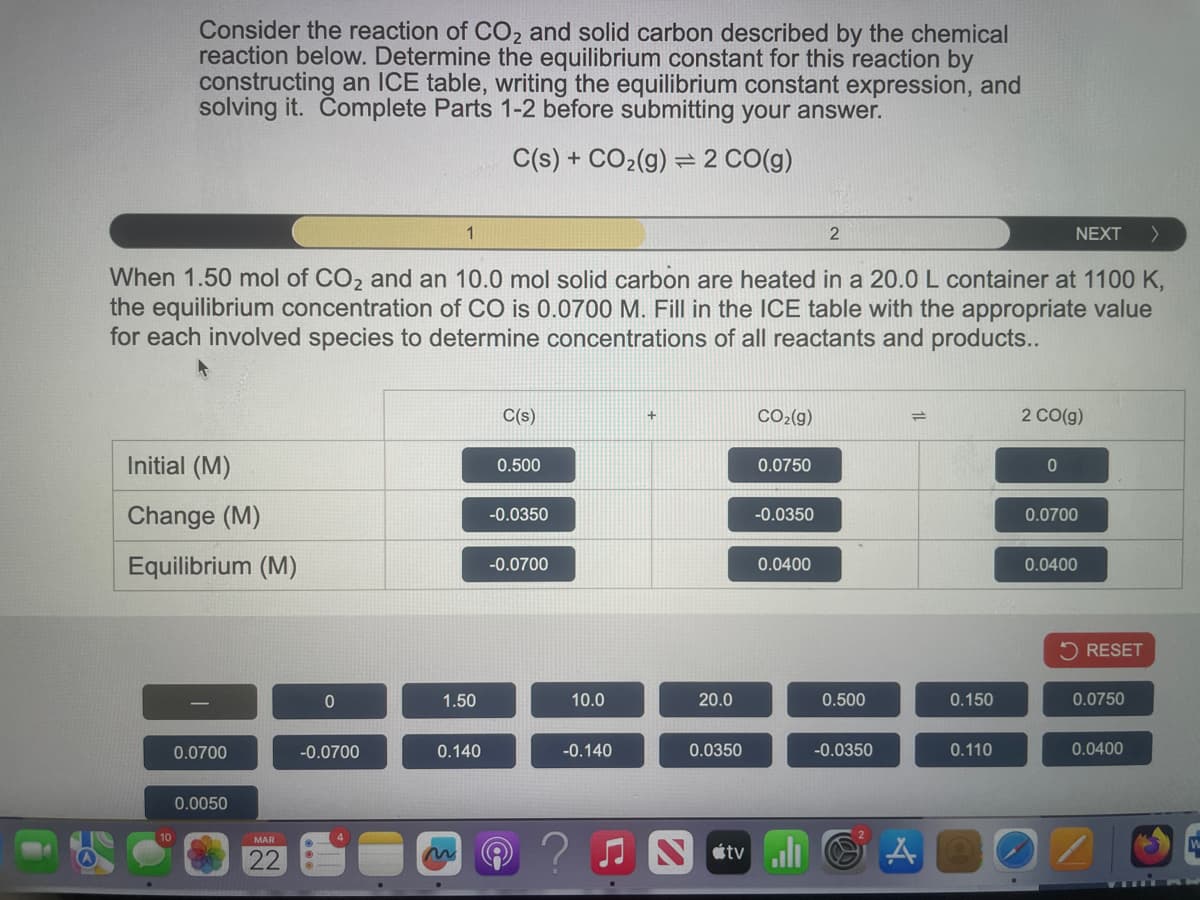
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the reaction of CO2 and solid carbon described by the chemical
reaction below. Determine the equilibrium constant for this reaction by
constructing an ICE table, writing the equilibrium constant expression, and
solving it. Complete Parts 1-2 before submitting your answer.
C(s) + CO2(g) 2 CO(g)
1
2
NEXT >
When 1.50 mol of CO2 and an 10.0 mol solid carbon are heated in a 20.0 L container at 1100 K,
the equilibrium concentration of CO is 0.0700 M. Fill in the ICE table with the appropriate value
for each involved species to determine concentrations of all reactants and products..
C(s)
+
CO2(g)
Initial (M)
0.500
0.0750
2 CO(g)
0
Change (M)
-0.0350
-0.0350
0.0700
Equilibrium (M)
-0.0700
0.0400
0.0400
10
RESET
0
1.50
10.0
20.0
0.500
0.150
0.0750
0.0700
-0.0700
0.140
-0.140
0.0350
-0.0350
0.110
0.0400
0.0050
MAR
22
Ntv A
W
![Consider the reaction of CO2 and solid carbon described by the chemical
reaction below. Determine the equilibrium constant for this reaction by
constructing an ICE table, writing the equilibrium constant expression, and
solving it. Complete Parts 1-2 before submitting your answer.
C(s) + CO2(g) 2 CO(g)
PREV
1
2
Based on the set up of your ICE table, construct the expression for Kc. Each reaction participant
must be represented by one tile. Do not combine terms.
Once the expression is constructed, solve for Kc.
[0.0700]²
Kc
=
0.123
=
[0.0400]
RESET
[1.50]
[0.500]
[0.150]
[0.0750]
[0.0700]
[0.140]
[0.0400]
[0.0050]
[1.50]²
[0.500]²
[0.150]²
[0.0750]²
[0.0700]²
[0.140]²
[0.0400]²
[0.0050]2
1.75
0.571
0.123
8.16
MAR
22
Stv
A](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F42021111-4ced-4c6f-84e9-5b1969157ec2%2F01bd0473-4bbe-44cb-8532-022857037739%2Ftgio59_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the reaction of CO2 and solid carbon described by the chemical
reaction below. Determine the equilibrium constant for this reaction by
constructing an ICE table, writing the equilibrium constant expression, and
solving it. Complete Parts 1-2 before submitting your answer.
C(s) + CO2(g) 2 CO(g)
PREV
1
2
Based on the set up of your ICE table, construct the expression for Kc. Each reaction participant
must be represented by one tile. Do not combine terms.
Once the expression is constructed, solve for Kc.
[0.0700]²
Kc
=
0.123
=
[0.0400]
RESET
[1.50]
[0.500]
[0.150]
[0.0750]
[0.0700]
[0.140]
[0.0400]
[0.0050]
[1.50]²
[0.500]²
[0.150]²
[0.0750]²
[0.0700]²
[0.140]²
[0.0400]²
[0.0050]2
1.75
0.571
0.123
8.16
MAR
22
Stv
A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
