Consider total cost and total revenue, given in the following table: In the final column, enter profit for each quantity. (Note: If the firm suffers a loss, enter a negative number in the appropriate cell.) Marginal Cost (Dollars) Total Cost Total Revenue Marginal Revenue (Dollars) Profit Quantity (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) 10 14 13 21 4 17 28 24 35 32 42 42 49 In order to maximize profit, how many units should the firm produce? Check all that apply. 6. In the previous table, enter marginal revenue and marginal cost for each quantity. On the following graph, use the green points (triangle symbol) to graph the marginal-revenue curve, then use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the marginal-cost curve. (Note: Be sure to plot from left to right and to plot between integers. For example, if the marginal cost of increasing production from 1 unit to 2 units is $5, then you would plot a point at (1.5, 5).) 10 Marginal Revenue 00 In the previous table, enter marginal revenue and marginal cost for each quantity. On the following graph, use the green points (triangle symbol) to graph the marginal-revenue curve, then use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the marginal-cost curve. (Note: Be sure to plot from left to right and to plot between integers. For example, if the marginal cost of increasing production from 1 unit to 2 units is $5, then you would plot a point at (1.5, 5).) 10 Marginal Revenue Marginal Cost 2 Quantity The marginal-revenue curve and the marginal-cost curve cross at a quantity This firm in a competitive industry, because marginal revenue is as quantity increases. True or False: The industry is in a long-run equilibrium. True False Revenue and C osts
Consider total cost and total revenue, given in the following table: In the final column, enter profit for each quantity. (Note: If the firm suffers a loss, enter a negative number in the appropriate cell.) Marginal Cost (Dollars) Total Cost Total Revenue Marginal Revenue (Dollars) Profit Quantity (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) 10 14 13 21 4 17 28 24 35 32 42 42 49 In order to maximize profit, how many units should the firm produce? Check all that apply. 6. In the previous table, enter marginal revenue and marginal cost for each quantity. On the following graph, use the green points (triangle symbol) to graph the marginal-revenue curve, then use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the marginal-cost curve. (Note: Be sure to plot from left to right and to plot between integers. For example, if the marginal cost of increasing production from 1 unit to 2 units is $5, then you would plot a point at (1.5, 5).) 10 Marginal Revenue 00 In the previous table, enter marginal revenue and marginal cost for each quantity. On the following graph, use the green points (triangle symbol) to graph the marginal-revenue curve, then use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the marginal-cost curve. (Note: Be sure to plot from left to right and to plot between integers. For example, if the marginal cost of increasing production from 1 unit to 2 units is $5, then you would plot a point at (1.5, 5).) 10 Marginal Revenue Marginal Cost 2 Quantity The marginal-revenue curve and the marginal-cost curve cross at a quantity This firm in a competitive industry, because marginal revenue is as quantity increases. True or False: The industry is in a long-run equilibrium. True False Revenue and C osts
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
5th Edition
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Chapter3: Benefits, Costs, And Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9MC
Related questions
Question
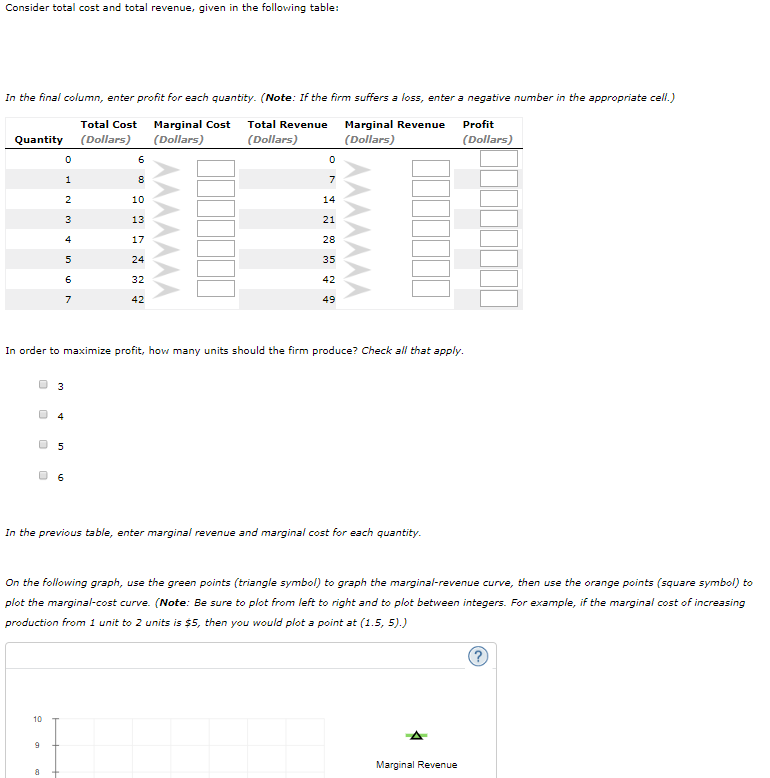
Transcribed Image Text:Consider total cost and total revenue, given in the following table:
In the final column, enter profit for each quantity. (Note: If the firm suffers a loss, enter a negative number in the appropriate cell.)
Marginal Cost
(Dollars)
Total Cost
Total Revenue
Marginal Revenue
(Dollars)
Profit
Quantity
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
10
14
13
21
4
17
28
24
35
32
42
42
49
In order to maximize profit, how many units should the firm produce? Check all that apply.
6.
In the previous table, enter marginal revenue and marginal cost for each quantity.
On the following graph, use the green points (triangle symbol) to graph the marginal-revenue curve, then use the orange points (square symbol) to
plot the marginal-cost curve. (Note: Be sure to plot from left to right and to plot between integers. For example, if the marginal cost of increasing
production from 1 unit to 2 units is $5, then you would plot a point at (1.5, 5).)
10
Marginal Revenue
00
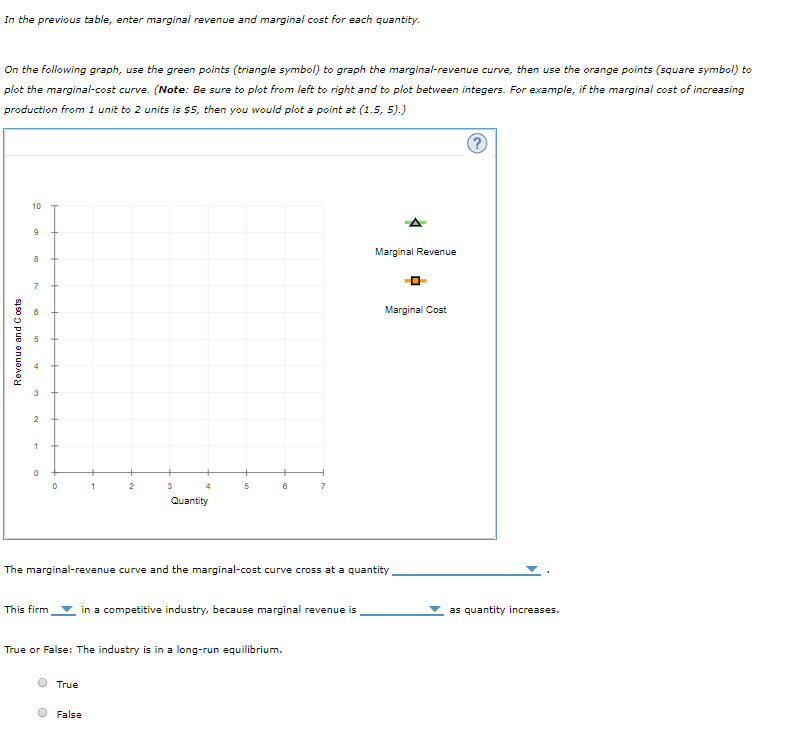
Transcribed Image Text:In the previous table, enter marginal revenue and marginal cost for each quantity.
On the following graph, use the green points (triangle symbol) to graph the marginal-revenue curve, then use the orange points (square symbol) to
plot the marginal-cost curve. (Note: Be sure to plot from left to right and to plot between integers. For example, if the marginal cost of increasing
production from 1 unit to 2 units is $5, then you would plot a point at (1.5, 5).)
10
Marginal Revenue
Marginal Cost
2
Quantity
The marginal-revenue curve and the marginal-cost curve cross at a quantity
This firm
in a competitive industry, because marginal revenue is
as quantity increases.
True or False: The industry is in a long-run equilibrium.
True
False
Revenue and C osts
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning