cooling tower designs that could be considered. Assuming that the cost of capital to the utility company is 12% per year, your job is to recommend the best alternative (ie, the least expensive during the servic life) Further, assume that each alternative is capable of satisfactorily removing waste heat from the condensers of a 200-MW power plant. What noneconomic factors can you identify that might also play a role the decision-making process? Click the icon to view the alternatives description. Click the icon to view the interest and annuity table for discrete compounding when /= 12% per year. The AW of Wet Tower, Mechanical Draft is $ (Round to the nearest dollar) Data table Alternative Initial cost Power for I.D. fans Power for pumps CI Dry Tower Mech. Draft Wet Tower Mech, Draft Wet Tower Natural Draft $8.8 million None $2.8 million. 40 200-hp I.D. fans 20 150-hp pumps $0.15 million Mechanical maintenance/year 20 150-hp pumps $0.13 million 30 years 0 30 years Service life 30 years 0 Market value 0 100 hp 74.6 kW, cost of power to plant is 2 2 cents per kWh or kilowatt-hour, induced-draft fans and pumps operate around the clock for 365 days/year (continuously). Assume that electric motors for pumps and fans are 90% efficient. Dry Tower Natural Draft $4.8 million 20 200-hp I.D. fans. 40 100-hp pumps $0.17 million 30 years 0 $8.9 million None 40 100-hp pumps $0.13 million
cooling tower designs that could be considered. Assuming that the cost of capital to the utility company is 12% per year, your job is to recommend the best alternative (ie, the least expensive during the servic life) Further, assume that each alternative is capable of satisfactorily removing waste heat from the condensers of a 200-MW power plant. What noneconomic factors can you identify that might also play a role the decision-making process? Click the icon to view the alternatives description. Click the icon to view the interest and annuity table for discrete compounding when /= 12% per year. The AW of Wet Tower, Mechanical Draft is $ (Round to the nearest dollar) Data table Alternative Initial cost Power for I.D. fans Power for pumps CI Dry Tower Mech. Draft Wet Tower Mech, Draft Wet Tower Natural Draft $8.8 million None $2.8 million. 40 200-hp I.D. fans 20 150-hp pumps $0.15 million Mechanical maintenance/year 20 150-hp pumps $0.13 million 30 years 0 30 years Service life 30 years 0 Market value 0 100 hp 74.6 kW, cost of power to plant is 2 2 cents per kWh or kilowatt-hour, induced-draft fans and pumps operate around the clock for 365 days/year (continuously). Assume that electric motors for pumps and fans are 90% efficient. Dry Tower Natural Draft $4.8 million 20 200-hp I.D. fans. 40 100-hp pumps $0.17 million 30 years 0 $8.9 million None 40 100-hp pumps $0.13 million
Chapter17: Capital And Time
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 17.6P
Related questions
Question
Use the charts to find aw of each.
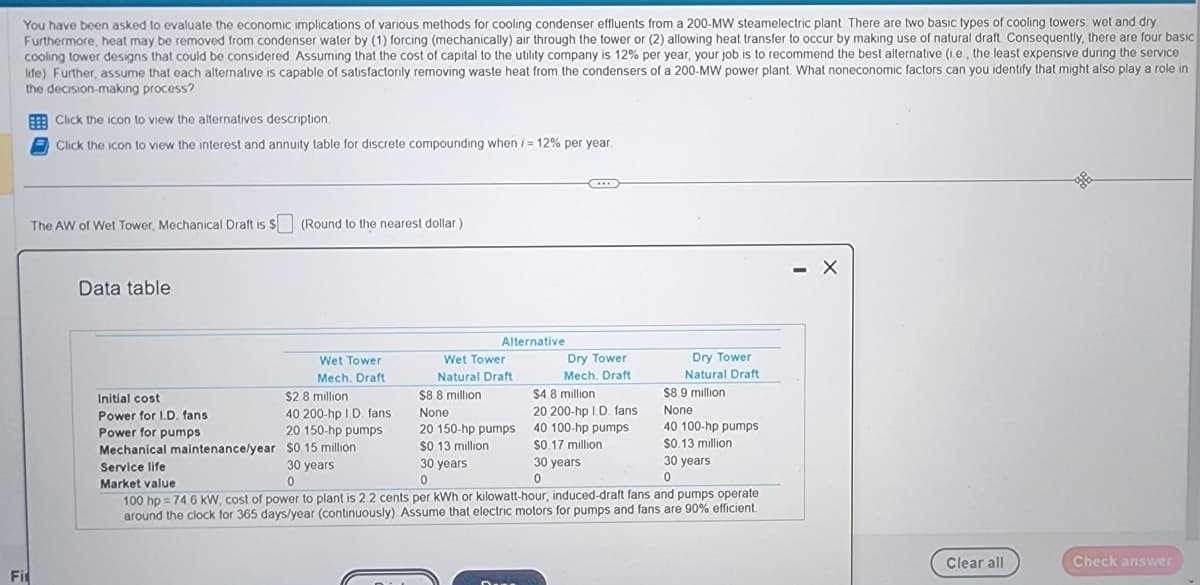
Transcribed Image Text:You have been asked to evaluate the economic implications of various methods for cooling condenser effluents from a 200-MW steamelectric plant. There are two basic types of cooling towers: wet and dry.
Furthermore, heat may be removed from condenser water by (1) forcing (mechanically) air through the tower or (2) allowing heat transfer to occur by making use of natural draft. Consequently, there are four basic
cooling tower designs that could be considered. Assuming that the cost of capital to the utility company is 12% per year, your job is to recommend the best alternative (i.e., the least expensive during the service
life) Further, assume that each alternative is capable of satisfactorily removing waste heat from the condensers of a 200-MW power plant. What noneconomic factors can you identify that might also play a role in
the decision-making process?
Fir
Click the icon to view the alternatives description.
Click the icon to view the interest and annuity table for discrete compounding when i = 12% per year.
The AW of Wet Tower, Mechanical Draft is $ (Round to the nearest dollar.)
Data table
Wet Tower
Mech. Draft
$2.8 million
40 200-hp I.D. fans
20 150-hp pumps
$0.15 million
Initial cost
Power for I.D. fans.
Power for pumps
Alternative
30 years
0
Wet Tower
Natural Draft
$8.8 million
None
20 150-hp pumps
$0.13 million
B
Dry Tower
Mech, Draft
$4.8 million
20 200-hp I.D. fans
40 100-hp pumps
$0.17 million
30 years
0
$8.9 million
None
Mechanical maintenance/year
40 100-hp pumps
$0.13 million
30 years
0
Service life
Market value
30 years
0
100 hp = 74.6 kW; cost of power to plant is 2.2 cents per kWh or kilowatt-hour, induced-draft fans and pumps operate
around the clock for 365 days/year (continuously). Assume that electric motors for pumps and fans are 90% efficient.
Dry Tower
Natural Draft
X
Clear all
gla
Check answer
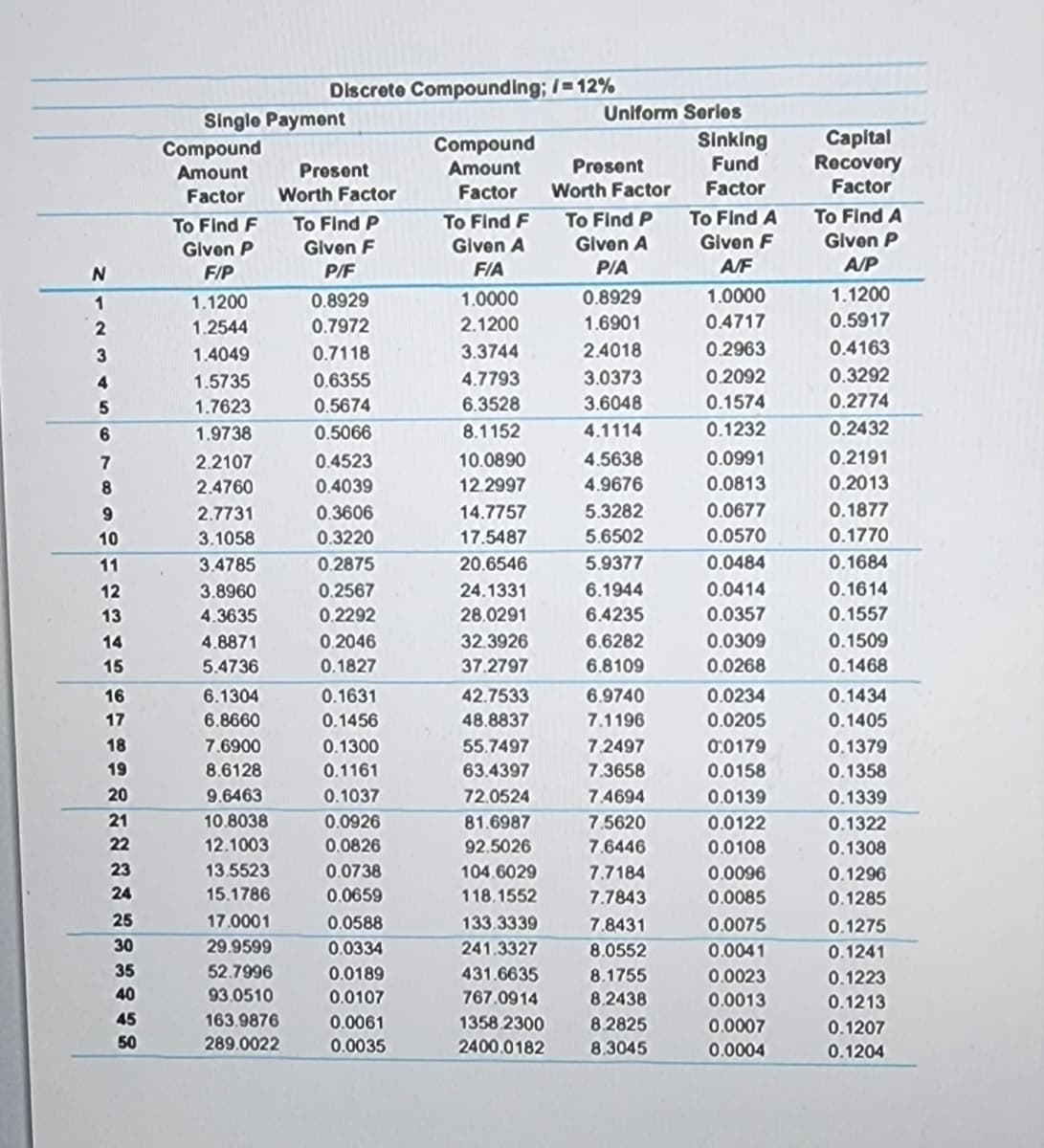
Transcribed Image Text:N
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
30
35
40
45
50
Single Payment
Compound
Amount
Factor
To Find F
Given P
F/P
1.1200
1.2544
1.4049
1.5735
1.7623
1.9738
2.2107
2.4760
2.7731
3.1058
3.4785
3.8960
4.3635
4.8871
5.4736
6.1304
6.8660
7.6900
8.6128
9.6463
10.8038
12.1003
13.5523
15.1786
17.0001
29.9599
52.7996
93.0510
Discrete Compounding; /=12%
Compound
Amount
Factor
Present
Worth Factor
To Find P
Given F
P/F
163.9876
289.0022
0.8929
0.7972
0.7118
0.6355
0.5674
0.5066
0.4523
0.4039
0.3606
0.3220
0.2875
0.2567
0.2292
0,2046
0.1827
0.1631
0.1456
0.1300
0.1161
0.1037
0.0926
0.0826
0.0738
0.0659
0.0588
0.0334
0.0189
0.0107
0.0061
0.0035
To Find F
Given A
FIA
1.0000
2.1200
3.3744
4.7793
6.3528
8.1152
10.0890
12.2997
14.7757
17.5487
20.6546
24.1331
28.0291
32.3926
37.2797
42.7533
48.8837
55.7497
63.4397
72.0524
81.6987
92.5026
104.6029
118.1552
133.3339
241.3327
431.6635
767.0914
1358.2300
2400.0182
Uniform Series
Present
Worth Factor
To Find P
Given A
P/A
0.8929
1.6901
2.4018
3.0373
3.6048
4.1114
4.5638
4.9676
5.3282
5.6502
5.9377
6.1944
6.4235
6.6282
6.8109
6.9740
7.1196
7.2497
7.3658
7.4694
7.5620
7.6446
7.7184
7.7843
7.8431
8.0552
8.1755
8.2438
8.2825
8.3045
Sinking
Fund
Factor
To Find A
Given F
A/F
1.0000
0.4717
0.2963
0.2092
0.1574
0.1232
0.0991
0.0813
0.0677
0.0570
0.0484
0.0414
0.0357
0.0309
0.0268
0.0234
0.0205
0:0179
0.0158
0.0139
0.0122
0.0108
0.0096
0.0085
0.0075
0.0041
0.0023
0.0013
0.0007
0.0004
Capital
Recovery
Factor
To Find A
Given P
A/P
1.1200
0.5917
0.4163
0.3292
0.2774
0.2432
0.2191
0.2013
0.1877
0.1770
0.1684
0.1614
0.1557
0.1509
0.1468
0.1434
0.1405
0.1379
0.1358
0.1339
0.1322
0.1308
0.1296
0.1285
0.1275
0.1241
0.1223
0.1213
0.1207
0.1204
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

