Cr3+(aq) → Cr(s) Zn2+(aq) → Zn(s) a. What will be the overall balanced reaction if you want to make a galvanic cell? b. What is the standard cell potential, E°cell?(use values from the provided SRP table) c. If the initial concentrations are [Cr3+]=0.010 M and [Zn2+]=0.0085 M, what is Ecell?
Cr3+(aq) → Cr(s) Zn2+(aq) → Zn(s) a. What will be the overall balanced reaction if you want to make a galvanic cell? b. What is the standard cell potential, E°cell?(use values from the provided SRP table) c. If the initial concentrations are [Cr3+]=0.010 M and [Zn2+]=0.0085 M, what is Ecell?
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter18: Electrochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5RQ: The Nernst equation allows determination of the cell potential for a galvanic cell at nonstandard...
Related questions
Question
Cr3+(aq) → Cr(s)
Zn2+(aq) → Zn(s)
a. What will be the overall balanced reaction if you want to make a galvanic cell?
b. What is the standard cell potential, E°cell?(use values from the provided SRP table)
c. If the initial concentrations are [Cr3+]=0.010 M and [Zn2+]=0.0085 M, what is Ecell?
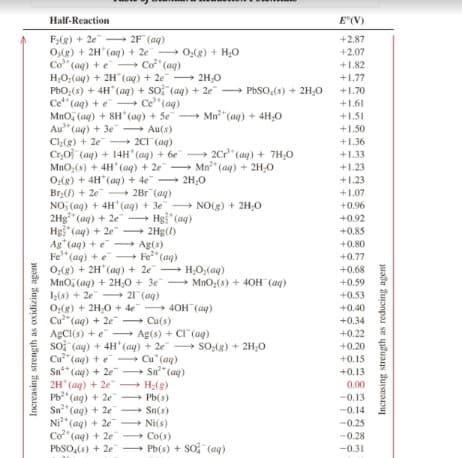
Transcribed Image Text:Half-Reaction
E"(V)
F(g) + 2e - 2F (aq)
O,(g) + 2H (aq) + 2e
Co" (ag) + e Co" (aq)
H;O;(aq) + 2H (aq) + 2e 2H;0
PbO;(s) + 4H (aq) + so (aq) + 2e PbSO,(s) + 2H,0
Cet" (ag) + e Ce"(aq)
Mno, (aq) + 8H' (aq) + Se Mn" (aq) + 4H,0
Au" (ag) + 3e Au(s)
Cl(g) + 2e - 2C1 (aq)
CrO (aq) + 14H' (ag) + be - 2Cr" (aq) + 7H;0
MnO;(s) + 4H' (aq) + 2e Mn" (aq) + 2H,0
O,(g) + 4H*(aq) + 4e 2H;0
Br() + 2e - 2Br (aq)
NO, (aq) + 4H' (aq) + 3e
2Hg" (aq) + 2e – Hg" (ag)
Hg" (aq) + 2e 2Hg()
Ag (aq) + e Ag(s)
Fe" (aq) + e
O;(g) + 2H* (aq) + 2e H;O,(aq)
MnO, (aq) + 2H;0 + 3e -
Iz(s) + 2e- 21 (ag)
O,(g) + 2H,0 + 4e 40H (ag)
Cu" (aq) + 2e Cu(s)
* ABCI(s) + e - Ag(s) + CI (aq)
so, (ag) + 4H'(aq) + 2e SO;(g) + 2H;0
Cu" (ag) + e
Sn* (ag) + 2e Sn" (aq)
2H (aq) + 2e"
Pb"
+2.87
+ 0,(8) + H,0
+2.07
+1.82
+1.77
+1.70
+1.61
+1.51
+1.50
+1.36
+1.33
+1.23
+1.23
+1.07
+ NO(g) + 2H;O
+0.96
+0.92
+0.85
+0.80
+0.77
- Fe* (aq)
+0.68
+ MnO,(s) + 4OH (aq)
+0.59
+0.53
+0.40
+0.34
+0.22
+0.20
Cu" (ag)
+0.15
+0.13
H(g)
0.00
(aq) + 2e - Pb(s)
Sn" (ag) + 2e
Ni* (aq) + 2e Ni(s)
Co" (aq) + 2e Co(s)
PbSO,(s) + 2e - Pb(s) + so (ag)
-0.13
Sn(s)
--0.14
-0.25
-0.28
-0.31
Increasing strength as oxidizing agent
Increasing strength as reducing agent

Transcribed Image Text:Co" (aq) + 2e
PbSO,(s) + 2e
Ca* (aq) + 2e
Fe" (aq) + 2e Fe(s)
C*(aq) + 3e Cr(s)
Zn* (aq) + 2e – Zn(s)
2H,0 + 2e H;(g) + 20H (aq)
Mn" (ag) + 2e
Al" (aq) + 3e Al(s)
Be" (aq) + 2e → Be(s)
Mg" (ag) + 2e - Mg(s)
Na (aq) + e
Ca" (aq) + 2e
Sr"(aq) + 2e Sr(s)
Ba"(aq) + 2e – Ba(s)
K'(aq) + e - K(s)
Li' (aq) + e - Li(s)
+ Co(s)
Pb(s) + So, (ag)
Cd(s)
-0.28
-0.31
-0.40
--0.44
-0.74
-0.76
-0.83
+ Mn(s)
-1.18
-1.66
-1.85
-2.37
+ Na(s)
+ Ca(s)
-2.71
-2.87
-2.89
-2.90
-2.93
-3.05
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning