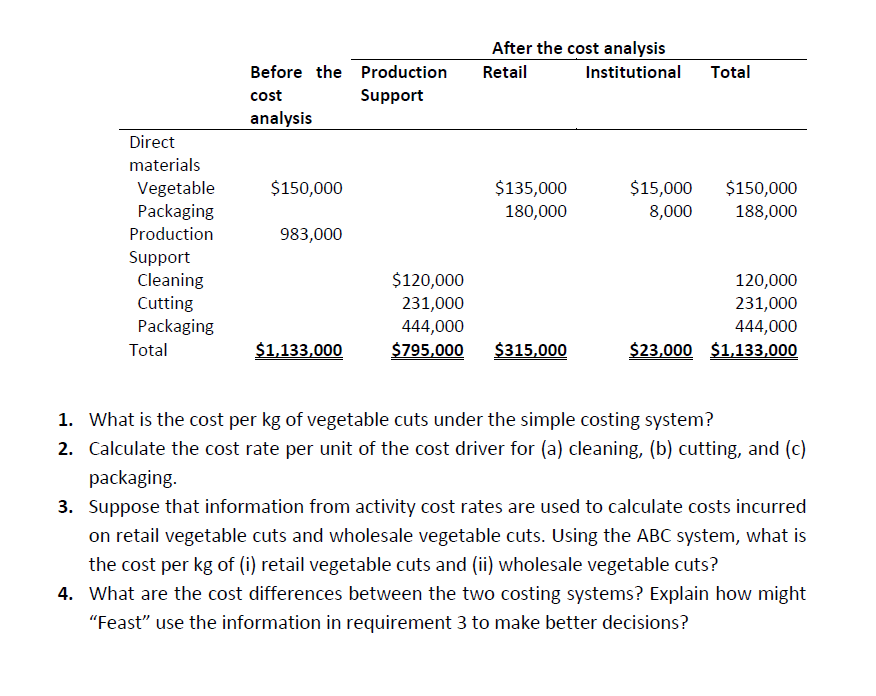
Currently they are using a simple which has a single direct-cost category (direct materials, i.e. raw vegetables) regardless of their targeted customers (retail and wholesale) and a single indirect-cost pool (production support, including packaging materials). Kilograms of vegetable cuts processed are used as allocation base of the indirect costs. In order to produce 1,000,000 kg of vegetable cuts, the company uses 1,200,000 kg of raw vegetables to process. At the end of 2018, "Feast" bid for a large wholesale contract for a restaurant chain. While making the bid, they included only a minimum profit margin. Later on, their bid was reported to be 30% above the winning bid. As a result of its review process of the lost contract bid, "Feast" decided to explore ways to find a better approach for their costing system. After the analysis they concluded that 90% of the direct materials (raw vegetables) related to the retail market and 10% to the wholesale market. In addition, the company identified that packaging materials could be directly traced to individual jobs ($180,000 for retail and $8,000 for wholesale). In order to decide on the costing structure, the company used ABC to identify three main activities that generated support costs: cleaning, cutting, and packaging. Following information is provided about the activities by the company; Cleaning-The cost-allocation base is kilograms of raw vegetables cleaned. Cutting-The production line produces (a) 250 kg of retail vegetable cuts per cutting-hour and (b) 400 kg of wholesale vegetable cuts per cutting-hour. The cost- allocation base is cutting-hours on the production line. Packaging-The packaging line packages (a) 25 kg of retail vegetable cuts per packaging-hour and (b) 100 kg of wholesale vegetable cuts per packaging-hour. The cost-allocation base is packaging-hours on the production line.
Process Costing
Process costing is a sort of operation costing which is employed to determine the value of a product at each process or stage of producing process, applicable where goods produced from a series of continuous operations or procedure.
Job Costing
Job costing is adhesive costs of each and every job involved in the production processes. It is an accounting measure. It is a method which determines the cost of specific jobs, which are performed according to the consumer’s specifications. Job costing is possible only in businesses where the production is done as per the customer’s requirement. For example, some customers order to manufacture furniture as per their needs.
ABC Costing
Cost Accounting is a form of managerial accounting that helps the company in assessing the total variable cost so as to compute the cost of production. Cost accounting is generally used by the management so as to ensure better decision-making. In comparison to financial accounting, cost accounting has to follow a set standard ad can be used flexibly by the management as per their needs. The types of Cost Accounting include – Lean Accounting, Standard Costing, Marginal Costing and Activity Based Costing.

Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 7 images









