Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an autosomal recessive disorder. Several different individual point mutations in the CFTR gene cause cystic fibrosis. Two of the most common mutations (A and B) are shown on the diagram below. The lines below the gene represent ASO (allele-specific oligonucleotide) probes and the regions of the gene to which they hybridize. The "wild type" probe hybridizes to the wild type allele and the "mutant" probe hybridizes to the mutant allele of this gene. А B CFTR gene Probe 1 wild type Probe 3 wild type Probe 2 mutant Probe 4 mutant Five people underwent ASO testing for cystic fibrosis using all four of the probes shown below. The results of this test are shown in the diagram. #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 Probe 1 Probe 2 Probe 3
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an autosomal recessive disorder. Several different individual point mutations in the CFTR gene cause cystic fibrosis. Two of the most common mutations (A and B) are shown on the diagram below. The lines below the gene represent ASO (allele-specific oligonucleotide) probes and the regions of the gene to which they hybridize. The "wild type" probe hybridizes to the wild type allele and the "mutant" probe hybridizes to the mutant allele of this gene. А B CFTR gene Probe 1 wild type Probe 3 wild type Probe 2 mutant Probe 4 mutant Five people underwent ASO testing for cystic fibrosis using all four of the probes shown below. The results of this test are shown in the diagram. #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 Probe 1 Probe 2 Probe 3
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter11: Genome Alterations: Mutation And Epigenetics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 16QP: Familial retinoblastoma, a rare autosomal dominant defect, arose in a large family that had no prior...
Related questions
Question
please help me very confused I have provided everything needed
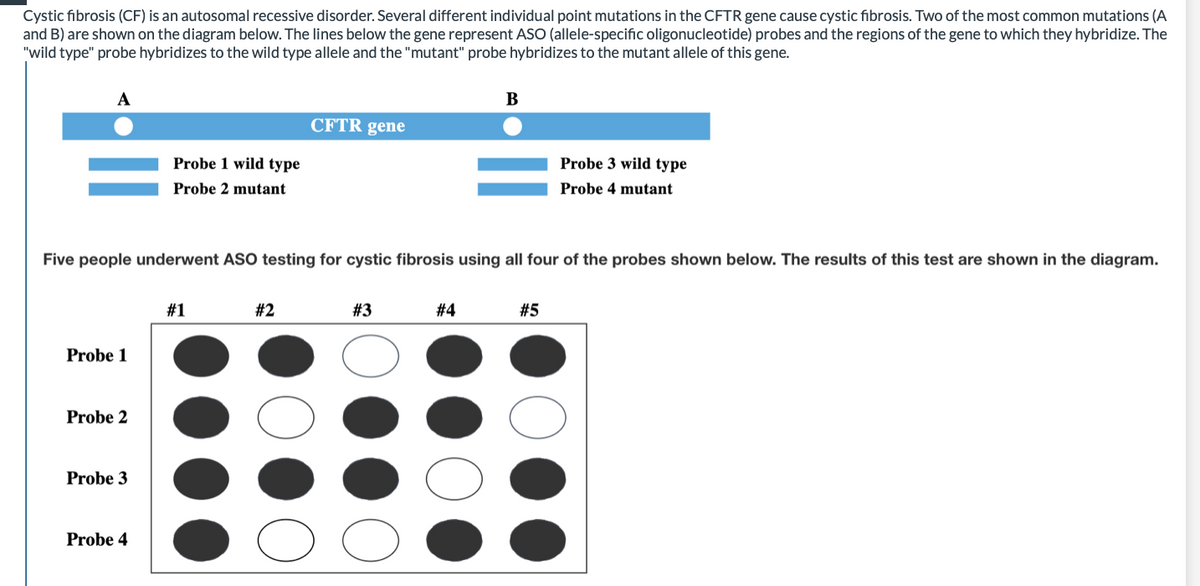
Transcribed Image Text:Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an autosomal recessive disorder. Several different individual point mutations in the CFTR gene cause cystic fibrosis. Two of the most common mutations (A
and B) are shown on the diagram below. The lines below the gene represent ASO (allele-specific oligonucleotide) probes and the regions of the gene to which they hybridize. The
"wild type" probe hybridizes to the wild type allele and the "mutant" probe hybridizes to the mutant allele of this gene.
В
CFTR gene
Probe 1 wild type
Probe 3 wild type
Probe 2 mutant
Probe 4 mutant
Five people underwent ASO testing for cystic fibrosis using all four of the probes shown below. The results of this test are shown in the diagram.
#1
#2
#3
# 4
#5
Probe 1
Probe 2
Probe 3
Probe 4

Transcribed Image Text:Which individual(s) have only wild type alleles (homozygous dominant)?
# 4
#1
#2
#5
#3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning