Decision Alternative Up S₁ Stable s2 Down S3 Investment A, d₁ Investment B, d₂ Investment C, d3 Probabilities $70,000 $45,000 $20,000 Profit Investment A, d Investment B, d₂ Investment C, d 100 70 0.95 Economic Conditions 45 Profit Decision Maker A 0.85 0.45 0.65 (a) Using the expected value approach, which decision is preferred? E(d₂) - $68 ✔ thousand E(d₂) = $56.25 thousand E(d₂) - $45 ✔ thousand The expected value approach recommends Investment A, d. ✔ 20 (b) For the lottery having a payoff of $100,000 with probability p and $0 with probability (1-p), two decision makers expressed the following indifference probabilities. Find the most preferred decision for each decision maker using the expected utility approach. Indifference Probability (p) 45 45 0.15 Decision Maker A 6.95 X 0.6 0.35 Decision Maker B 0.2 Expected Utilities 0 20 Calculate the expected utility for each of the decision alternatives for each of the decision makers. (Assign a utility of 10 to the payoff of $100,000 and a utility of 0 to the payoff of $0.) 45 0.20 Enter a number. Decision Maker B
Decision Alternative Up S₁ Stable s2 Down S3 Investment A, d₁ Investment B, d₂ Investment C, d3 Probabilities $70,000 $45,000 $20,000 Profit Investment A, d Investment B, d₂ Investment C, d 100 70 0.95 Economic Conditions 45 Profit Decision Maker A 0.85 0.45 0.65 (a) Using the expected value approach, which decision is preferred? E(d₂) - $68 ✔ thousand E(d₂) = $56.25 thousand E(d₂) - $45 ✔ thousand The expected value approach recommends Investment A, d. ✔ 20 (b) For the lottery having a payoff of $100,000 with probability p and $0 with probability (1-p), two decision makers expressed the following indifference probabilities. Find the most preferred decision for each decision maker using the expected utility approach. Indifference Probability (p) 45 45 0.15 Decision Maker A 6.95 X 0.6 0.35 Decision Maker B 0.2 Expected Utilities 0 20 Calculate the expected utility for each of the decision alternatives for each of the decision makers. (Assign a utility of 10 to the payoff of $100,000 and a utility of 0 to the payoff of $0.) 45 0.20 Enter a number. Decision Maker B
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
5th Edition
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Chapter20: The Problem Of Adverse Selection Moral Hazard
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2MC
Related questions
Question
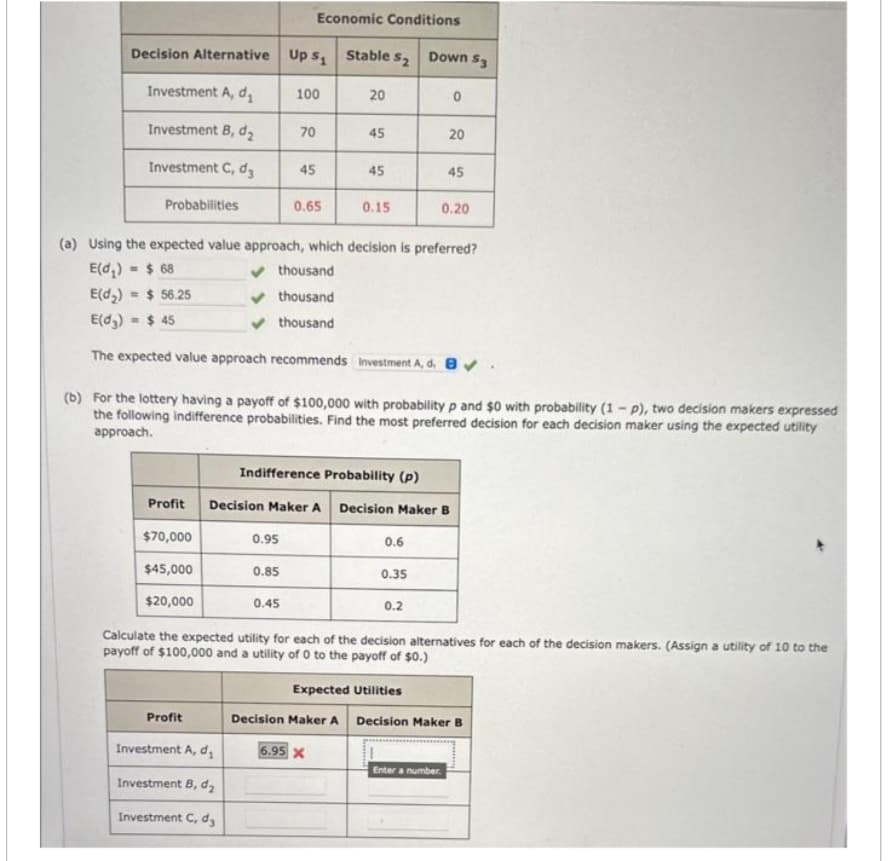
Transcribed Image Text:Decision Alternative Up S₁ Stable s₂ Down S3
Investment A, d₁
Investment B, d₂
Investment C, d3
Probabilities
Profit
Investment A, d₂
Investment B, d₂
Investment C, dz
100
70
Economic Conditions
45
0.95
thousand
thousand
thousand
0.85
0.65
0.45
Profit Decision Maker A
$70,000
$45,000
$20,000
20
(a) Using the expected value approach, which decision is preferred?
E(d₂) $ 68
E(d₂) = $ 56.25
E(d3) = $45
The expected value approach recommends Investment A, d. ✔
Indifference Probability (p)
45
45
(b) For the lottery having a payoff of $100,000 with probability p and $0 with probability (1-p), two decision makers expressed
the following indifference probabilities. Find the most preferred decision for each decision maker using the expected utility
approach.
0.15
6.95 X
Decision Maker A
0.6
Decision Maker B
0.35
0.2
Expected Utilities
0
20
45
0.20
Calculate the expected utility for each of the decision alternatives for each of the decision makers. (Assign a utility of 10 to the
payoff of $100,000 and a utility of 0 to the payoff of $0.)
Enter a number.
Decision Maker B
presning
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
