der these chemical species by increasing pH of an 0.1 M aqueous solution of each. That is, imagine making an 0.1 M solution of each species. Select I next to the species that makes the solution with the lowest pH. Select 2 next to the species that makes the solution with the next higher pH, and so on. Notice that some of the rankings have been filled in for you already. Also notice that water is on the list. For that particular case, just compare the pH of pure water to the pH of the other solutions. Note for advanced students: for all charged species, you may assume the necessary counterions act as neither acids nor bases. relative pH of species 0.1 M aqueous solution H₂O HN3 C₂H5N 2 7 F N3 (Choose one) 1 (lowest) 234 OH C,HẠNH HF 5 6 + 7 8 (highest) 1 (lowest)
der these chemical species by increasing pH of an 0.1 M aqueous solution of each. That is, imagine making an 0.1 M solution of each species. Select I next to the species that makes the solution with the lowest pH. Select 2 next to the species that makes the solution with the next higher pH, and so on. Notice that some of the rankings have been filled in for you already. Also notice that water is on the list. For that particular case, just compare the pH of pure water to the pH of the other solutions. Note for advanced students: for all charged species, you may assume the necessary counterions act as neither acids nor bases. relative pH of species 0.1 M aqueous solution H₂O HN3 C₂H5N 2 7 F N3 (Choose one) 1 (lowest) 234 OH C,HẠNH HF 5 6 + 7 8 (highest) 1 (lowest)
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Chapter13: Acids And Bases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 26QAP: Find [H+] and the pH of the following solutions. (a) A 456-mL sample of a 12.0% (by mass) solution...
Related questions
Question
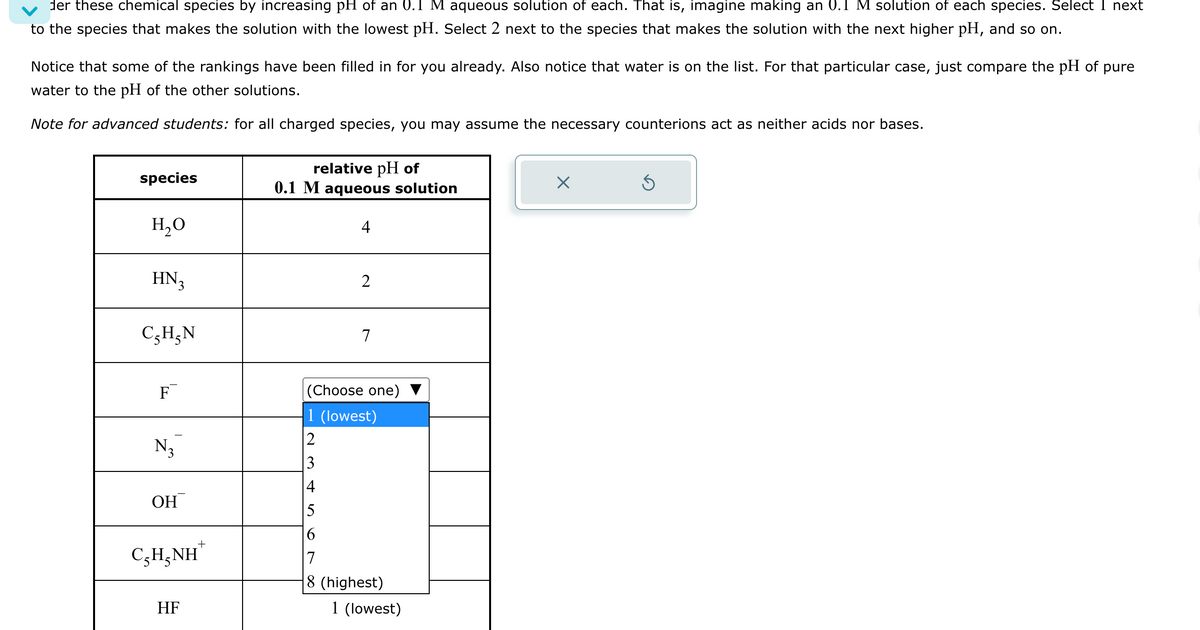
Transcribed Image Text:der these chemical species by increasing pH of an 0.1 M aqueous solution of each. That is, imagine making an 0.1 M solution of each species. Select I next
to the species that makes the solution with the lowest pH. Select 2 next to the species that makes the solution with the next higher pH, and so on.
Notice that some of the rankings have been filled in for you already. Also notice that water is on the list. For that particular case, just compare the pH of pure
water to the pH of the other solutions.
Note for advanced students: for all charged species, you may assume the necessary counterions act as neither acids nor bases.
relative pH of
species
0.1 M aqueous solution
H₂O
HN3
C₂H5N
2
7
F
N3
(Choose one)
1 (lowest)
234
OH
C,HẠNH
HF
5
6
+
7
8 (highest)
1 (lowest)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning