dmania Pricing High Low Capturesque Pricing High Low 8,8 13,4 4, 13 7,7 mple, the lower-left cell shows that if Padmania prices low and Capturesque prices high, Padmania will earn a profit of $13 million, and esque will earn a profit of $4 million. Assume this is a simultaneous game and that Padmania and Capturesque are both profit-maximizing hania prices high, Capturesque will make more profit if it chooses a it chooses a price. high uresque prices high, Padmania will make more profit if it chooses a it chooses a price. ering all of the information given, pricing low rms do not collude, what strategies will they end up choosing? low price, and if Padmania prices low, Capturesque will make more a dominant strategy for both Padmania and Capturesque. Both Padmania and Capturesque will choose a high price. price, and if Capturesque prices low, Padmania will make more OPadmania will choose a high price, and Capturesque will choose a low price. OBoth Padmania and Capturesque will choose a low price. O Padmania will choose a low price, and Capturesque will choose a high price. False: The game between Padmania and Capturesque is not an example of the prisoners' dilemma.
dmania Pricing High Low Capturesque Pricing High Low 8,8 13,4 4, 13 7,7 mple, the lower-left cell shows that if Padmania prices low and Capturesque prices high, Padmania will earn a profit of $13 million, and esque will earn a profit of $4 million. Assume this is a simultaneous game and that Padmania and Capturesque are both profit-maximizing hania prices high, Capturesque will make more profit if it chooses a it chooses a price. high uresque prices high, Padmania will make more profit if it chooses a it chooses a price. ering all of the information given, pricing low rms do not collude, what strategies will they end up choosing? low price, and if Padmania prices low, Capturesque will make more a dominant strategy for both Padmania and Capturesque. Both Padmania and Capturesque will choose a high price. price, and if Capturesque prices low, Padmania will make more OPadmania will choose a high price, and Capturesque will choose a low price. OBoth Padmania and Capturesque will choose a low price. O Padmania will choose a low price, and Capturesque will choose a high price. False: The game between Padmania and Capturesque is not an example of the prisoners' dilemma.
Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305971493
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter17: Oligopoly
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9PA
Related questions
Question
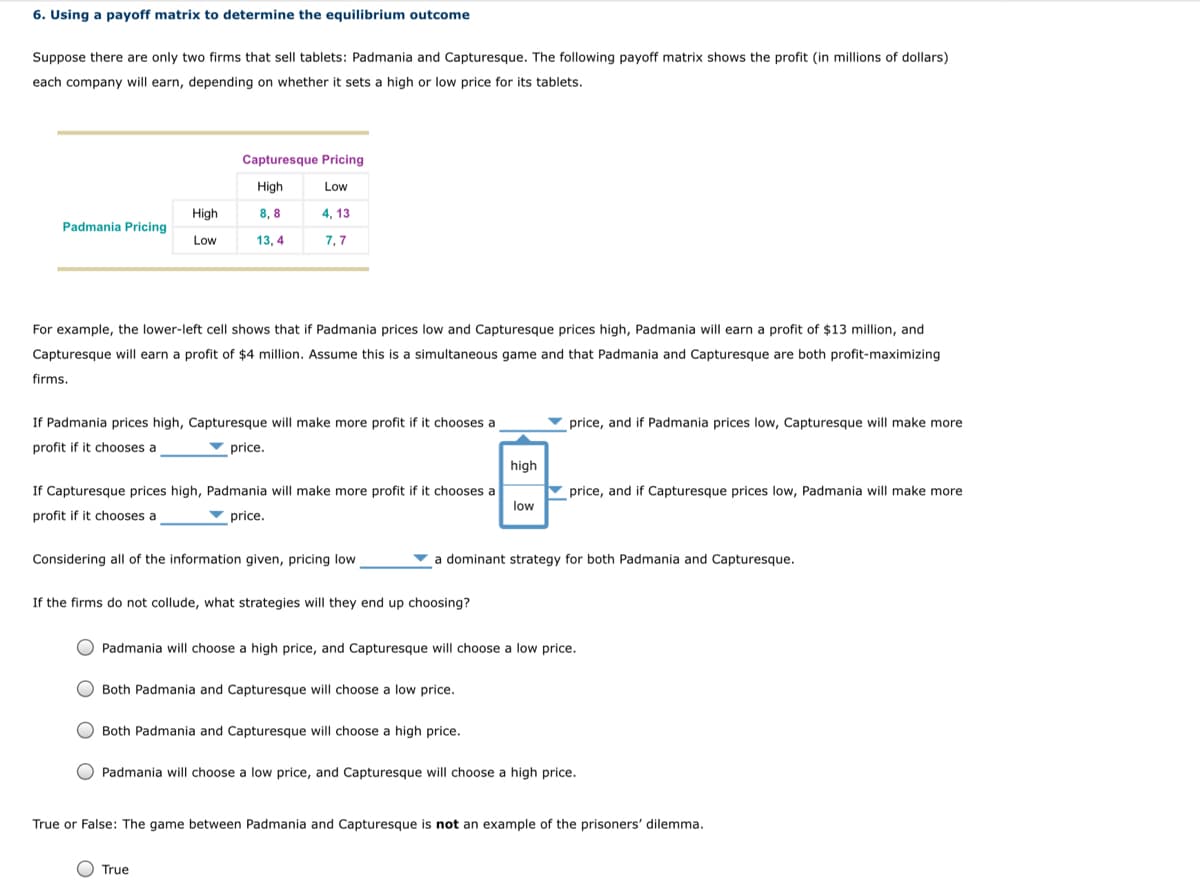
Transcribed Image Text:6. Using a payoff matrix to determine the equilibrium outcome
Suppose there are only two firms that sell tablets: Padmania and Capturesque. The following payoff matrix shows the profit (in millions of dollars)
each company will earn, depending on whether it sets a high or low price for its tablets.
Padmania Pricing
firms.
High
Low
Capturesque Pricing
Low
4, 13
7,7
For example, the lower-left cell shows that if Padmania prices low and Capturesque prices high, Padmania will earn a profit of $13 million, and
Capturesque will earn profit of $4 million. Assume this is a simultaneous game and that Padmania and Capturesque are both profit-maximizing
High
8,8
13,4
If Padmania prices high, Capturesque will make more profit if it chooses a
profit if it chooses a
price.
If Capturesque prices high, Padmania will make more profit if it chooses a
profit if it chooses a
price.
Considering all of the information given, pricing low
If the firms do not collude, what strategies will they end up choosing?
True
high
Both Padmania and Capturesque will choose a low price.
low
price, and if Padmania prices low, Capturesque will make more
a dominant strategy for both Padmania and Capturesque.
price, and if Capturesque prices low, Padmania will make more.
O Padmania will choose a high price, and Capturesque will choose a low price.
OBoth Padmania and Capturesque will choose a high price.
O Padmania will choose a low price, and Capturesque will choose a high price.
True or False: The game between Padmania and Capturesque is not an example of the prisoners' dilemma.

Transcribed Image Text:6. Using a payoff matrix to determine the equilibrium outcome
Suppose there are only two firms that sell tablets: Padmania and Capturesque. The following payoff matrix shows the profit (in millions of dollars)
each company will earn, depending on whether it sets a high or low price for its tablets.
Padmania Pricing
High
Low
Capturesque Pricing
High
LOW
8,8
13,4
4, 13
7,7
For example, the lower-left cell shows that if Padmania prices low and Capturesque prices high, Padmania will earn a profit of $13 million, and
Capturesque will earn a profit of $4 million. Assume this is a simultaneous game and that Padmania and Capturesque are both profit-maximizing
firms.
If Padmania prices high, Capturesque will make more profit if it chooses a
profit if it chooses a
price.
If Capturesque prices high, Padmania will make more profit if it chooses a
profit if it chooses a
▼price.
Considering all of the information given, pricing low
If the firms do not collude, what strategies will they end up choosing?
a dominant strategy for both Padmania and Capturesque.
Both Padmania and Capturesque will choose a low price.
True
price, and if Padmania prices low, Capturesque will make more
O Padmania will choose a high price, and Capturesque will choose a low price.
OBoth Padmania and Capturesque will choose a high price.
price, and if Capturesque prices low, Padmania will make more
Padmania will choose a low price, and Capturesque will choose a high price.
True or False: The game between Padmania and Capturesque is not an example of the prisoners' dilemma.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning