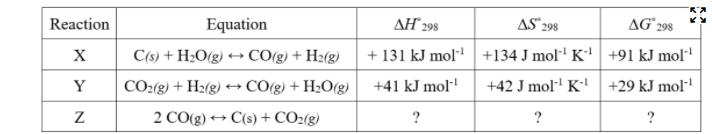
e) Is the following statement true or false? Justify your answer. “On the basis of the data in the table, it can be predicted that reaction Y will occur more rapidly than reaction X will occur.” f. Consider reaction Z at 298 K. (i) Is ∆S˚ for the reaction positive, negative, or zero? Justify your answer. (ii) Determine the value of ∆H˚ for the reaction. (iii) A sealed glass reaction vessel contains only CO(g) and a small amount of C(s). If a reaction occurs and the temperature is held constant at 298 K, will the pressure in the reaction vessel increase, decrease, or remain the same over time? Explain. Note: Please answer all the questions, it will be truly appreciated.
Answer the following questions using the information related to reactions X, Y, and Z in the image below.
e) Is the following statement true or false? Justify your answer.
“On the basis of the data in the table, it can be predicted that reaction Y will occur more rapidly than reaction X will occur.”
f. Consider reaction Z at 298 K.
(i) Is ∆S˚ for the reaction positive, negative, or zero? Justify your answer.
(ii) Determine the value of ∆H˚ for the reaction.
(iii) A sealed glass reaction vessel contains only CO(g) and a small amount of C(s). If a reaction occurs and the temperature is held constant at 298 K, will the pressure in the reaction vessel increase, decrease, or remain the same over time? Explain.
Note: Please answer all the questions, it will be truly appreciated.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps









