Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Chapter3: Atomic Shells And Classical Models Of Chemical Bonding
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 57P: Draw Lewis diagrams for the following compounds. In the formula the symbol of the central atom is...
Related questions
Question
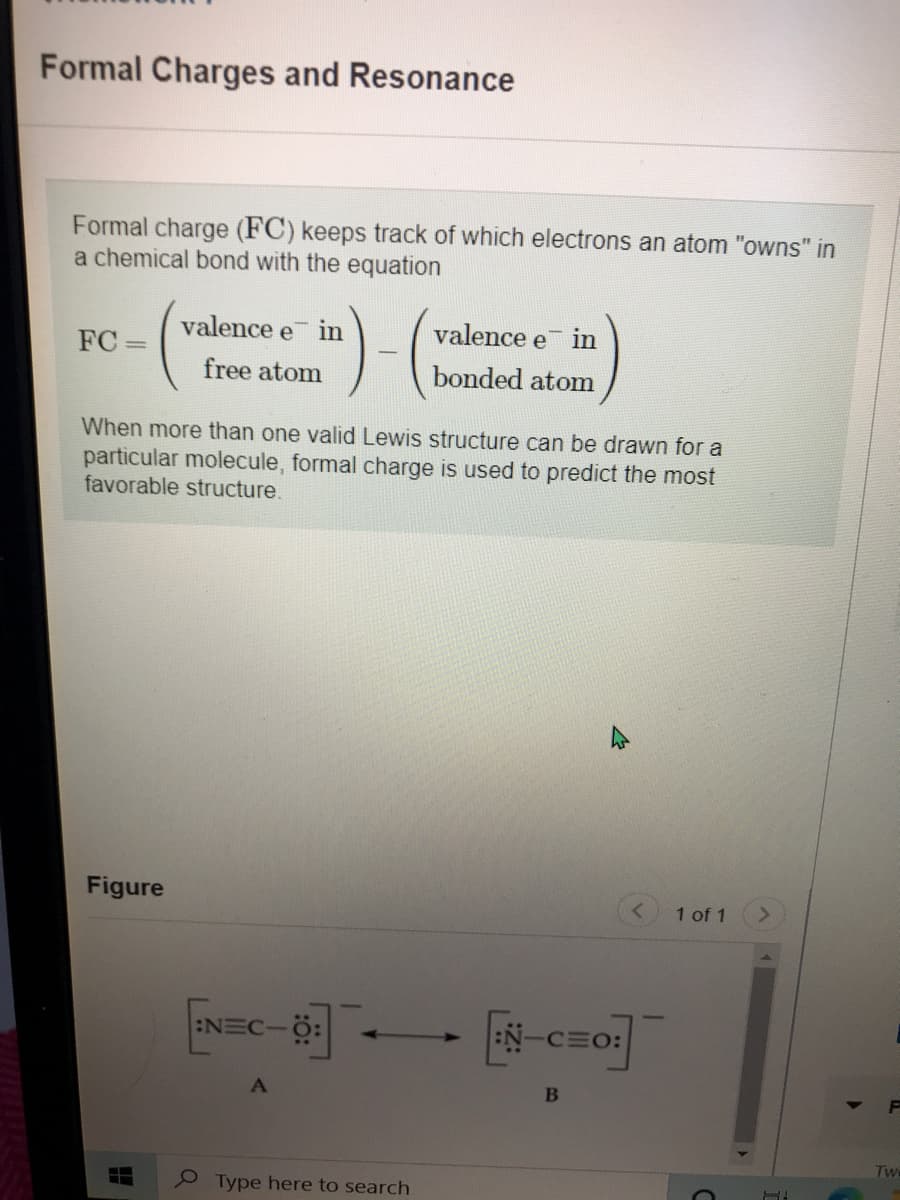
Transcribed Image Text:Formal Charges and Resonance
Formal charge (FC) keeps track of which electrons an atom "owns" in
a chemical bond with the equation
valence e in
valence e
in
FC =
free atom
bonded atom
When more than one valid Lewis structure can be drawn for a
particular molecule
favorable structure.
ormal charge is used to predict the most
Figure
1 of 1
:NEC-
:N-CEO:
Tw
Type here to search
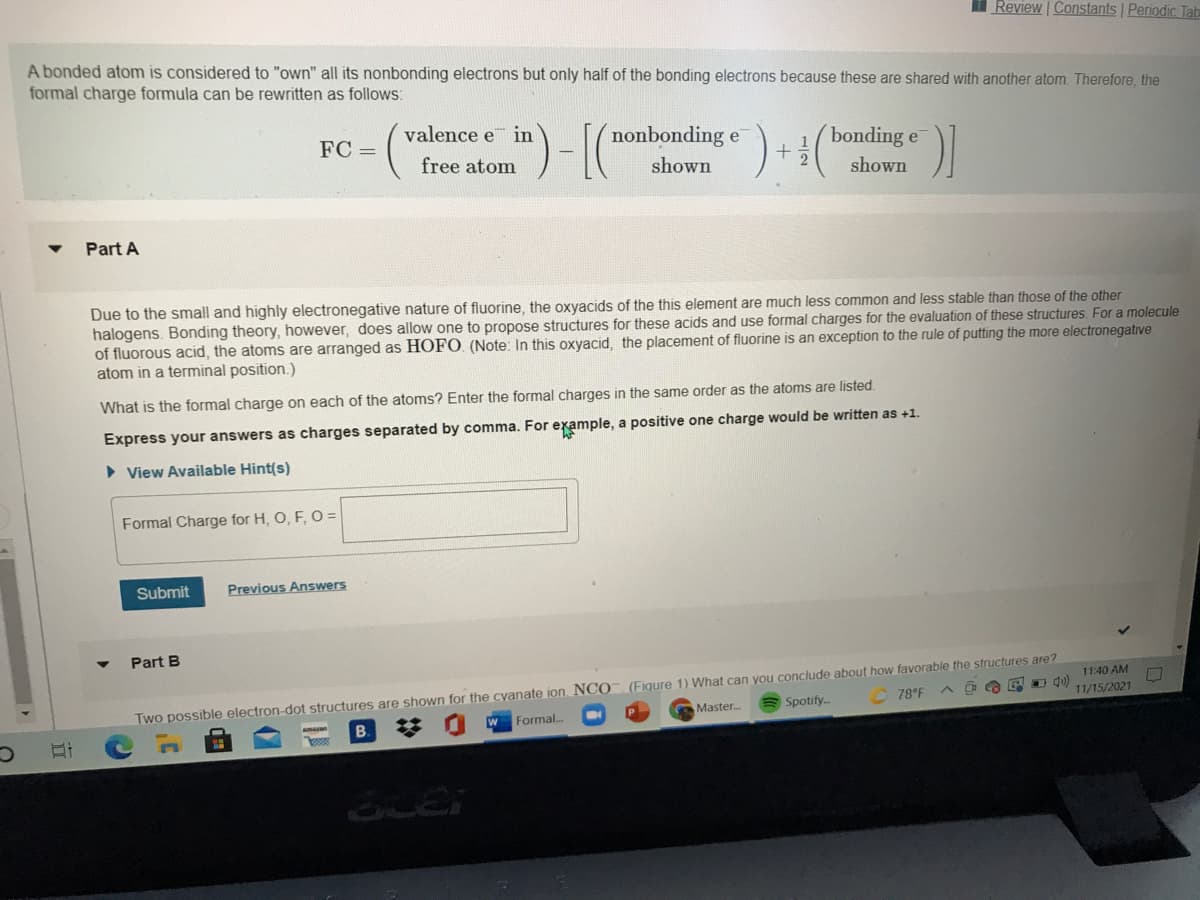
Transcribed Image Text:I Review | Constants Periodic Tab
A bonded atom is considered to "own" all its nonbonding electrons but only half of the bonding electrons because these are shared with another atom. Therefore, the
formal charge formula can be rewritten as follows:
valence e in
nonbonding e
bonding e
2.
FC =
free atom
shown
shown
Part A
Due to the small and highly electronegative nature of fluorine, the oxyacids of the this element are much less common and less stable than those of the other
halogens. Bonding theory, however, does allow one to propose structures for these acids and use formal charges for the evaluation of these structures. For a molecule
of fluorous acid, the atoms are arranged as HOFO. (Note: In this oxyacid, the placement of fluorine is an exception to the rule of putting the more electronegative
atom in a terminal position.)
What is the formal charge on each of the atoms? Enter the formal charges in the same order as the atoms are listed.
Express your answers as charges separated by comma. For example, a positive one charge would be written as +1.
• View Available Hint(s)
Formal Charge for H, O, F, O =
Submit
Previous Answers
Part B
11:40 AM
O du)
11/15/2021
78°F
Two possible electron-dot structures are shown for the cyanate ion. NCO (Figure 1) What can you conclude about how favorable the structures are?
Spotify.
Master..
W Formal.
梦
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285853918
Author:
H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285853918
Author:
H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning