Establishing the relative reactivity of metals requires a comparison of their relative tendency to either gain or lose electrons. Which of the following does not accurately describe the phenomena you observed in order to determine these tendencies? O When a more reactive metal is placed in a solution of a less reactive metal cation, the more reactive metal dissolves and donates its electrons to the cation of the less reactive metal. O The relative reactivity of Group IA metals increases as you go down a group on the periodic table because as you proceed down the group, the metal is more easily oxidized. O A less reactive metal cation gains electrons when placed into a solution with a more reactive metal, converting the metal cation to a solid. When copper metal is placed in a solution of silver nitrate, the copper metal disappears, shiny flakes appear, and the solution turns blue. O A more reactive metal gains electrons when placed into a solution with a less metal, converting the metal to a solid.
Establishing the relative reactivity of metals requires a comparison of their relative tendency to either gain or lose electrons. Which of the following does not accurately describe the phenomena you observed in order to determine these tendencies? O When a more reactive metal is placed in a solution of a less reactive metal cation, the more reactive metal dissolves and donates its electrons to the cation of the less reactive metal. O The relative reactivity of Group IA metals increases as you go down a group on the periodic table because as you proceed down the group, the metal is more easily oxidized. O A less reactive metal cation gains electrons when placed into a solution with a more reactive metal, converting the metal cation to a solid. When copper metal is placed in a solution of silver nitrate, the copper metal disappears, shiny flakes appear, and the solution turns blue. O A more reactive metal gains electrons when placed into a solution with a less metal, converting the metal to a solid.
Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Chapter17: Electrochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: What is a half-reaction? Why must the number of electrons lost in the oxidation half-reaction equal...
Related questions
Question
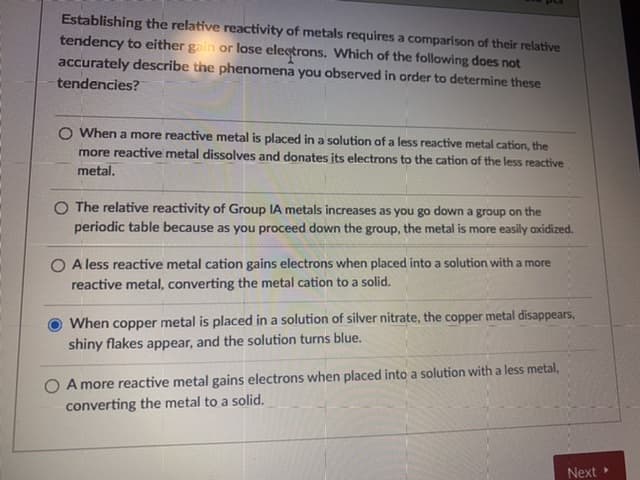
Transcribed Image Text:Establishing the relative reactivity of metals requires a comparison of their relative
tendency to either gain or lose electrons. Which of the following does not
accurately describe the phenomena you observed in order to determine these
tendencies?
O When a more reactive metal is placed in a solution of a less reactive metal cation, the
more reactive metal dissolves and donates its electrons to the cation of the less reactive
metal.
O The relative reactivity of Group IA metals increases as you go down a group on the
periodic table because as you proceed down the group, the metal is more easily oxidized.
O A less reactive metal cation gains electrons when placed into a solution with a more
reactive metal, converting the metal cation to a solid.
When copper metal is placed in a solution of silver nitrate, the copper metal disappears,
shiny flakes appear, and the solution turns blue.
O A more reactive metal gains electrons when placed into a solution with a less metal,
converting the metal to a solid.
Next
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning