Ethylene glycol is a common ingredient in antifreeze. It has a molar mass of 62.068 g mol-1 and a density of 1.1132 g cm-3 when liquid. Calculate the change in the molar Gibbs energy of liquid ethylene glycol when the pressure increases by 3.0 bar. 5578 J/mol 167.3 kJ/mol 5.58 J/mol O 16.73 J/mol O 5.8 kJ/mol O 167.3 J/mol
Ethylene glycol is a common ingredient in antifreeze. It has a molar mass of 62.068 g mol-1 and a density of 1.1132 g cm-3 when liquid. Calculate the change in the molar Gibbs energy of liquid ethylene glycol when the pressure increases by 3.0 bar. 5578 J/mol 167.3 kJ/mol 5.58 J/mol O 16.73 J/mol O 5.8 kJ/mol O 167.3 J/mol
Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Chapter14: Chemical Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 68P
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Question 1
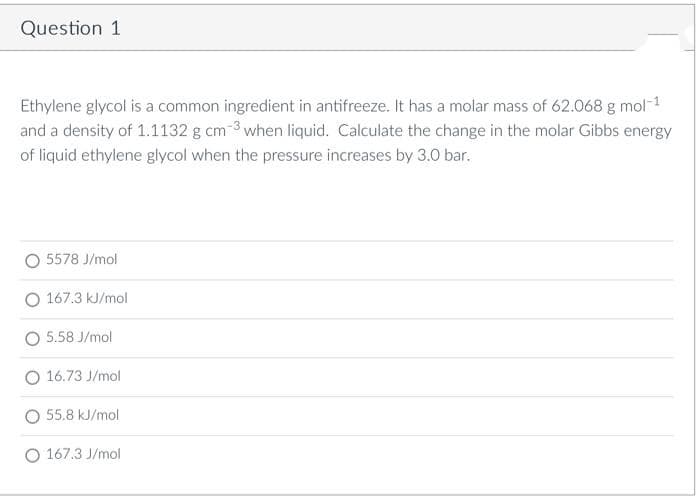
Ethylene glycol is a common ingredient in antifreeze. It has a molar mass of 62.068 g mol-1
and a density of 1.1132 g cm 3 when liquid. Calculate the change in the molar Gibbs energy
of liquid ethylene glycol when the pressure increases by 3.0 bar.
O 5578 J/mol
O 167.3 kJ/mol
5.58 J/mol
O 16.73 J/mol
O 55.8 kJ/mol
O 167.3 J/mol
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning