Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter6: Vector Spaces
Section6.5: The Kernel And Range Of A Linear Transformation
Problem 30EQ
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Q
Type here to search
A
y 1-
Z
Video Example
W
S
X
3
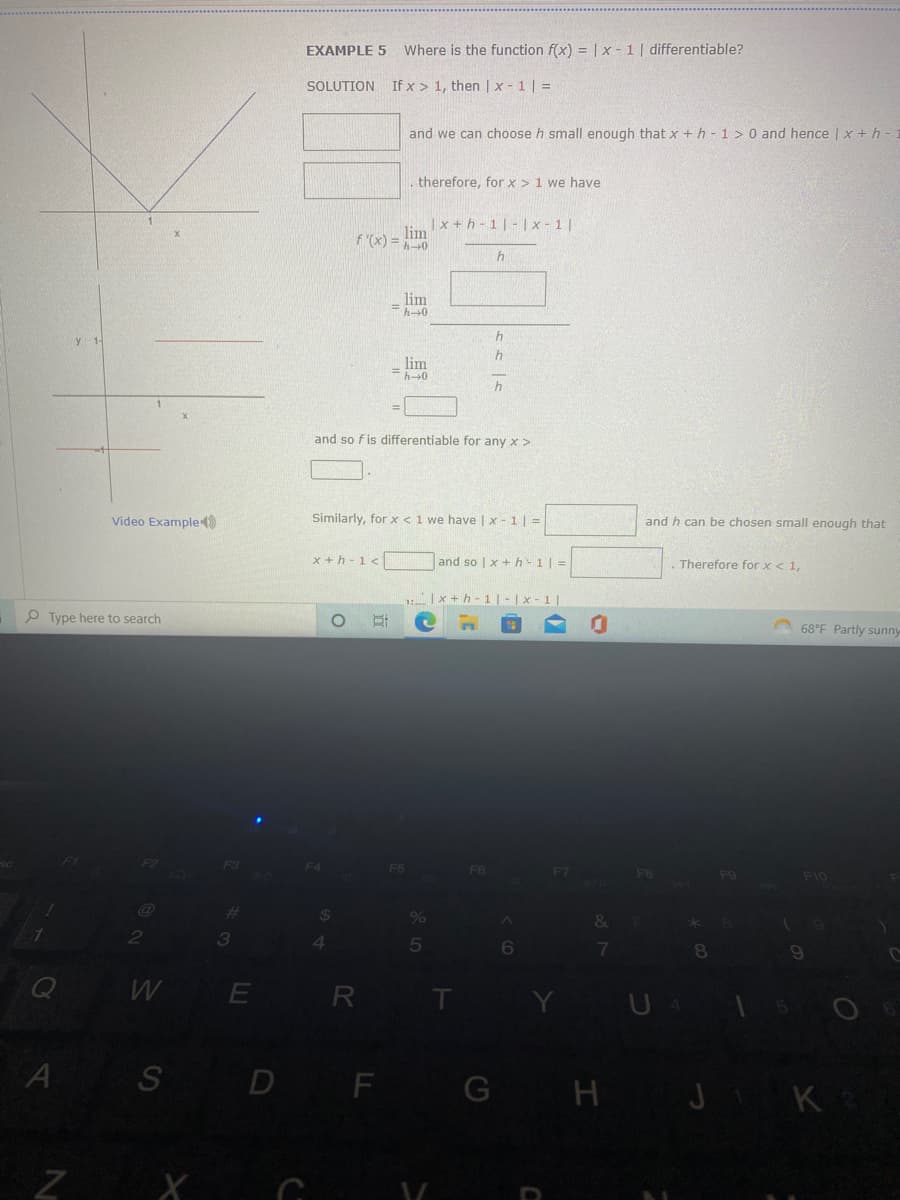
EXAMPLE 5
C
SOLUTION
x+h-1<
F4
Where is the function f(x) = |x-1| differentiable?
If x 1, then | x - 1 | =
$
4
f'(x) = 0
lim
O BI
and we can choose h small enough that x + h - 1 > 0 and hence | x + h-
. therefore, for x > 1 we have
lim
h-0
lim
=h→0
and so f is differentiable for any x >
Similarly, for x < 1 we have |x-1| =
F5
|x+h-1|-|x-1|
%
5
h
h
h
h
R T
and so I x + h-1 | =
F6
|x+h-1|-|x-1|
F7
n
7
and h can be chosen small enough that
FB
Therefore for x < 1,
U 4
8
68°F Partly sunny
D F G H J1 K ²
Transcribed Image Text:F3
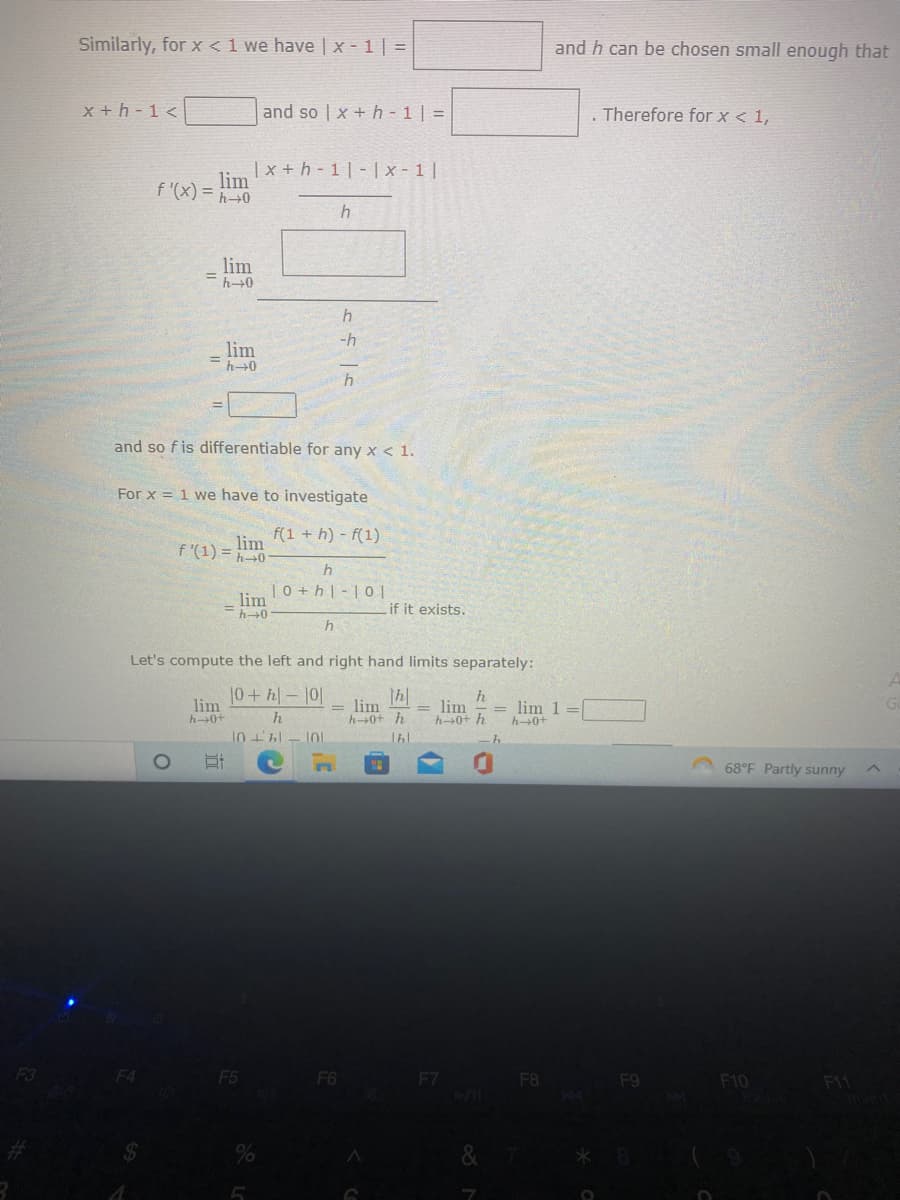
Similarly, for x < 1 we have |x-1|=|
x + h-1<
lim
f'(x) = h→0
=
F4
lim
h→0
1x+h-1|-|x-1|
lim
h→0
lim
h→0+
and so | x + h-1 | =
lim
f(1) = h 01
O Et
and so f is differentiable for any x < 1.
For x = 1 we have to investigate
f(1+h)-f(1)
lim
h→0
F5
%
h
h
-h
-
h
Let's compute the left and right hand limits separately:
10+ h|-|0|
h
101-101
h
h
10+hI-101
F6
if it exists.
Th|
= lim = lim =
h→0+ h
|h|
h
h→0+ h
h
F7
&
and h can be chosen small enough that
lim 1 =
h→0+
F8
. Therefore for x < 1,
*
O
F9
68°F Partly sunny
F10
F11
A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning