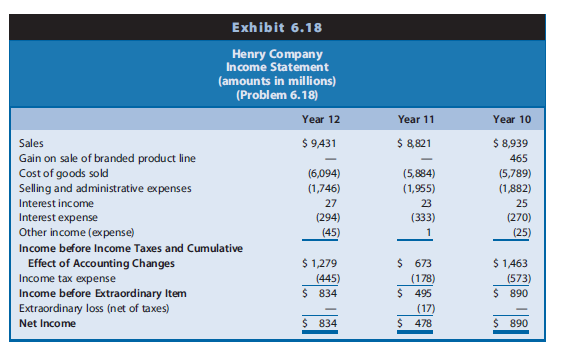
Exhibit 6.18 Henry Company Income Statement (amounts in millions) (Problem 6.18) Year 12 Year 11 Year 10 $ 9,431 $ 8821 $ 8,939 Sales Gain on sale of branded product line Cost of goods sold Selling and administrative expenses 465 (6,094) (1,746) (5,884) (5,789) (1,955) (1,882) Interest income 27 23 25 (333) Interest expense Other income (expense) (294) (270) (45) (25) Income before Income Taxes and Cumulative Effect of Accounting Changes Income tax expense Income before Extraordinary Item $ 1,279 (445) $ 834 $ 673 (178) $ 495 $ 1,463 (573) $ 890 Extraordinary loss (net of taxes) (17) $ 478 Net Income $ 834 $ 890
Reporting Cash Flows
Reporting of cash flows means a statement of cash flow which is a financial statement. A cash flow statement is prepared by gathering all the data regarding inflows and outflows of a company. The cash flow statement includes cash inflows and outflows from various activities such as operating, financing, and investment. Reporting this statement is important because it is the main financial statement of the company.
Balance Sheet
A balance sheet is an integral part of the set of financial statements of an organization that reports the assets, liabilities, equity (shareholding) capital, other short and long-term debts, along with other related items. A balance sheet is one of the most critical measures of the financial performance and position of the company, and as the name suggests, the statement must balance the assets against the liabilities and equity. The assets are what the company owns, and the liabilities represent what the company owes. Equity represents the amount invested in the business, either by the promoters of the company or by external shareholders. The total assets must match total liabilities plus equity.
Financial Statements
Financial statements are written records of an organization which provide a true and real picture of business activities. It shows the financial position and the operating performance of the company. It is prepared at the end of every financial cycle. It includes three main components that are balance sheet, income statement and cash flow statement.
Owner's Capital
Before we begin to understand what Owner’s capital is and what Equity financing is to an organization, it is important to understand some basic accounting terminologies. A double-entry bookkeeping system Normal account balances are those which are expected to have either a debit balance or a credit balance, depending on the nature of the account. An asset account will have a debit balance as normal balance because an asset is a debit account. Similarly, a liability account will have the normal balance as a credit balance because it is amount owed, representing a credit account. Equity is also said to have a credit balance as its normal balance. However, sometimes the normal balances may be reversed, often due to incorrect journal or posting entries or other accounting/ clerical errors.
Henry Company is a marketer of branded foods to retail and foodservice channels. Exhibit 6.18 presents Henry’s income statements for Year 10, Year 11, and Year 12. Notes to the financial statements reveal the following information:
1. Gain on sale of a portion of the branded product line. In Year 10, Henry completed the sale of a portion of one of its branded product lines for $735 million. The transaction resulted in a pretax gain of $464.5 million. The sale did not qualify as a discontinued operation. Henry did not disclose the tax effect of the gain reported in Exhibit 6.18.
2. Extraordinary loss. In Year 11, Henry experienced an extraordinary loss when a subsidiary was expropriated during a military coup in a previously stable country. The loss was $17 million, net of income taxes of $10 million.
3. Sale and promotion costs. In Year 11, Henry changed the classification of certain sale and promotion incentives provided to customers and consumers. In the past, Henry classified these incentives as selling and administrative expenses (see Exhibit 6.18), with the gross amount of the revenue associated with the incentives reported in sales. Beginning
in Year 11, Henry changed to reporting the incentives as a reduction of revenues. As a result of this change, the firm reduced reported revenues by $693 million in Year 12, $610 million in Year 11, and $469 million in Year 10. The firm stated that selling and administrative expenses were ‘‘correspondingly reduced such that net earnings were not affected.’’ Exhibit 6.18 already reflects the adjustments to sales revenues and selling and
administrative expenses for Years 10 through 12.
4. Tax rate. The U.S. federal statutory income tax rate was 35% for each of the years presented in Exhibit 6.18.
REQUIRED
a. Discuss whether you would adjust for each of the following items when using earnings to
(1) Gain on sale of a portion of the branded product line
(2) Extraordinary loss
b. Indicate the adjustment you would make to Henry’s net income for each item in Part a.
c. Discuss whether you believe the reclassification adjustments made by Henry for the sale and promotion incentive costs (Item 3) are appropriate.
d. Prepare a common-size income statement for Year 10, Year 11, and Year 12 using the amounts in Exhibit 6.18. Set sales equal to 100%.
e. Repeat Requirement d after making the income statement adjustments in Requirement b.
f. Assess the changes in the profitability of Henry during the three-year period.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps








