
Analyze and compare Costco, Wal-Mart, and Nordstrom
The general merchandise retail industry has a number of segments represented by the following companies:
| Company Name | Merchandise Concept |
| Costco Wholesale Corporation (COST) | Membership warehouse |
| Wal-Mart Stores, Inc. (WMT) | Discount general merchandise |
| Nordstrom, Inc. (JWN) | Fashion department store |
For a recent war, the following cost of goods sold and beginning and ending inventories are provided from corporate annual reports (in millions) for these three companies:
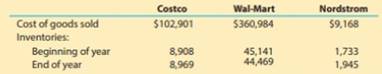
- a. Determine the inventory turnover ratio for all three companies. Round all calculations to one decimal place.
- b. Determine the number of days’ sales in inventory for all three companies. Use 365 days and round all calculations to one decimal place.
- c.
 Interpret these results based on each company’s merchandising concept.
Interpret these results based on each company’s merchandising concept.
(a)
Inventory turnover ratio: Inventory turnover ratio is used to determine the number of times inventory used or sold during the particular accounting period. The formula to calculate the inventory turnover ratio is as follows:
To determine: the inventory turnover for Company C, Company W and Company N
Answer to Problem 6.3MAD
Explanation of Solution
The inventory turnover ratio for Company C is calculated as follows:
Working notes:
The average inventory is calculated as follows:
The inventory turnover ratio for Company W is calculated as follows:
Working notes:
The average inventory is calculated as follows:
The inventory turnover ratio for Company N is calculated as follows:
Working notes:
The average inventory is calculated as follows:
The inventory turnover of Company C is 11.5 Times, the inventory turnover of Company W is 8 Times and the inventory turnover of Company N is 5 Times.
(b)
Days’ sales in inventory: Days’ sales in inventory are used to determine number of days a particular company takes to make sales of the inventory available with them. The formula to calculate the days’ sales in inventory ratio is as follows:
To determine: the Days’ sales in inventory ratio for Company C, Company W and Company N.
Answer to Problem 6.3MAD
Explanation of Solution
The Days’ sale in inventory ratio for Company C is calculated as follows:
The Days’ sale in inventory ratio for Company W is calculated as follows:
The Days’ sale in inventory ratio for Company N is calculated as follows:
The Days’ sales in inventory of Company C is 31.7 days, the Days’ sales in inventory of Company W is 45.6 days, & the Days’ sales in inventory of Company N is 73 days.
(c)
Inventory turnover ratio: Inventory turnover ratio is used to determine the number of times inventory used or sold during the particular accounting period. The formula to calculate the inventory turnover ratio is as follows:
Days’ sales in inventory: Days’ sales in inventory are used to determine number of days a particular company takes to make sales of the inventory available with them. The formula to calculate the days’ sales in inventory ratio is as follows:
To interpret: the above calculated ratios.
Explanation of Solution
The inventory turnover ratio and number of days’ sales in inventory of all the three companies reflect the merchandising approaches of all companies. Company C is a club warehouse and it has approach of holding only items which are quickly sold. Most of the items are sold in bulk at very attractive prices.
In case of company W, it has a traditional discounter approach. Even though it has attractive pricing, the inventory movement is slower than in the case of company C.
In the case of company N, it is a high-end fashioner retailer. It offers a wide collection of specialty and unique goods that are specifically designed for fashion market rather than for general mass market. Therefore, the movement is slower than other two companies yet it has highest margin.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Corporate Financial Accounting
- Amazon.com, Inc. (AMZN) is one of the largest Internet retailers in the world. Target Corporation (TGT) is one of the largest value-priced general merchandisers operating in the United States. Target sells through nearly 1,800 brick-and-mortar stores and through the Internet. Amazon and Target compete for customers across a wide variety of products, including media, general merchandise, apparel, and consumer electronics. Cost of goods sold and inventory information from a recent annual report are provided for both companies as follows (in millions): a. Compute the inventory turnover for both companies. Round all calculations to one decimal place. b. Compute the number of days sales in inventory for both companies. Use 365 days and round all calculations to one decimal place. c. Which company has the better inventory efficiency? d. What might explain the difference in inventory efficiency between the two companies?arrow_forwardThe following information is from Good Read Books. Good Read is a regional book store with three regional stores. The May income statement for all stores is shown. A. Comment on the operating income results for each store. B. Now assume the costs allocated from corporate is an uncontrollable cost for each store. How does this change your assessment of each store?arrow_forwardMonster Beverage Corporation (MNST) develops, markets, and sells energy and other alternative beverage brands. Brown-Forman Corporation (BF.B) manufactures and sells a wide variety of spirit and wine beverages, such as Jack Daniels. The cost of goods sold and inventory were obtained from a recent annual report for both companies as follows (in millions): a. Determine the inventory turnover for both companies. Round all calculations to one decimal place. b. Determine the number of days sales in inventory for both companies. Use 365 days and round all calculations to one decimal place. c. Interpret the difference in inventory efficiency based on the companies respective product types.arrow_forward
- The following information is from Daves Sporting Goods. Daves is a Midwest sporting goods store with three regional stores. The August income statement for all stores is shown. A. Comment on the operating income results for each store. B. Now assume the costs allocated from corporate is an uncontrollable cost for each store. How does this change your assessment of each store?arrow_forwardGolden Eagle Company began operations on April 1 by selling a single product. Data on purchases and sales for the year are as follows: Purchases: Sales: The president of the company, Connie Kilmer, has asked for your advice on which inventory cost flow method should be used for the 32,000-unit physical inventory that was taken on December 31. The company plans to expand its product line in the future and uses the periodic inventory system. Write a brief memo to Ms. Kilmer comparing and contrasting the LIFO and FIFO inventory cost flow methods and their potential impacts on the companys financial statements.arrow_forwardThe Home Depot is a leading specialty retailer of hardware and home improvement products and is the second-largest retail store chain in the United States. It operates large warehouse-style stores. Despite declining sales and difficult economic conditions in 20X1 and 20X2, The Home Depot continued to invest in new stores. The following table provides summary hypothetical data for The Home Depot. REQUIRED a. Use the preceding data for The Home Depot to compute average revenues per store, capital spending per new store, and ending inventory per store in 20X2. b. Assume that The Home Depot will add 100 new stores by the end of Year +1. Use the data from 20X2 to project Year +1 sales revenues, capital spending, and ending inventory. Assume that each new store will be open for business for an average of one-half year in Year +1. For simplicity, assume that in Year +1, Home Depots sales revenues will grow, but only because it will open new stores.arrow_forward
- Lower of Cost or Market Shaw Systems sells a limited line of specially made products, using television advertising campaigns in large cities. At year end, Shaw has the following data for its inventory: Required: 1. Compute the carrying value of the ending inventory using the lower of cost or market rule applied on an item-by-item basis. 2. Prepare the journal entry required to value the inventory at lower of cost or market. 3. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION What is the impact of applying the lower of cost or market rule on the financial statements of the current period? What is the impact on the financial statements of a subsequent period in which the inventory is sold?arrow_forwardCustomers as a Cost Object Morrisom National Bank has requested an analysis of checking account profitability by customer type. Customers are categorized according to the size of their account: low balances, medium balances, and high balances. The activities associated with the three different customer categories and their associated annual costs are as follows: Additional data concerning the usage of the activities by the various customers are also provided: Required: (Note: Round answers to two decimal places.) 1. Calculate a cost per account per year by dividing the total cost of processing and maintaining checking accounts by the total number of accounts. What is the average fee per month that the bank should charge to cover the costs incurred because of checking accounts? 2. Calculate a cost per account by customer category by using activity rates. 3. Currently, the bank offers free checking to all of its customers. The interest revenues average 90 per account; however, the interest revenues earned per account by category are 80, 100, and 165 for the low-, medium-, and high-balance accounts, respectively. Calculate the average profit per account (average revenue minus average cost from Requirement 1). Then calculate the profit per account by using the revenue per customer type and the unit cost per customer type calculated in Requirement 2. 4. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION After the analysis in Requirement 3, a vice president recommended eliminating the free checking feature for low-balance customers. The bank president expressed reluctance to do so, arguing that the low-balance customers more than made up for the loss through cross-sales. He presented a survey that showed that 50% of the customers would switch banks if a checking fee were imposed. Explain how you could verify the presidents argument by using ABC.arrow_forwardCan you please help me find the answers to the question marks below:Todrick Company is a merchandiser that reported the following information based on 1,000 units sold:Sales $ 180,000Beginning merchandise inventory $ 12,000Purchases $ 120,000Ending merchandise inventory $ 6,000Fixed selling expense $ ?Fixed administrative expense $ 7,200Variable selling expense $ 9,000Variable administrative expense $ ?Contribution margin $ 36,000Net operating income $ 10,800arrow_forward
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning





