Explain f and g only factor in determining the usefulness of an examination as a measure of demonstrated ability is the amount of spread that occurs in the grades. If the spread or variation of examination scores is very small, it usually means that the examination was either too hard or too easy. However, if the variance of scores is moderately large, then there is a definite difference in scores between "better," "average," and "poorer" students. A group of attorneys in a Midwest state has been given the task of making up this year's bar examination for the state. The examination has 500 total possible points, and from the history of past examinations, it is known that a standard deviation of around 60 points is desirable. Of course, too large or too small a standard deviation is not good. The attorneys want to test their examination to see how good it is. A preliminary version of the examination (with slight modifications to protect the integrity of the real examination) is given to a random sample of 20 newly graduated law students. Their scores give a sample standard deviation of 70 points. Using a 0.01 level of significance, test the claim that the population standard deviation for the new examination is 60 against the claim that the population standard deviation is different from 60. (a) What is the level of significance? State the null and alternate hypotheses. Ho: σ = 60; H1: σ < 60Ho: σ > 60; H1: σ = 60 Ho: σ = 60; H1: σ > 60Ho: σ = 60; H1: σ ≠ 60 (b) Find the value of the chi-square statistic for the sample. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) What are the degrees of freedom? What assumptions are you making about the original distribution? We assume a binomial population distribution.We assume a exponential population distribution. We assume a normal population distribution.We assume a uniform population distribution. (c) Find or estimate the P-value of the sample test statistic. P-value > 0.1000.050 < P-value < 0.100 0.025 < P-value < 0.0500.010 < P-value < 0.0250.005 < P-value < 0.010P-value < 0.005 (d) Based on your answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Since the P-value > α, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.Since the P-value > α, we reject the null hypothesis. Since the P-value ≤ α, we reject the null hypothesis.Since the P-value ≤ α, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. (e) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application. At the 1% level of significance, there is insufficient evidence to conclude that the standard deviation of test scores on the preliminary exam is different from 60.At the 1% level of significance, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the standard deviation of test scores on the preliminary exam is different from 60. (f) Find a 99% confidence interval for the population variance. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) lower limit upper limit (g) Find a 99% confidence interval for the population standard deviation. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) lower limit points upper limit points
Inverse Normal Distribution
The method used for finding the corresponding z-critical value in a normal distribution using the known probability is said to be an inverse normal distribution. The inverse normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution with a family of two parameters.
Mean, Median, Mode
It is a descriptive summary of a data set. It can be defined by using some of the measures. The central tendencies do not provide information regarding individual data from the dataset. However, they give a summary of the data set. The central tendency or measure of central tendency is a central or typical value for a probability distribution.
Z-Scores
A z-score is a unit of measurement used in statistics to describe the position of a raw score in terms of its distance from the mean, measured with reference to standard deviation from the mean. Z-scores are useful in statistics because they allow comparison between two scores that belong to different normal distributions.
Explain f and g only
factor in determining the usefulness of an examination as a measure of demonstrated ability is the amount of spread that occurs in the grades. If the spread or variation of examination scores is very small, it usually means that the examination was either too hard or too easy. However, if the variance of scores is moderately large, then there is a definite difference in scores between "better," "average," and "poorer" students. A group of attorneys in a Midwest state has been given the task of making up this year's bar examination for the state. The examination has 500 total possible points, and from the history of past examinations, it is known that a standard deviation of around 60 points is desirable. Of course, too large or too small a standard deviation is not good. The attorneys want to test their examination to see how good it is. A preliminary version of the examination (with slight modifications to protect the integrity of the real examination) is given to a random sample of 20 newly graduated law students. Their scores give a sample standard deviation of 70 points. Using a 0.01 level of significance, test the claim that the population standard deviation for the new examination is 60 against the claim that the population standard deviation is different from 60.
State the null and alternate hypotheses.
(b) Find the value of the chi-square statistic for the sample. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
What are the degrees of freedom?
What assumptions are you making about the original distribution?
(c) Find or estimate the P-value of the sample test statistic.
(d) Based on your answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis?
(e) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application.
(f) Find a 99% confidence interval for the population variance. (Round your answers to two decimal places.)
| lower limit | |
| upper limit |
(g) Find a 99% confidence interval for the population standard deviation. (Round your answers to two decimal places.)
| lower limit | points |
| upper limit | points |
Given
sample standard deviation = 70
confidence interval = 99%
sample size = 20
degree of freedom = 19
a)
For 99% confidence interval,
The upper critical value has right tail area = (1 - 0.99)/2 = 0.005 and for 19 degree of freedom the critical value is 38.582
The lower critical value has right tail area = (1+0.99)/2 = 0.995 and for 19 degree of freedom the critical value is 6.844
The confidence interval for variance is calculated as shown below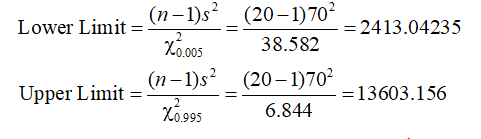
The 99% confidence interval for variance is
Lower limit = 2413.04 (rounded to 2 decimals)
Upper limit = 13603.16 (rounded to 2 decimals)
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images






