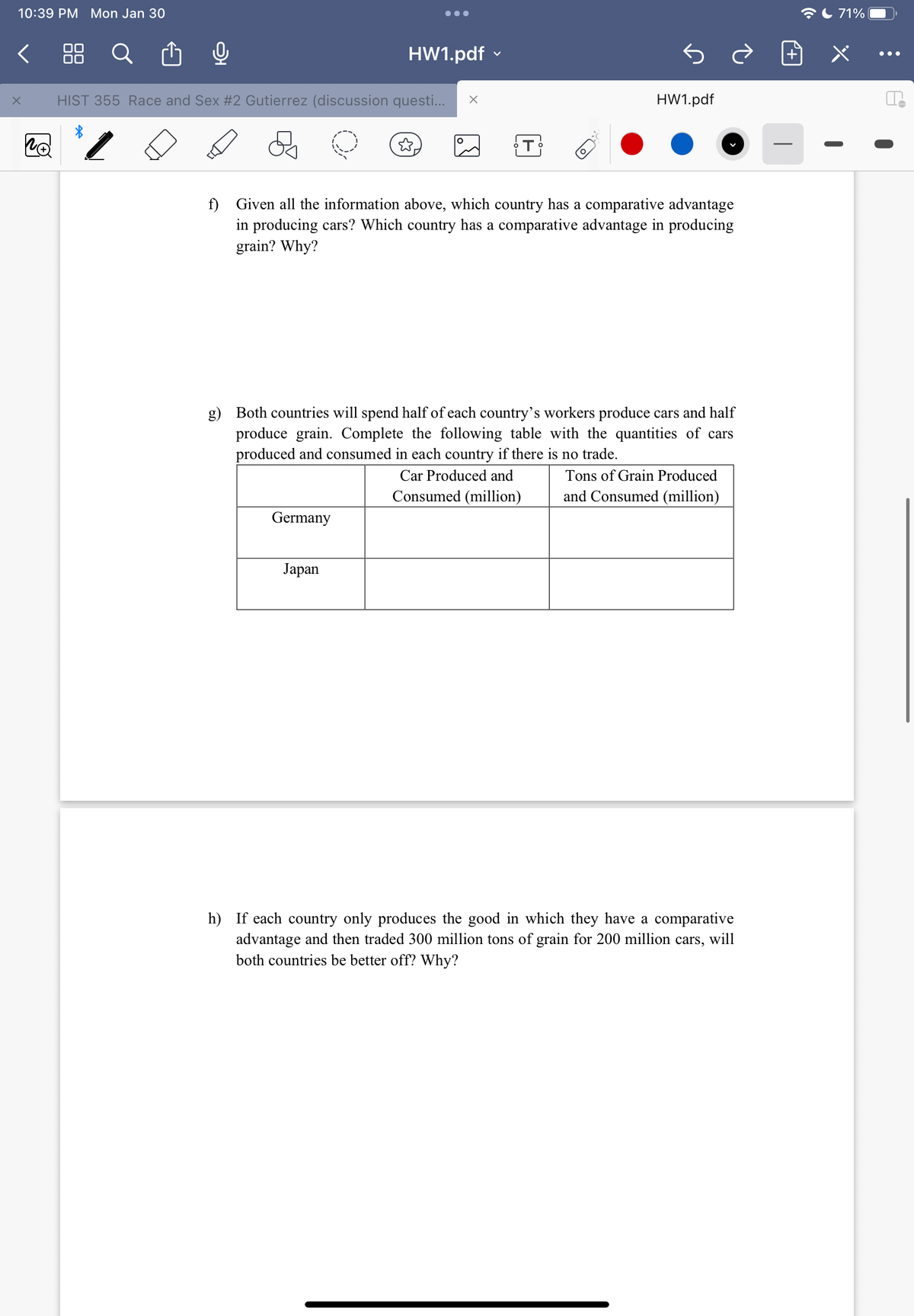
f) Given all the information above, which country has a comparative advantage in producing cars? Which country has a comparative advantage in producing grain? Why? g) Both countries will spend half of each country's workers produce cars and half produce grain. Complete the following table with the quantities of cars produced and consumed in each country if there is no trade. Car Produced and Tons of Grain Produced Consumed (million) and Consumed (million) Germany Japan h) If each country only produces the good in which they have a comparative advantage and then traded 300 million tons of grain for 200 million cars, will both countries be better off? Why?
f) Given all the information above, which country has a comparative advantage in producing cars? Which country has a comparative advantage in producing grain? Why? g) Both countries will spend half of each country's workers produce cars and half produce grain. Complete the following table with the quantities of cars produced and consumed in each country if there is no trade. Car Produced and Tons of Grain Produced Consumed (million) and Consumed (million) Germany Japan h) If each country only produces the good in which they have a comparative advantage and then traded 300 million tons of grain for 200 million cars, will both countries be better off? Why?
Chapter18: International Trade And Comparative Advantage
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2TY
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:10:39 PM Mon Jan 30
X
no
O
ננט
HIST 355 Race and Sex #2 Gutierrez (discussion questi... X
●●●
HW1.pdf
Germany
Japan
O
f) Given all the information above, which country has a comparative advantage
in producing cars? Which country has a comparative advantage in producing
grain? Why?
HW1.pdf
g) Both countries will spend half of each country's workers produce cars and half
produce grain. Complete the following table with the quantities of cars
produced and consumed in each country if there is no trade.
Car Produced and
Consumed (million)
Tons of Grain Produced
and Consumed (million)
h) If each country only produces the good in which they have a comparative
advantage and then traded 300 million tons of grain for 200 million cars, will
both countries be better off? Why?
71%
te
Transcribed Image Text:10:39 PM Mon Jan 30
X
no
O
1 of 5
HIST 355 Race and Sex #2 Gutierrez (discussion questi...
C
1000
Grains (millions)
●●●
HW1.pdf
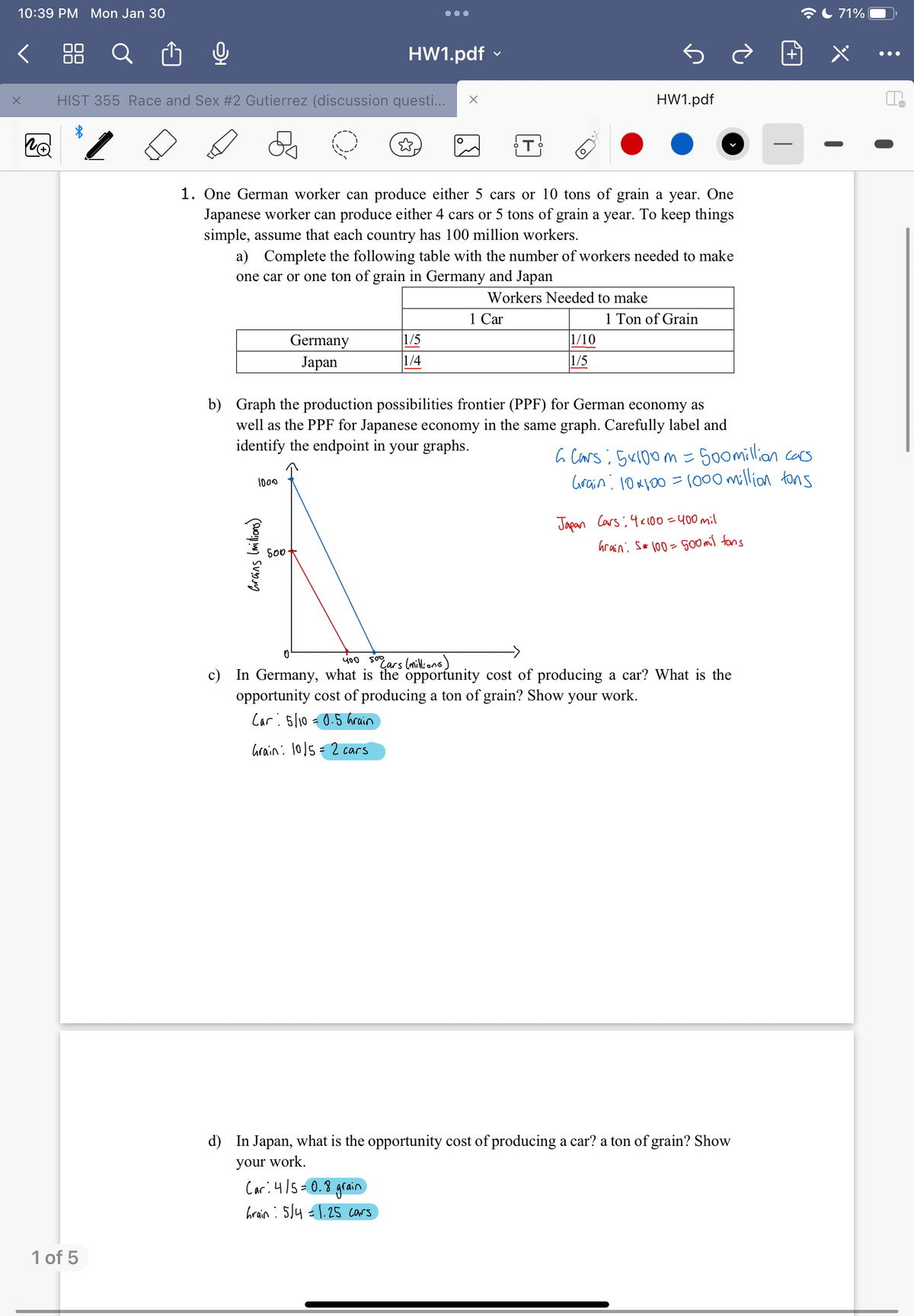
1. One German worker can produce either 5 cars or 10 tons of grain a year. One
Japanese worker can produce either 4 cars or 5 tons of grain a year. To keep things
simple, assume that each country has 100 million workers.
Germany
Japan
500
a) Complete the following table with the number of workers needed to make
one car or one ton of grain in Germany and Japan
Workers Needed to make
1 Car
O
1/5
1/4
X
= 1.25 cars
HW1.pdf
b) Graph the production possibilities frontier (PPF) for German economy as
well as the PPF for Japanese economy in the same graph. Carefully label and
identify the endpoint in your graphs.
1/10
1/5
1 Ton of Grain
500 million cars
6 Cars: 5x100 m =
Grain : 10*100=1000 million tons
Japan Cars: 4×100 = 400 mil
Grain S* 100 = 500 mil tons
400 So Cars (millions
c) In Germany, what is the opportunity cost of producing a car? What is the
opportunity cost of producing a ton of grain? Show your work.
Car: 5/10 = 0.5 Grain
Grain: 10/5= 2 cars
d) In Japan, what is the opportunity cost of producing a car? a ton of grain? Show
your work.
Car: 4/5=0.8 grain
hrain : 5/4
71%
te
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning