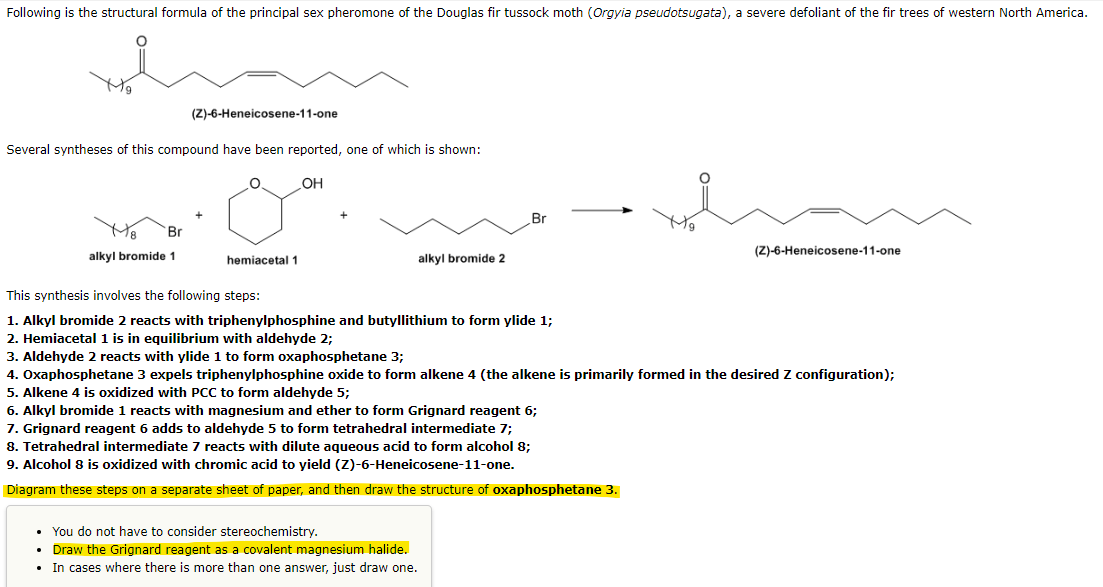
Following is the structural formula of the principal sex pheromone of the Douglas fir tussock moth (Orgyia pseudotsugata), a severe defoliant of the fir trees of western North America. Several syntheses of this compound have been reported, one of which is shown: O. _OH Br (Z)-6-Heneicosene-11-one alkyl bromide 1 hemiacetal 1 alkyl bromide 2 Br This synthesis involves the following steps: 1. Alkyl bromide 2 reacts with triphenylphosphine and butyllithium to form ylide 1; 2. Hemiacetal 1 is in equilibrium with aldehyde 2; 3. Aldehyde 2 reacts with ylide 1 to form oxaphosphetane 3; 4. Oxaphosphetane 3 expels triphenylphosphine oxide to form alkene 4 (the alkene is primarily formed in the desired Z configuration); 5. Alkene 4 is oxidized with PCC to form aldehyde 5; 6. Alkyl bromide 1 reacts with magnesium and ether to form Grignard reagent 6; 7. Grignard reagent 6 adds to aldehyde 5 to form tetrahedral intermediate 7; 8. Tetrahedral intermediate 7 reacts with dilute aqueous acid to form alcohol 8; 9. Alcohol 8 is oxidized with chromic acid to yield (Z)-6-Heneicosene-11-one. Diagram these steps on a separate sheet of paper, and then draw the structure of oxaphosphetane 3. • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. Draw the Grignard reagent as a covalent magnesium halide. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. (Z)-6-Heneicosene-11-one
Analyzing Infrared Spectra
The electromagnetic radiation or frequency is classified into radio-waves, micro-waves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays. The infrared spectra emission refers to the portion between the visible and the microwave areas of electromagnetic spectrum. This spectral area is usually divided into three parts, near infrared (14,290 – 4000 cm-1), mid infrared (4000 – 400 cm-1), and far infrared (700 – 200 cm-1), respectively. The number set is the number of the wave (cm-1).
IR Spectrum Of Cyclohexanone
It is the analysis of the structure of cyclohexaone using IR data interpretation.
IR Spectrum Of Anisole
Interpretation of anisole using IR spectrum obtained from IR analysis.
IR Spectroscopy
Infrared (IR) or vibrational spectroscopy is a method used for analyzing the particle's vibratory transformations. This is one of the very popular spectroscopic approaches employed by inorganic as well as organic laboratories because it is helpful in evaluating and distinguishing the frameworks of the molecules. The infra-red spectroscopy process or procedure is carried out using a tool called an infrared spectrometer to obtain an infrared spectral (or spectrophotometer).
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images




