For each price in the following table, calculate the firm's optimal quantity of units produced and determine the economic profit or loss if it produces at that quantity. Use the data from the previous graph to identify its total variable cost. Assume that if the firm is indifferent between producing and shutting down, it will produce. (Note: You can mouse over the purple points [diamond symbols) on the previous graph to see precise information on average variable cost.) Price Quantity Total Revenue (TR=PxQ) Fixed Cost (FC) Variable Cost (VC) Profit (TR-TC) (P) (9) 16 $162,000 12 162,000 18 162,000 If a firm shuts down, it incurs its fixed costs (FC) in the short run. In this case, the feed cost of the firm producing shirts is $162,000 per day. In other words, if it shuts down, the firm would suffer losses of $152,000 per day until its fixed costs end (such as the expiration of a building lease). This firm's shutdown price-that is, the price below which it is optimal for the firm to shut down-is per shirt.
For each price in the following table, calculate the firm's optimal quantity of units produced and determine the economic profit or loss if it produces at that quantity. Use the data from the previous graph to identify its total variable cost. Assume that if the firm is indifferent between producing and shutting down, it will produce. (Note: You can mouse over the purple points [diamond symbols) on the previous graph to see precise information on average variable cost.) Price Quantity Total Revenue (TR=PxQ) Fixed Cost (FC) Variable Cost (VC) Profit (TR-TC) (P) (9) 16 $162,000 12 162,000 18 162,000 If a firm shuts down, it incurs its fixed costs (FC) in the short run. In this case, the feed cost of the firm producing shirts is $162,000 per day. In other words, if it shuts down, the firm would suffer losses of $152,000 per day until its fixed costs end (such as the expiration of a building lease). This firm's shutdown price-that is, the price below which it is optimal for the firm to shut down-is per shirt.
Principles of Microeconomics
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305156050
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter14: Firms In Competitive Markets
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10PA
Related questions
Question
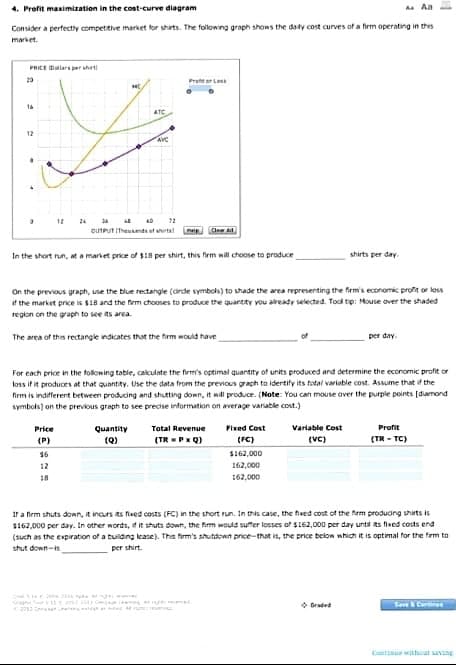
Transcribed Image Text:4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram
A
Consider a perfectly competitive market for shirts. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this
market.
PRICE Dollars per sht
20
HE
16
12
34 LE AD
72
OUTPUT (Theunts of shirts!
Chow Ad
In the short run, at a market price of $185 per shirt, this firm will choose to produce
shirts per day.
On the previous graph, use the blue rectangle (dirde symbols) to shade the area representing the firm's economic profit or loss
if the market price is $18 and the firm chooses to produce the quantity you already selected. Tool tip: Mouse over the shaded
region on the graph to see its area.
The area of this rectangle indicates that the firm would have
per day.
For each price in the following table, calculate the firm's optimal quantity of units produced and determine the economic profit or
loss if it produces at that quantity. Use the data from the previous graph to identify its total variable cost. Assume that if the
firm is indifferent between producing and shutting down, it will produce. (Note: You can mouse over the purple points [diamond
symbols) on the previous graph to see precise information on average variable cost.)
Price
Variable Cost
Quantity
(Q)
Total Revenue
(TR=PxQ)
Fixed Cost
(FC)
Profit
(TR-TC)
(P)
(VC)
56
$162,000
162,000
162,000
18
If a firm shuts down, it incurs its fixed costs (FC) in the short run. In this case, the fived cost of the firm producing shirts is
$162,000 per day. In other words, if it shuts down, the firm would suffer losses of $162,000 per day until its fixed costs and
(such as the expiration of a building lease). This firm's shutdown price-that is, the price below which it is optimal for the firm to
shut down-
per shirt.
ATC
AVC
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax