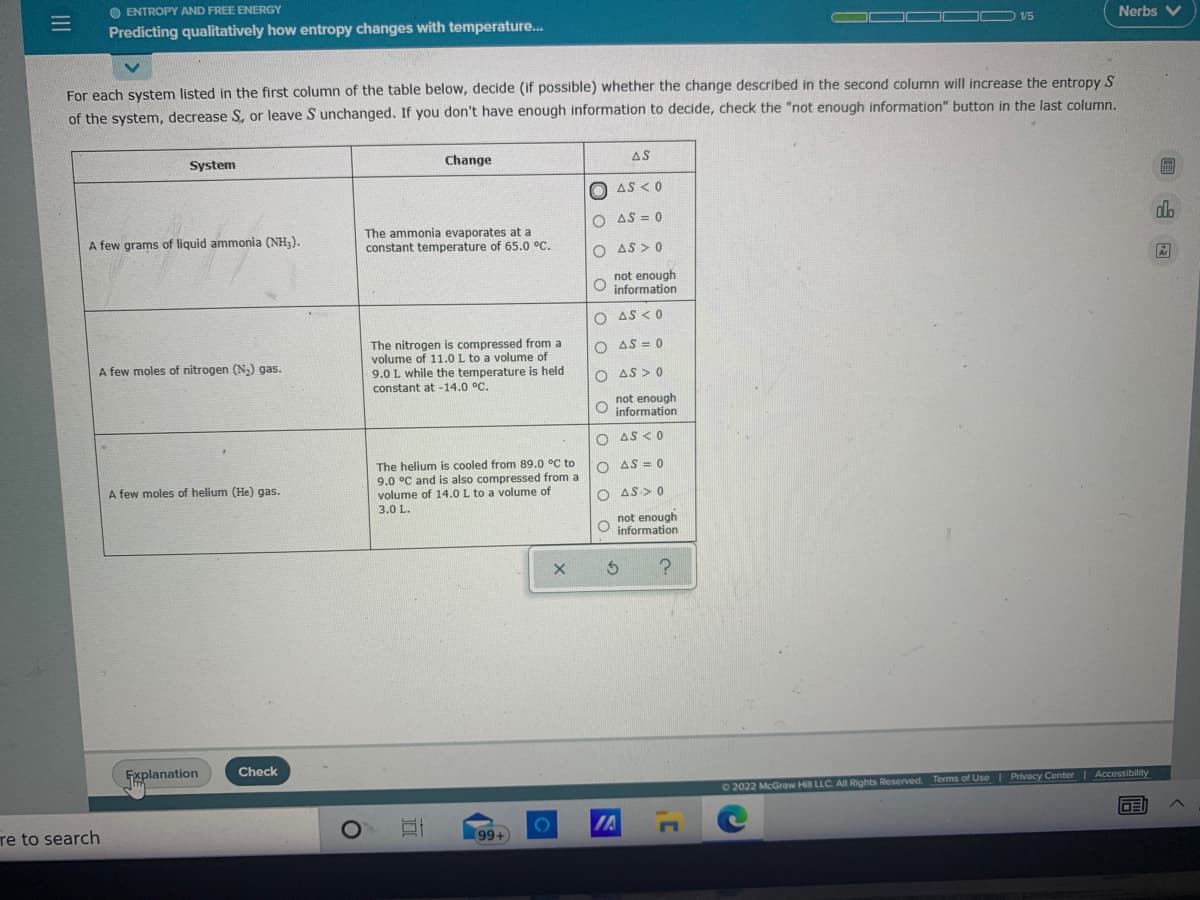
For each system listed in the first column of the table below, decide (if possible) whether the change described in the second column will increase the entropy S of the system, decrease S, or leave S unchanged. If you don't have enough information to decide, check the "not enough information" button in the last column. System Change AS O AS < 0 O AS = 0 The ammonia evaporates at a constant temperature of 65.0 °C. A few grams of liquid ammonia (NH,). O AS > 0 not enough information O AS <0 The nitrogen is compressed from a volume of 11.0 L to a volume of 9.0 L while the temperature is held O AS = 0 A few moles of nitrogen (N) gas. O AS > 0 constant at -14.0 °C. not enough O information O AS < 0 The helium is cooled from 89.0 °C to 9.0 °C and is also compressed from a volume of 14.0 L to a volume of O AS = 0 A few moles of helium (He) gas. O AS> 0 3.0 L. not enough information O O O O O o 0 0
For each system listed in the first column of the table below, decide (if possible) whether the change described in the second column will increase the entropy S of the system, decrease S, or leave S unchanged. If you don't have enough information to decide, check the "not enough information" button in the last column. System Change AS O AS < 0 O AS = 0 The ammonia evaporates at a constant temperature of 65.0 °C. A few grams of liquid ammonia (NH,). O AS > 0 not enough information O AS <0 The nitrogen is compressed from a volume of 11.0 L to a volume of 9.0 L while the temperature is held O AS = 0 A few moles of nitrogen (N) gas. O AS > 0 constant at -14.0 °C. not enough O information O AS < 0 The helium is cooled from 89.0 °C to 9.0 °C and is also compressed from a volume of 14.0 L to a volume of O AS = 0 A few moles of helium (He) gas. O AS> 0 3.0 L. not enough information O O O O O o 0 0
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Chapter16: Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 61E: The evaporation of one mole of water at 298 K has a standard free allergy change of 8.58 kJ....
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:O ENTROPY AND FREE ENERGY
Predicting qualitatively how entropy changes with temperature.
OD 15
Nerbs V
For each system listed in the first column of the table below, decide (if possible) whether the change described in the second column will increase the entropy S
of the system, decrease S, or leave S unchanged. If you don't have enough information to decide, check the "not enough information" button in the last column.
System
Change
AS
O AS <0
O AS = 0
do
The ammonia evaporates at a
constant temperature of 65.0 °C.
A few grams of liquid ammonia (NH,).
O AS > 0
not enough
O information
AS < 0
The nitrogen is compressed from a
volume of 11.0 L to a volume of
9.0 L while the temperature is held
constant at -14.0 °C.
O AS = 0
A few moles of nitrogen (N2) gas.
O AS > 0
not enough
information
O AS < 0
The helium is cooled from 89.0 °C to
9.0 °C and is also compressed from a
O AS = 0
A few moles of helium (He) gas.
volume of 14.0 L to a volume of
3.0 L.
O AS > 0
not enough
information
Fxplanation
Check
0 Terms of Use I Privacy Center| Accessibility
O 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved.
re to search
99+
IA
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning