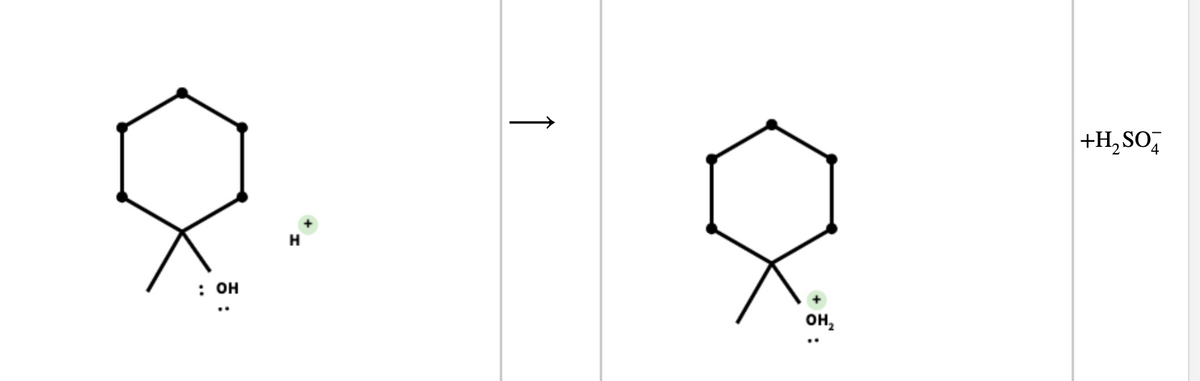
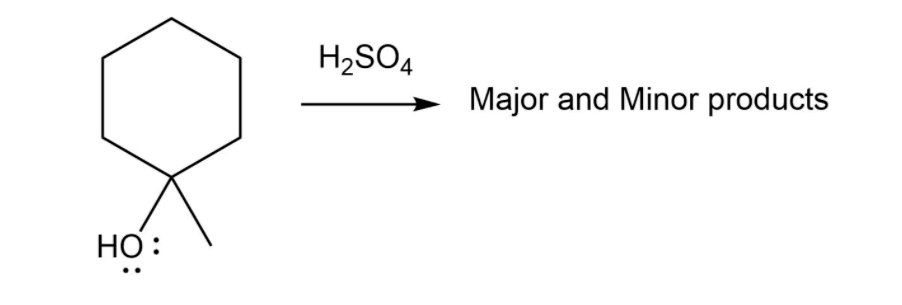
For the dehydration shown, use curved arrows to show the formation of the carbocation intermediate in the presence of sulfuric acid H2SO4H2SO4, then draw the structures of the minor and major products of the elimination. Picture: Cyclohexane (no double or triple bonds) with a methyl group and an alcohol group (HO 4e- on O) on C1 (bottom) reacting with H2SO4 -> "Major and Minor Products" -The H2SO4H2SO4 is abbreviated as H+H+ in the drawing module. Do not delete any pre‑drawn bonds, charges, or lone pairs. If you accidentally make a mistake, remove the last change by using the undo button on the lower left or revert the drawing palette to the original state by selecting the More menu, then select Reset Drawing. Step 1: Use curved arrows to complete the protonation mechanism of the alcohol. Step 2: Use a curved arrow to show the formation of the carbocation intermediate for the elimination. (Picture 1) -Step 3: This tertiary carbocation intermediate readily undergoes elimination with any weak base to form two possible products. (Picture 2) 3a) Draw the minor organic product of elimination. 3b) Draw the major organic product of elimination.
Reactive Intermediates
In chemistry, reactive intermediates are termed as short-lived, highly reactive atoms with high energy. They rapidly transform into stable particles during a chemical reaction. In specific cases, by means of matrix isolation and at low-temperature reactive intermediates can be isolated.
Hydride Shift
A hydride shift is a rearrangement of a hydrogen atom in a carbocation that occurs to make the molecule more stable. In organic chemistry, rearrangement of the carbocation is very easily seen. This rearrangement can be because of the movement of a carbocation to attain stability in the compound. Such structural reorganization movement is called a shift within molecules. After the shifting of carbocation over the different carbon then they form structural isomers of the previous existing molecule.
Vinylic Carbocation
A carbocation where the positive charge is on the alkene carbon is known as the vinyl carbocation or vinyl cation. The empirical formula for vinyl cation is C2H3+. In the vinyl carbocation, the positive charge is on the carbon atom with the double bond therefore it is sp hybridized. It is known to be a part of various reactions, for example, electrophilic addition of alkynes and solvolysis as well. It plays the role of a reactive intermediate in these reactions.
Cycloheptatrienyl Cation
It is an aromatic carbocation having a general formula, [C7 H7]+. It is also known as the aromatic tropylium ion. Its name is derived from the molecule tropine, which is a seven membered carbon atom ring. Cycloheptatriene or tropylidene was first synthesized from tropine.
Stability of Vinyl Carbocation
Carbocations are positively charged carbon atoms. It is also known as a carbonium ion.
- For the dehydration shown, use curved arrows to show the formation of the carbocation intermediate in the presence of sulfuric acid H2SO4H2SO4, then draw the structures of the minor and major products of the elimination.
Picture: Cyclohexane (no double or triple bonds) with a methyl group and an alcohol group (HO 4e- on O) on C1 (bottom) reacting with H2SO4 -> "Major and Minor Products"
-The H2SO4H2SO4 is abbreviated as H+H+ in the drawing module. Do not delete any pre‑drawn bonds, charges, or lone pairs. If you accidentally make a mistake, remove the last change by using the undo button on the lower left or revert the drawing palette to the original state by selecting the More menu, then select Reset Drawing.
Step 1: Use curved arrows to complete the protonation mechanism of the alcohol.
(Picture 2)
3a) Draw the minor organic product of elimination.
3b) Draw the major organic product of elimination.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images


