Formula Calculations with atomic masses Formula mass 119.00amu 75amul 146.00am K= 39 + Br=80 KBr Ca-40 CLこ35 CaCl2 Naz=40 CO3 = Na,CO, (NH),PO. The mole (Sec 6 2 and 6 2) in n voeful ueit fe
Formula Calculations with atomic masses Formula mass 119.00amu 75amul 146.00am K= 39 + Br=80 KBr Ca-40 CLこ35 CaCl2 Naz=40 CO3 = Na,CO, (NH),PO. The mole (Sec 6 2 and 6 2) in n voeful ueit fe
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Chapter10: Quantity Relationships In Chemical Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 49E: A mixture of tetraphosphorus trisulfide and powdered glass is in the white tip of strike-anywhere...
Related questions
Question
100%
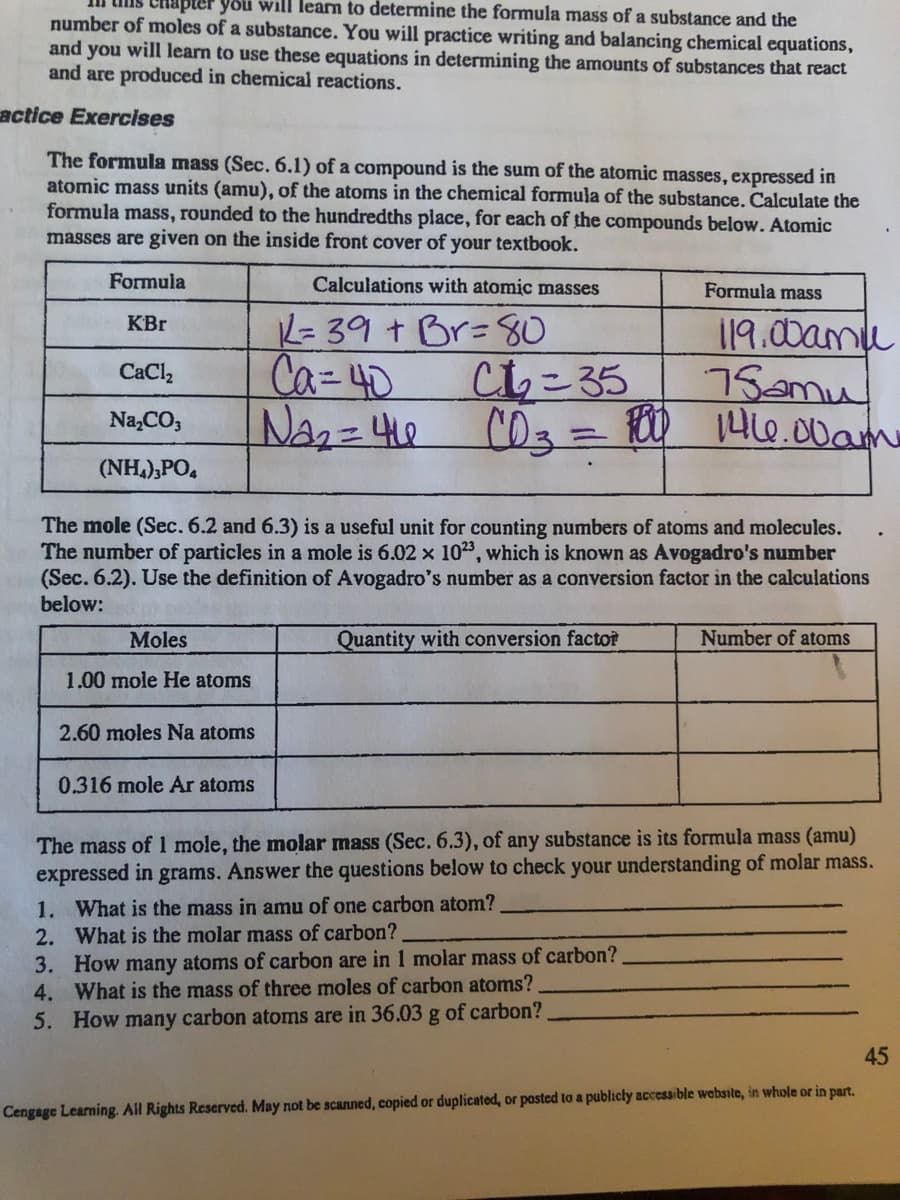
Transcribed Image Text:will learn to determine the formula mass of a substance and the
number of moles of a substance. You will practice writing and balancing chemical equations,
and you will learn to use these equations in determining the amounts of substances that react
and are produced in chemical reactions.
actice Exercises
The formula mass (Sec. 6.1) of a compound is the sum of the atomic masses, expressed in
atomic mass units (amu), of the atoms in the chemical formula of the substance. Calculate the
formula mass, rounded to the hundredths place, for each of the compounds below. Atomic
masses are given on the inside front cover of your textbook.
Formula
Calculations with atomic masses
Formula mass
K= 39 + Br=80
Chこ35
C03%3D100
119.00amu
75amu
146.00am
KBr
Ca=40
CaCl,
Na,CO,
(NH,),PO,
The mole (Sec. 6.2 and 6.3) is a useful unit for counting numbers of atoms and molecules.
The number of particles in a mole is 6.02 x 103, which is known as Avogadro's number
(Sec. 6.2). Use the definition of Avogadro's number as a conversion factor in the calculations
below:
Moles
Quantity with conversion factoř
Number of atoms
1.00 mole He atoms
2.60 moles Na atoms
0.316 mole Ar atoms
The mass of mole, the molar mass (Sec. 6.3), of any substance is its formula mass (amu)
expressed in grams. Answer the questions below to check your understanding of molar mass.
1. What is the mass in amu of one carbon atom?
2. What is the molar mass of carbon?
3. How many atoms of carbon are in 1 molar mass of carbon?
4. What is the mass of three moles of carbon atoms?
5. How many carbon atomns are in 36.03 g of carbon?
45
Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or pastcd to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
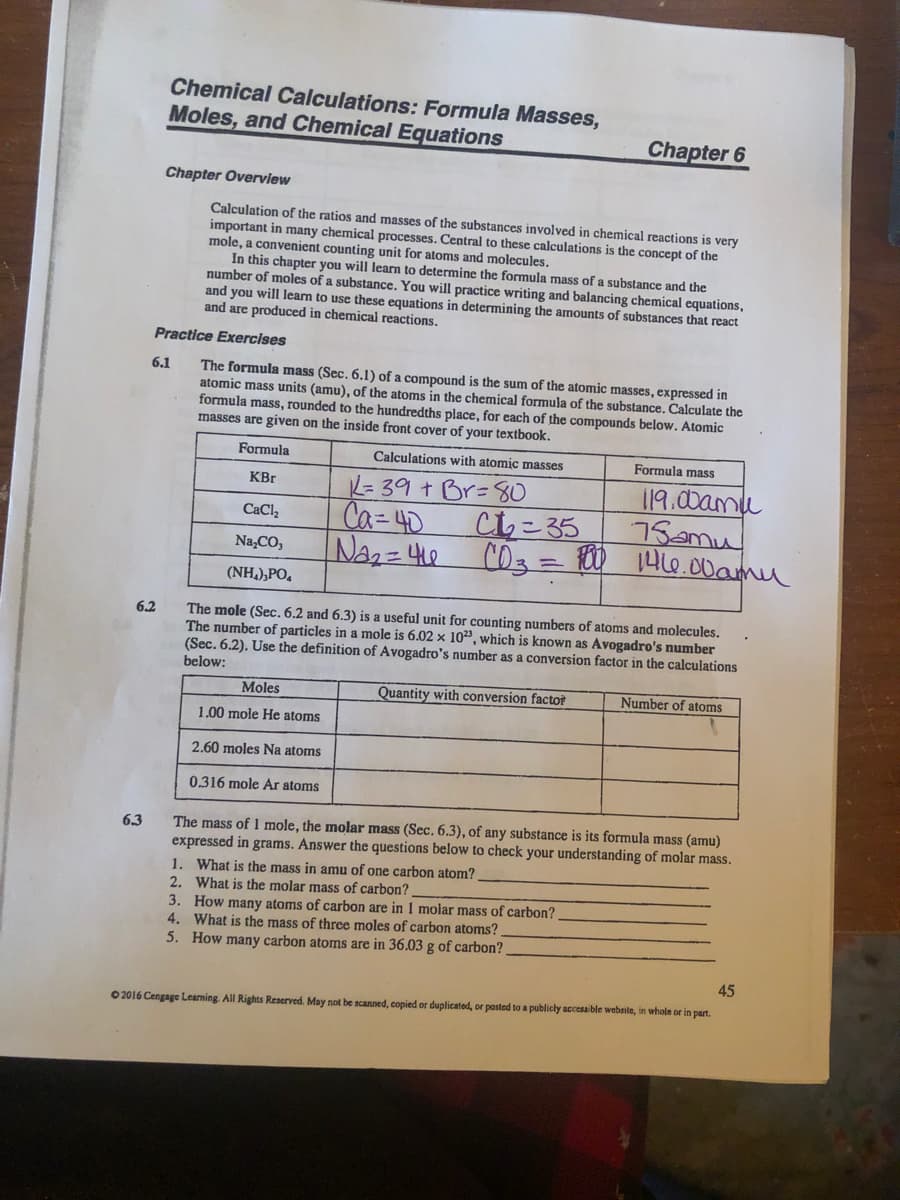
Transcribed Image Text:Chemical Calculations: Formula Masses,
Moles, and Chemical Equations
Chapter 6
Chapter Overview
Calculation of the ratios and masses of the substances involved in chemical reactions is very
important in
mole, a convenient counting unit for atoms and molecules.
In this chapter you will learm to determine the formula mass of a substance and the
number of moles of a substance. You will practice writing and balancing chemical equations,
and you will leam to use these equations in determining the amounts of substances that react
and are produced in chemical reactions.
a many chemical processes. Central to these calculations is the concept of the
Practice Exercises
6.1
The formula mass (Sec. 6.1) of a compound is the sum of the atomic masses, expressed in
atomic mass units (amu), of the atoms in the chemical formula of the substance. Calculate the
formula mass, rounded to the hundredths place, for each of the compounds below. Atomic
masses are given on the inside front cover of your textbook.
Formula
Calculations with
omic masses
Formula mass
119.00amu
75amu
NA2= 410 CO3 = 0H6.00amu
= 39 + Br=80
KBr
Ca=40
Chこ35
CaCl,
Na,CO,
(NH,),PO,
6.2
The mole (Sec. 6.2 and 6.3) is a useful unit for counting numbers of atoms and molecules.
The number of particles in a mole is 6.02 x 10, which is known as Avogadro's number
(Sec. 6.2). Use the definition of Avogadro's number as a conversion factor in the calculations
below:
Moles
Quantity with conversion factor
Number of atoms
1.00 mole He atoms
2.60 moles Na atoms
0.316 mole Ar atoms
The mass of 1 mole, the molar mass (Sec. 6.3), of any substance is its formula mass (amu)
expressed in grams. Answer the questions below to check your understanding of molar mass.
6.3
1. What is the mass in amu of one carbon atom?
2. What is the molar mass of carbon?
3. How many atoms of carbon are in 1 molar mass of carbon?
4. What is the mass of three moles of carbon atoms?
5. How many carbon atoms are in 36.03 g of carbon?
45
O 2016 Cengage Learning All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accesa ble webaite, in whole or in part.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133109655
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning


Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133109655
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning


Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning