Gamma(y)-amino butyric acid (GABA) is a neurotransmitter (a chemical that is used to send signals from one neuron to another) of the mammalian central nervous system. In order to understand how GABA works, conformationally restricted analogues, such as compound 1, have been made. During a synthesis of compound 1, compound 2 was subjected to allylic bromination using NBS and a radical initiator (AIBN) instead of light (Aust. J. Chem. 1981, 34, 2231-2236). H₂N. GABA CO₂H H₂N CO₂H dddd solddd 2 Modify the structures given below to draw all eight possible allylic bromides that can be formed when compound 2 undergoes allylic bromination, considering all possible regiochemical and stereochemical outcomes. You can use the single bond tool to add/remove pi bonds. CH₂ CO₂Et
Gamma(y)-amino butyric acid (GABA) is a neurotransmitter (a chemical that is used to send signals from one neuron to another) of the mammalian central nervous system. In order to understand how GABA works, conformationally restricted analogues, such as compound 1, have been made. During a synthesis of compound 1, compound 2 was subjected to allylic bromination using NBS and a radical initiator (AIBN) instead of light (Aust. J. Chem. 1981, 34, 2231-2236). H₂N. GABA CO₂H H₂N CO₂H dddd solddd 2 Modify the structures given below to draw all eight possible allylic bromides that can be formed when compound 2 undergoes allylic bromination, considering all possible regiochemical and stereochemical outcomes. You can use the single bond tool to add/remove pi bonds. CH₂ CO₂Et
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Chapter23: Amines
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 23.28P
Related questions
Question
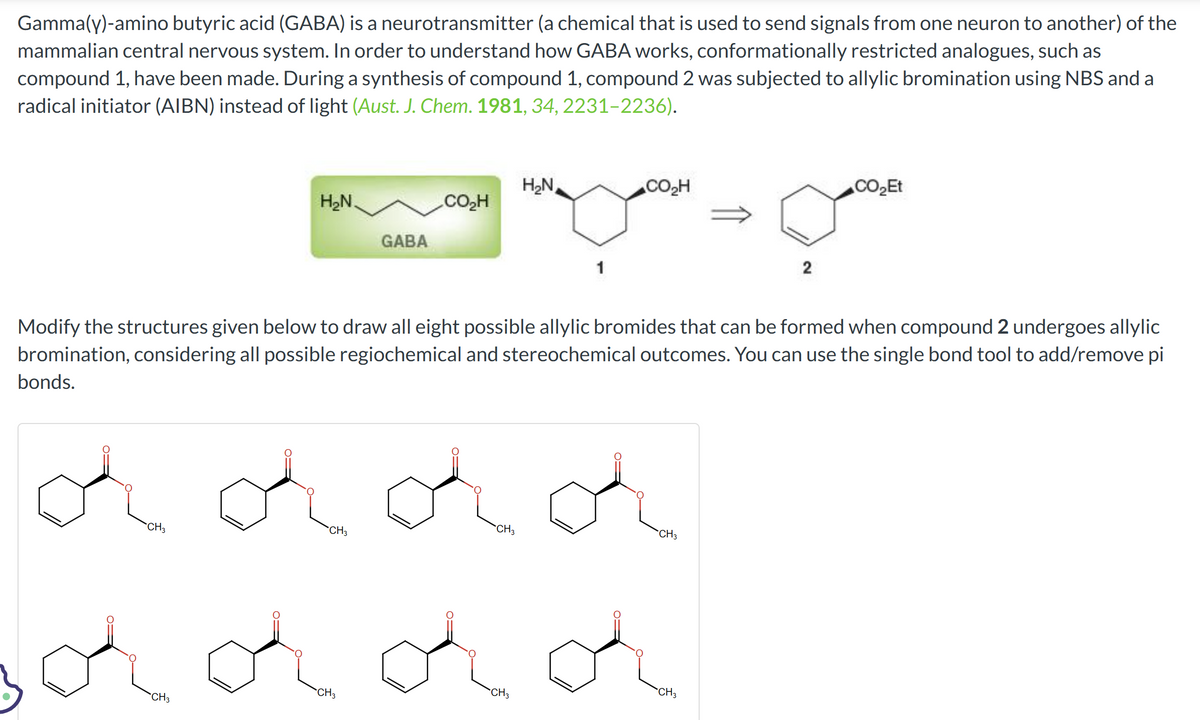
Transcribed Image Text:Gamma(y)-amino butyric acid (GABA) is a neurotransmitter (a chemical that is used to send signals from one neuron to another) of the
mammalian central nervous system. In order to understand how GABA works, conformationally restricted analogues, such as
compound 1, have been made. During a synthesis of compound 1, compound 2 was subjected to allylic bromination using NBS and a
radical initiator (AIBN) instead of light (Aust. J. Chem. 1981, 34, 2231-2236).
H₂N.
CH3
GABA
CO₂H
CH3
dddd
CH3
H₂N
Modify the structures given below to draw all eight possible allylic bromides that can be formed when compound 2 undergoes allylic
bromination, considering all possible regiochemical and stereochemical outcomes. You can use the single bond tool to add/remove pi
bonds.
CH3
CO₂H
CH3
solddd
CH3
CH3
2
CH₂
CO₂Et
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
