How do I Compute Tates (1) weighted average cost of capital and (2) hurdle rate? Round answers to one decimal place.
Cost of Debt, Cost of Preferred Stock
This article deals with the estimation of the value of capital and its components. we'll find out how to estimate the value of debt, the value of preferred shares , and therefore the cost of common shares . we will also determine the way to compute the load of every cost of the capital component then they're going to estimate the general cost of capital. The cost of capital refers to the return rate that an organization gives to its investors. If an organization doesn’t provide enough return, economic process will decrease the costs of their stock and bonds to revive the balance. A firm’s long-run and short-run financial decisions are linked to every other by the assistance of the firm’s cost of capital.
Cost of Common Stock
Common stock is a type of security/instrument issued to Equity shareholders of the Company. These are commonly known as equity shares in India. It is also called ‘Common equity
How do I Compute Tates (1) weighted average cost of capital and (2) hurdle rate? Round answers to one decimal place.
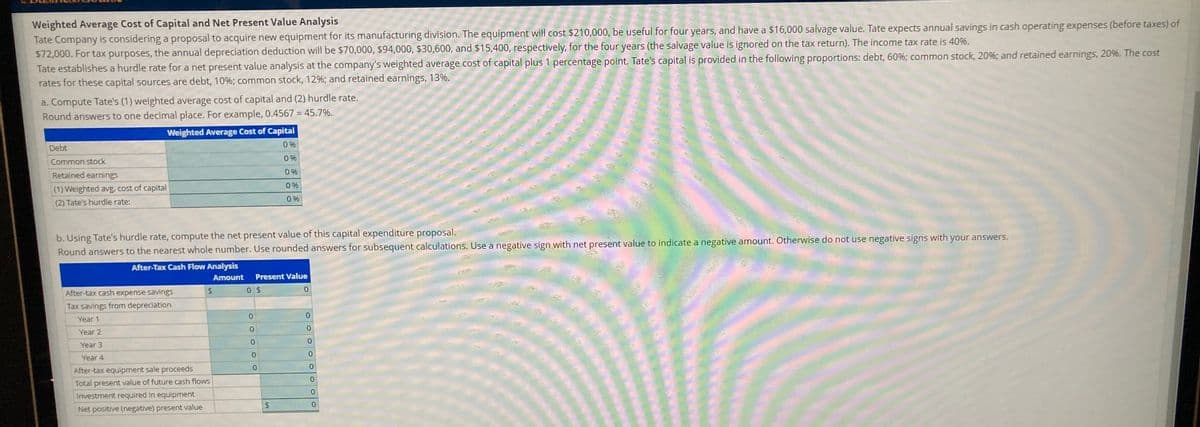
Answer -
Working Note -
| Particular | Weighted Average Cost of Capital |
| Debt ( 10% * 60%) | 6% |
| Common Stock (12% * 20%) |
2.40% |
| Retained Earnings (13% * 20%) |
2.60% |
| Weighted Average Cost of Capital | 11% |
| Tate Hurdle Rate | 12% |
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps









