How has Covid-19 affected the market for gasoline? Which of the main influences of supply and demand do you think were responsible for the price changes? (See textbook pages 90-91 and 97-98.) Be specific and explain why and how the “main influences” you chose had an impact on the gasoline market.
How has Covid-19 affected the market for gasoline? Which of the main influences of supply and demand do you think were responsible for the price changes? (See textbook pages 90-91 and 97-98.) Be specific and explain why and how the “main influences” you chose had an impact on the gasoline market.
Chapter1: Making Economics Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1QTC
Related questions
Question
-How has Covid-19 affected the market for gasoline? Which of the main influences of
Transcribed Image Text:b Answered: Gas x G On the deman x
← → C
M Gmail
Chrome File Edit View History Bookmarks Profiles Tab Window Help
G
!!!!
<O>
Q
ip
A₁
X
Content x G-How has Covi XG How has Covic X | Homework and X
plus.pearson.com/products/160693/pages/134?locale=&isTpi=Y&redirectURL=https://plus.pearson.com/bookshelf&lms=Y
YouTube
Knowing the Love...
increases.
Chapter 4: Demand and Supply
Content
X
P Page 98
X
98 □
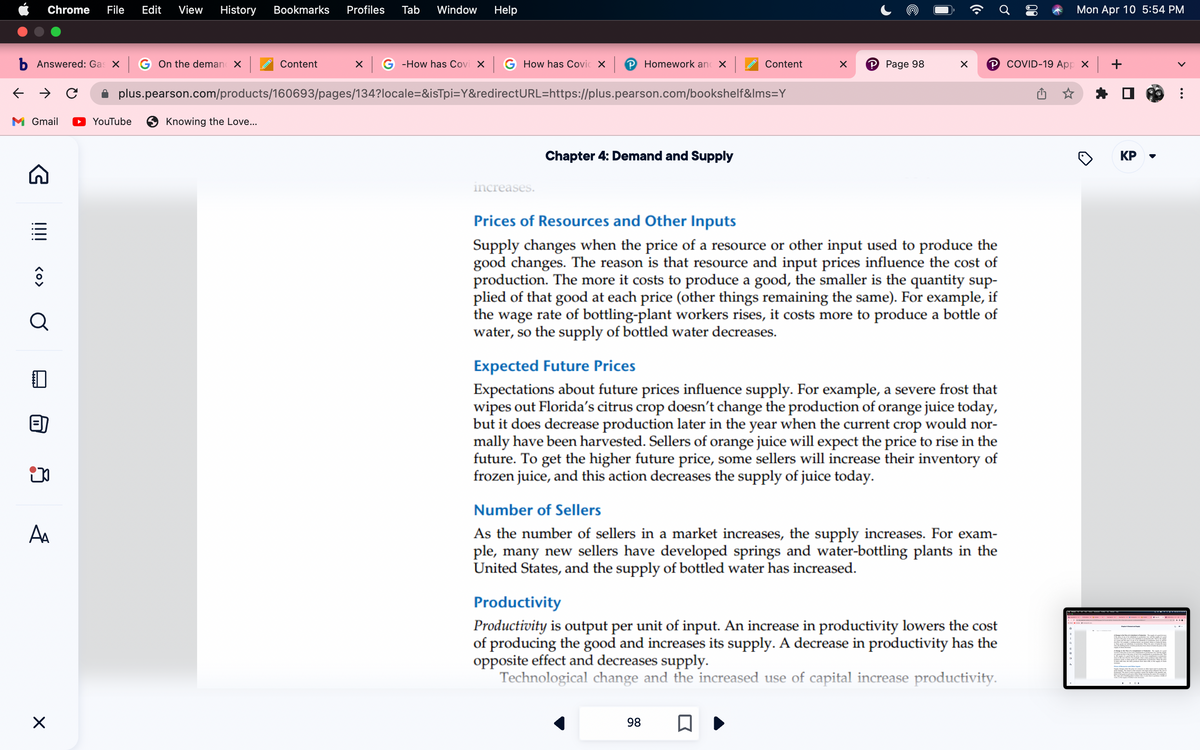
Prices of Resources and Other Inputs
Supply changes when the price of a resource or other input used to produce the
good changes. The reason is that resource and input prices influence the cost of
production. The more it costs to produce a good, the smaller is the quantity sup-
plied of that good at each price (other things remaining the same). For example, if
the wage rate of bottling-plant workers rises, it costs more to produce a bottle of
water, so the supply of bottled water decreases.
℗COVID-19 App X +
Expected Future Prices
Expectations about future prices influence supply. For example, a severe frost that
wipes out Florida's citrus crop doesn't change the production of orange juice today,
but it does decrease production later in the year when the current crop would nor-
mally have been harvested. Sellers of orange juice will expect the price to rise in the
future. To get the higher future price, some sellers will increase their inventory of
frozen juice, and this action decreases the supply of juice today.
Number of Sellers
As the number of sellers in a market increases, the supply increases. For exam-
ple, many new sellers have developed springs and water-bottling plants in the
United States, and the supply of bottled water has increased.
Productivity
Productivity is output per unit of input. An increase in productivity lowers the cost
of producing the good and increases its supply. A decrease in productivity has the
opposite effect and decreases supply.
Technological change and the increased use of capital increase productivity.
Mon Apr 10 5:54 PM
KP
M
Transcribed Image Text:b Answered: Gas x G On the deman x
← → C
M Gmail
Chrome File Edit View History Bookmarks Profiles Tab Window Help
G
!!!!
<O>
Q
ip
A₁
X
Content x G-How has Covi XG How has Covic X | Homework and X
plus.pearson.com/products/160693/pages/134?locale=&isTpi=Y&redirectURL=https://plus.pearson.com/bookshelf&lms=Y
YouTube
Knowing the Love...
98
Part 1 • INTRODUCTION
Chapter 4: Demand and Supply
Content
X
98
P Page 98
□
X
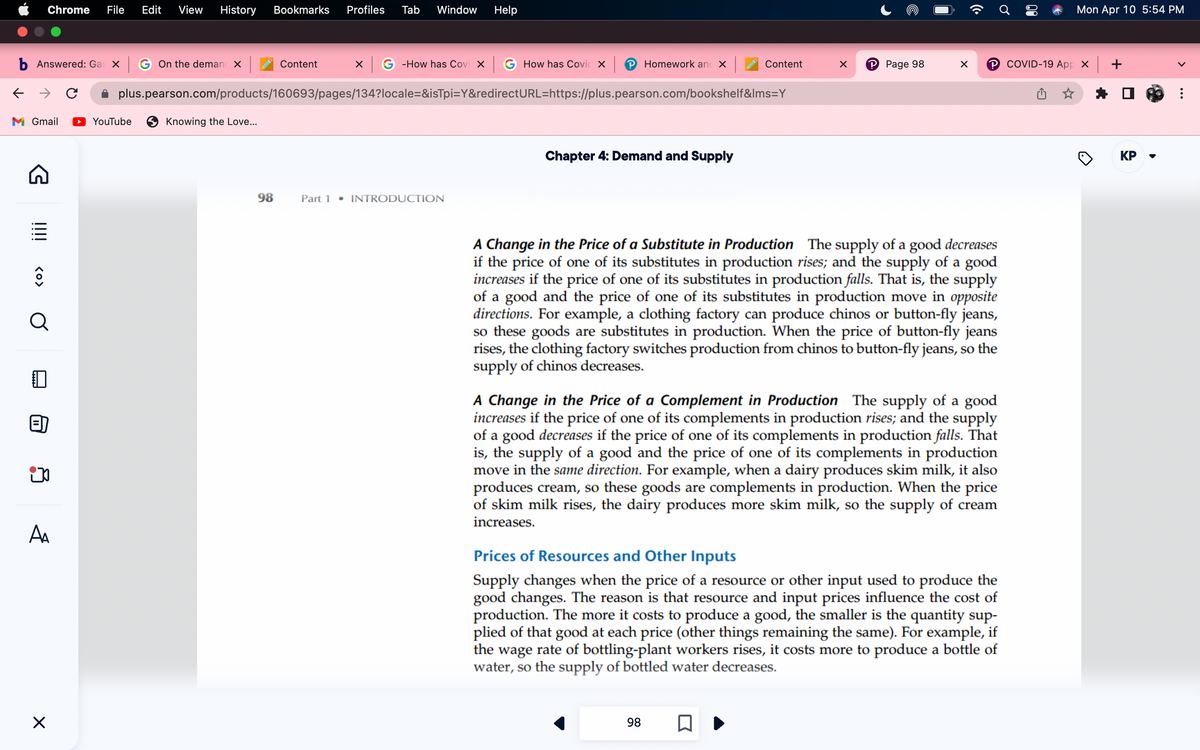
A Change in the Price of a Substitute in Production The supply of a good decreases
if the price of one of its substitutes in production rises; and the supply of a good
increases if the price of one of its substitutes in production falls. That is, the supply
of a good and the price of one of its substitutes in production move in opposite
directions. For example, a clothing factory can produce chinos or button-fly jeans,
so these goods are substitutes in production. When the price of button-fly jeans
rises, the clothing factory switches production from chinos to button-fly jeans, so the
supply of chinos decreases.
A Change in the Price of a Complement in Production The supply of a good
increases if the price of one of its complements in production rises; and the supply
of a good decreases if the price of one of its complements in production falls. That
is, the supply of a good and the price of one of its complements in production
move in the same direction. For example, when a dairy produces skim milk, it also
produces cream, so these goods are complements in production. When the price
of skim milk rises, the dairy produces more skim milk, so the supply of cream
increases.
℗COVID-19 App X +
Prices of Resources and Other Inputs
Supply changes when the price of a resource or other input used to produce the
good changes. The reason is that resource and input prices influence the cost of
production. The more it costs to produce a good, the smaller is the quantity sup-
plied of that good at each price (other things remaining the same). For example, if
the wage rate of bottling-plant workers rises, it costs more to produce a bottle of
water, so the supply of bottled water decreases.
Mon Apr 10 5:54 PM
KP
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-…
Economics
ISBN:
9781259290619
Author:
Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education