If we know c of the object being heated (or cooled), we can measure the mass and the temperature change and calculate the heat absorbed (or released): q = c X mass X AT (6.7) Table 6.2 Specific Heat Capacities (c) of Some Elements, Compounds, and Materials c (J/g-K)* Elements Aluminum, Al 0.900 Graphite, C Iron, Fe 0.711 0.450 Соpper, Cu Gold, Au 0.387 0.129 Compounds 4.184 Water, H,O(1) Ethyl alcohol, 2.46 ()HOʻHƆ Ethylene glycol, (CH,OH),() Carbon tetrachloride, CCL,(1) 2.42 0.862 Solid Materials Wood 1.76 Cement 0.88 Glass 0.84 Granite 0.79 0.45 Steel *At 298 K (25°C).
Thermochemistry
Thermochemistry can be considered as a branch of thermodynamics that deals with the connections between warmth, work, and various types of energy, formed because of different synthetic and actual cycles. Thermochemistry describes the energy changes that occur as a result of reactions or chemical changes in a substance.
Exergonic Reaction
The term exergonic is derived from the Greek word in which ‘ergon’ means work and exergonic means ‘work outside’. Exergonic reactions releases work energy. Exergonic reactions are different from exothermic reactions, the one that releases only heat energy during the course of the reaction. So, exothermic reaction is one type of exergonic reaction. Exergonic reaction releases work energy in different forms like heat, light or sound. For example, a glow stick releases light making that an exergonic reaction and not an exothermic reaction since no heat is released. Even endothermic reactions at very high temperature are exergonic.
A layer of copper welded to the bottom of a skillet weighs 125 g. How much
heat is needed to raise the temperature of the copper layer from 25°C to 300.°C? The specific heat capacity (c) of Cu is given as shown.
Plan We know the mass (125 g) and c (0.387 J/g⋅K) of Cu and can find ΔT in °C, which equals ΔT in K. We then as shown to calculate the heat.
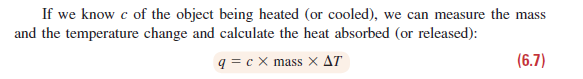
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps




