Ike's Bikes is a major manufacturer of bicycles. Currently, the company produces bikes using only one factory. However, it is consi production to two or even three factories. The following table shows the company's short-run average total cost (SRATC) each mc of production if it uses one, two, or three factories. (Note: Q equals the total quantity of bikes produced by all factories.) Number of Factories 1 2 Q=50 Q = 100 140 230 320 60 110 160 Average Total Cost (Dollars per bike) Q = 150 Q = 200 40 40 80 80 40 40 Q=250 Q = 300 160 320 110 230 60 140
Ike's Bikes is a major manufacturer of bicycles. Currently, the company produces bikes using only one factory. However, it is consi production to two or even three factories. The following table shows the company's short-run average total cost (SRATC) each mc of production if it uses one, two, or three factories. (Note: Q equals the total quantity of bikes produced by all factories.) Number of Factories 1 2 Q=50 Q = 100 140 230 320 60 110 160 Average Total Cost (Dollars per bike) Q = 150 Q = 200 40 40 80 80 40 40 Q=250 Q = 300 160 320 110 230 60 140
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
5th Edition
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Chapter5: Investment Decisions: Look Ahead And Reason Back
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5.5IP
Related questions
Question
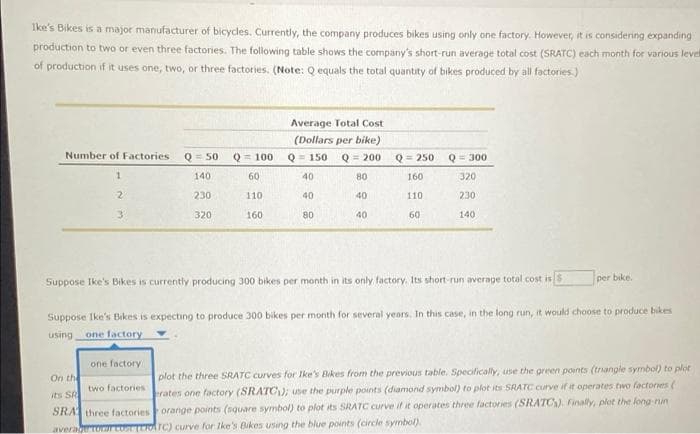
Transcribed Image Text:Ike's Bikes is a major manufacturer of bicycles. Currently, the company produces bikes using only one factory. However, it is considering expanding
production to two or even three factories. The following table shows the company's short-run average total cost (SRATC) each month for various level
of production if it uses one, two, or three factories. (Note: Q equals the total quantity of bikes produced by all factories.)
Number of Factories. Q = 50
1
140
2
230
3
320
Q = 100
60
110
160
Average Total Cost
(Dollars per bike)
Q = 150
Q = 200
40
40
80
80
40
40
Q = 250
160
110
60
Q = 300
320
230
140
per bike.
Suppose Ike's Bikes is currently producing 300 bikes per month in its only factory. Its short-run average total cost is $
Suppose Ike's Bikes is expecting to produce 300 bikes per month for several years. In this case, in the long run, it would choose to produce bikes
using one factory
one factory
On the
two factories
its SR
plot the three SRATC curves for Ike's Bikes from the previous table. Specifically, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot
erates one factory (SRATC); use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot its SRATC curve if it operates two factores (
SRA three factories orange points (square symbol) to plot its SRATC curve if it operates three factories (SRATCs). Finally, plot the long-run
average torar cost (ATC) curve for Ike's Bikes using the blue points (circle symbol)
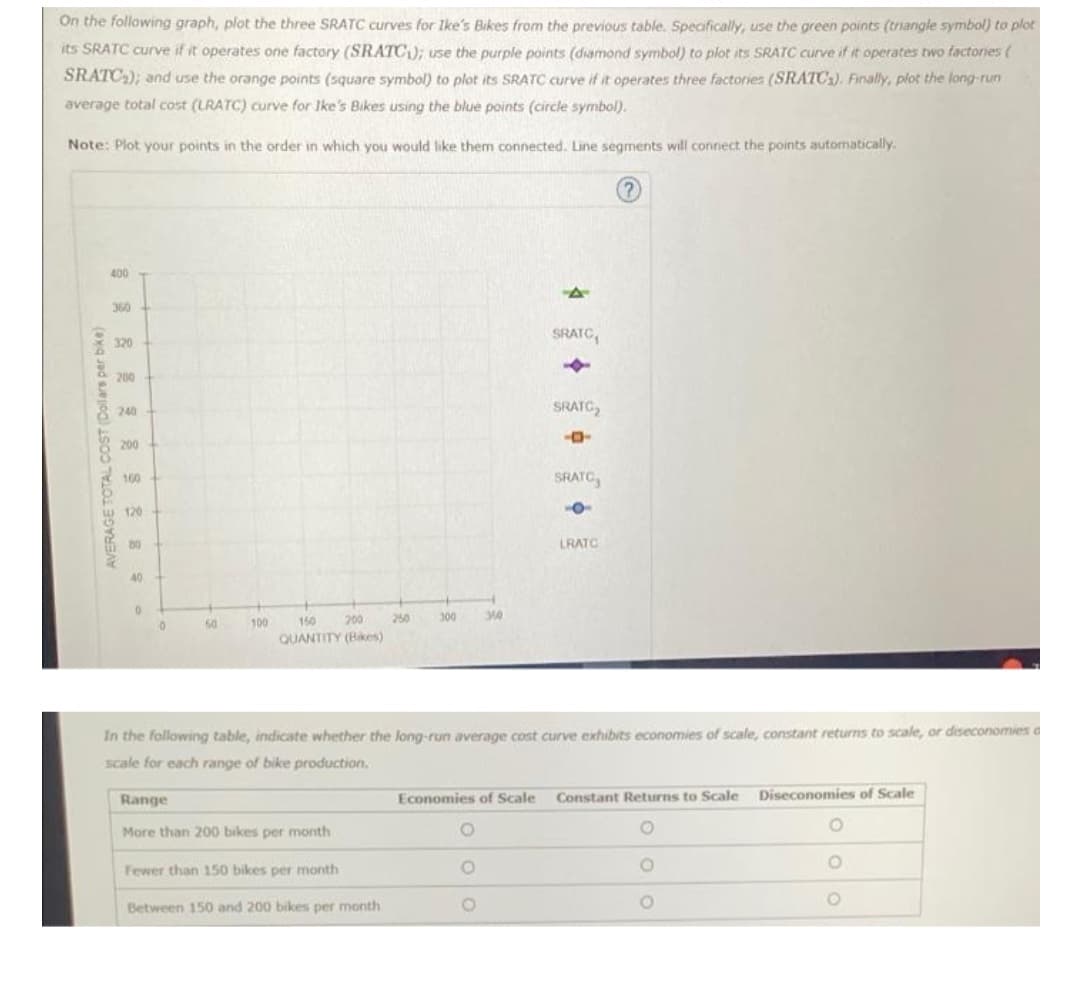
Transcribed Image Text:On the following graph, plot the three SRATC curves for Ike's Bikes from the previous table. Specifically, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot
its SRATC curve if it operates one factory (SRATC); use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot its SRATC curve if it operates two factories (
SRATC₂); and use the orange points (square symbol) to plot its SRATC curve if it operates three factories (SRATC3). Finally, plot the long-run
average total cost (LRATC) curve for Ike's Bikes using the blue points (circle symbol).
Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.
AVERAGE TOTAL COST (Collars per bike)
8 & & & & $ 8 8 9
400
360
320
200
240
200
160
120
40
0
0
50
100
200
150
QUANTITY (Bikes)
Range
More than 200 bikes per month
Fewer than 150 bikes per month
300
Between 150 and 200 bikes per month
350
SRATC
In the following table, indicate whether the long-run average cost curve exhibits economies of scale, constant returns to scale, or diseconomies a
scale for each range of bike production,
O
SRATC₂
P
SRATO
-0
LRATO
Economies of Scale Constant Returns to Scale
O
O
Diseconomies of Scale
OO
O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

