In a 300-rough incline, a 2.15 kg block is initially at rest beside a spring that is compressed by 42 cm as shown in the figure below. The spring has a spring constant of 180 N/m and the coefficient of sliding friction between the incline and the block is 0.32. When the spring is released, (a) how far up the incline (with respect to its initial position) will the block slide before sliding back? (b) What is the speed of the block at the instant it is 0.43 m from its initial position? Solve by the Work-energy equation. 1 30⁰ Transcribed Image Text: In a 300-rough incline, a 2.15 kg block is initially at rest beside a spring that is compressed by 42 cm as shown in the figure below. The spring has a spring constant of 180 N/m and the coefficient of sliding friction between the incline and the block is 0.32. When the spring is released, (a) how far up the incline (with respect to its initial position) will the block slide before sliding back? (b) What is the speed of the block at the instant it is 0.43 m from its initial position? Solve by the Work-energy equation. ww 30° ww
In a 300-rough incline, a 2.15 kg block is initially at rest beside a spring that is compressed by 42 cm as shown in the figure below. The spring has a spring constant of 180 N/m and the coefficient of sliding friction between the incline and the block is 0.32. When the spring is released, (a) how far up the incline (with respect to its initial position) will the block slide before sliding back? (b) What is the speed of the block at the instant it is 0.43 m from its initial position? Solve by the Work-energy equation. 1 30⁰ Transcribed Image Text: In a 300-rough incline, a 2.15 kg block is initially at rest beside a spring that is compressed by 42 cm as shown in the figure below. The spring has a spring constant of 180 N/m and the coefficient of sliding friction between the incline and the block is 0.32. When the spring is released, (a) how far up the incline (with respect to its initial position) will the block slide before sliding back? (b) What is the speed of the block at the instant it is 0.43 m from its initial position? Solve by the Work-energy equation. ww 30° ww
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter8: Potential Energy And Conservation Of Energy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 79AP: Consider a block of mass 0.200 kg attached to a spring of spring constant 100 N/m. The block is...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
explain the solution
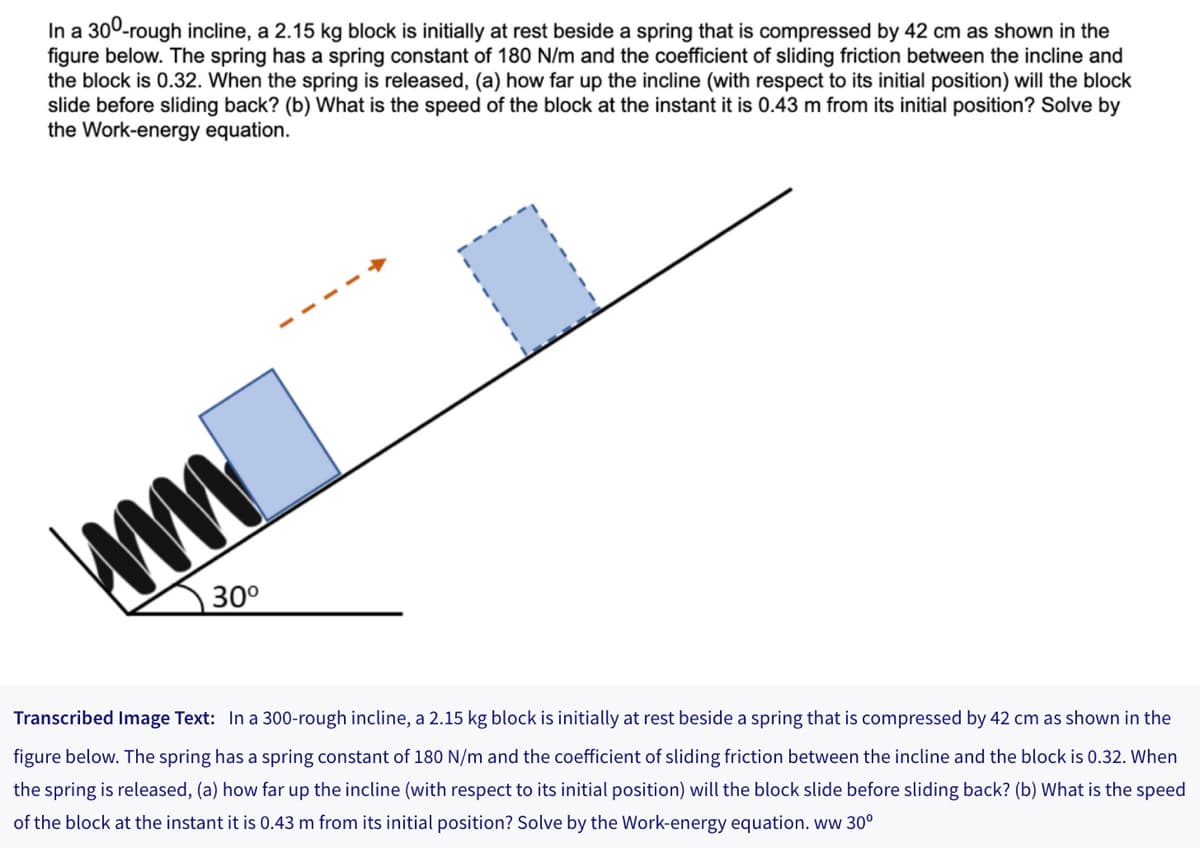
Transcribed Image Text:In a 300-rough incline, a 2.15 kg block is initially at rest beside a spring that is compressed by 42 cm as shown in the
figure below. The spring has a spring constant of 180 N/m and the coefficient of sliding friction between the incline and
the block is 0.32. When the spring is released, (a) how far up the incline (with respect to its initial position) will the block
slide before sliding back? (b) What is the speed of the block at the instant it is 0.43 m from its initial position? Solve by
the Work-energy equation.
1
ww
30⁰
Transcribed Image Text: In a 300-rough incline, a 2.15 kg block is initially at rest beside a spring that is compressed by 42 cm as shown in the
figure below. The spring has a spring constant of 180 N/m and the coefficient of sliding friction between the incline and the block is 0.32. When
the spring is released, (a) how far up the incline (with respect to its initial position) will the block slide before sliding back? (b) What is the speed
of the block at the instant it is 0.43 m from its initial position? Solve by the Work-energy equation. ww 30°

Transcribed Image Text:Free-Body Diagram
Fs
mg coso
v
30°
y
Sin 30= 4
भ
mg sino
mg
30°
Mass, m= 2.15 kg
Angle Q=30°
{ y = x/2
Compression, 5=0.42m
Spring Constant, K= 180 N/m
friction coefficient 4x= 0·32
Calculating spring force,
fs KXS =
Calculating the friction force,
f₁=
= xx my coso
-0.3242-15x9-8x (0830
2 8.26 N
The energy loss by the block to slid
х
Eloss = fix=8-26x
At the top the potential energy is.
P.Etop= mgh
Applying conservation of energy:
115² = mgly + Eloss
8.26x
180x (0-42)² = 215x9.8 xy +
:: Y= x/2
x=84.5 cm
(6)
Answer
when x=0.43m
0.43
Applying conservation of energy
1 mv² = 1 ks²_mgy - Fixy
215²x100x (0-42) ² - 1.25 x 9.8 x 0.43 8.26x 0-43
Vz 204 mls
2
= 180x 0.42=75-6N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning