In a generic chemical reaction involving reactants A and B and products C and D, aA + 6B>cC+ dD, the standard enthalpy A;H° of the reaction is given by A,H° = CA¢H° (C) +dA; H° (D) -aA; H°(A) – bA;H° (B) Notice that the stoichiometric coefficients, a, b, c d, are an important part of this equation. This formula is often generalized as follows, where the first sum on the right-hand side of the equation is a sum over the products and the second sum is over the reactants: A;H° =Lproducts nAç H° – Ereactants mAç H° where m and n represent the appropriate stoichiometric coefficients for each substance. Part A What is A,H° for the following chemical reaction? CO(g) + NH3(9)→HCN(g)+H2O(g) You can use the following table of standard heats of formation (Af H°) to calculate the enthalpy of the given reaction. Standard Heat of Standard Heat of Element/ Compound Formation Element/ Compound Formation (kJ mol-1) (kJ mol-') H(g) 218 N(g) 473 H2(9) O2 (g) NH3(g) 45.90 O(g) 249 CO(g) -110,5 H2O(g) -241.8 C(g) 71 HCN(g) 130.5 C(s) HNO3 (aq) -206.6 Express the standard enthalpy of reaction to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
In a generic chemical reaction involving reactants A and B and products C and D, aA + 6B>cC+ dD, the standard enthalpy A;H° of the reaction is given by A,H° = CA¢H° (C) +dA; H° (D) -aA; H°(A) – bA;H° (B) Notice that the stoichiometric coefficients, a, b, c d, are an important part of this equation. This formula is often generalized as follows, where the first sum on the right-hand side of the equation is a sum over the products and the second sum is over the reactants: A;H° =Lproducts nAç H° – Ereactants mAç H° where m and n represent the appropriate stoichiometric coefficients for each substance. Part A What is A,H° for the following chemical reaction? CO(g) + NH3(9)→HCN(g)+H2O(g) You can use the following table of standard heats of formation (Af H°) to calculate the enthalpy of the given reaction. Standard Heat of Standard Heat of Element/ Compound Formation Element/ Compound Formation (kJ mol-1) (kJ mol-') H(g) 218 N(g) 473 H2(9) O2 (g) NH3(g) 45.90 O(g) 249 CO(g) -110,5 H2O(g) -241.8 C(g) 71 HCN(g) 130.5 C(s) HNO3 (aq) -206.6 Express the standard enthalpy of reaction to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter6: Thermochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 68E: In a coffee-cup calorimeter, 1.60 g NH4NO3 is mixed with 75.0 g water at an initial temperature of...
Related questions
Question
ab
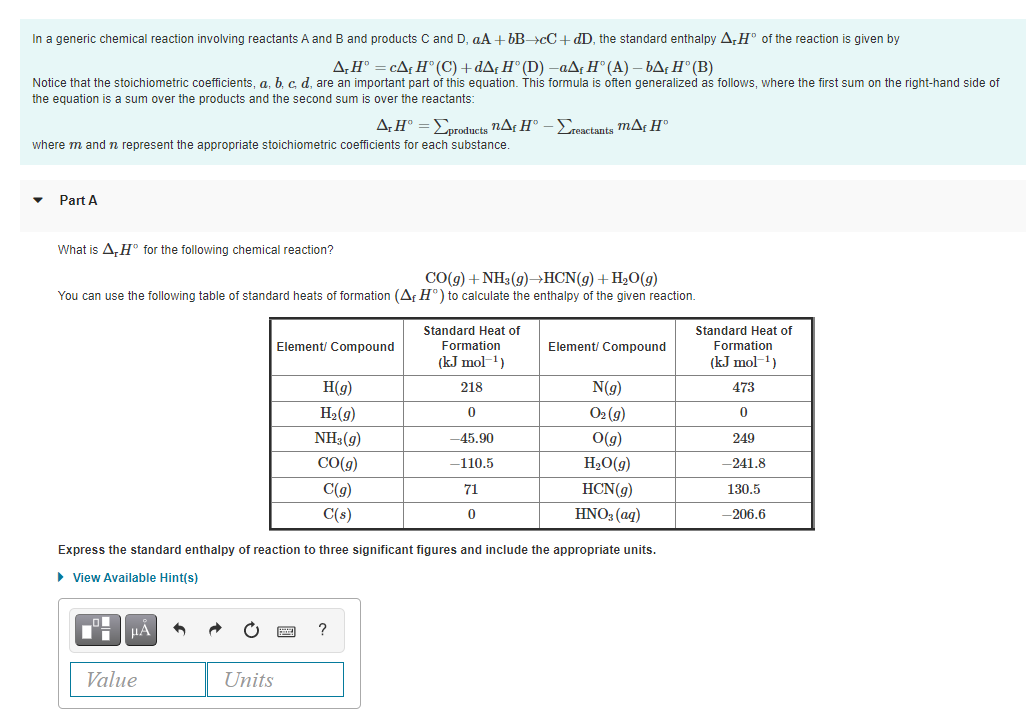
Transcribed Image Text:In a generic chemical reaction involving reactants A and B and products C and D, aA + 6B>cC+ dD, the standard enthalpy A,H° of the reaction is given by
A,H° = cA¢ H° (C) +dA¡ H° (D) -aAf H° (A) – bA;H° (B)
Notice that the stoichiometric coefficients, a, b, c d, are an important part of this equation. This formula is often generalized as follows, where the first sum on the right-hand side of
the equation is a sum over the products and the second sum is over the reactants:
A:H° =Eprodncts nAf H°
-Ereactants mAf H®
where m andn represent the appropriate stoichiometric coefficients for each substance.
Part A
What is A,H° for the following chemical reaction?
CO(g) + NH3 (9)→HCN(g) + H2O(g)
You can use the following table of standard heats of formation (Af H°) to calculate the enthalpy of the given reaction.
Standard Heat of
Formation
(kJ mol-1)
Standard Heat of
Element/ Compound
Element/ Compound
Formation
(kJ mol-1)
H(g)
218
N(g)
473
H2(g)
O2 (g)
NH3(g)
-45.90
O(g)
249
CO(g)
-110.5
H,0(g)
-241.8
C(g)
71
HCN(g)
130.5
C(s)
HNO3 (aq)
-206.6
Express the standard enthalpy of reaction to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
• View Available Hint(s)
HA
?
Value
Units
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning