In a strategy meeting, the Chief Operating Officer (COO) discusses production planning for the next year. She observes that, in recent years, the price we could charge depended not only on our own, but also on the main competitor's, decisions. When they supplied a lot of product, the price would drop. In fact, the behavior of the price has been estimated as follows: P = 630 - 15q1 - 15q2, where P is the market price, q₁ is the quantity sold by your company, and q2 is the quantity sold by your competitor. Since the price impacts the profitability of our choices, the COO says we need to plan flexibly until we get some sense of how the competitor is planning. You are being tasked with designing a strategy that responds to each possible output level q2 of the competitor with our best response q₁. In order to solve this problem, you decide to model the industry as a Cournot duopoly and find your company's reaction function. You shoot a quick e-mail to the COO to find out about costs of production. It turns out that the cost increases with every additional unit that is produced and can therefore be expressed as MC₁ = 5q1. The competitor uses the same technology and therefore has the same cost structure (i.e. MC2 5q2). Based on these data, you derive the reaction function for your firm as:
In a strategy meeting, the Chief Operating Officer (COO) discusses production planning for the next year. She observes that, in recent years, the price we could charge depended not only on our own, but also on the main competitor's, decisions. When they supplied a lot of product, the price would drop. In fact, the behavior of the price has been estimated as follows: P = 630 - 15q1 - 15q2, where P is the market price, q₁ is the quantity sold by your company, and q2 is the quantity sold by your competitor. Since the price impacts the profitability of our choices, the COO says we need to plan flexibly until we get some sense of how the competitor is planning. You are being tasked with designing a strategy that responds to each possible output level q2 of the competitor with our best response q₁. In order to solve this problem, you decide to model the industry as a Cournot duopoly and find your company's reaction function. You shoot a quick e-mail to the COO to find out about costs of production. It turns out that the cost increases with every additional unit that is produced and can therefore be expressed as MC₁ = 5q1. The competitor uses the same technology and therefore has the same cost structure (i.e. MC2 5q2). Based on these data, you derive the reaction function for your firm as:
Chapter1: Making Economics Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1QTC
Related questions
Question
1
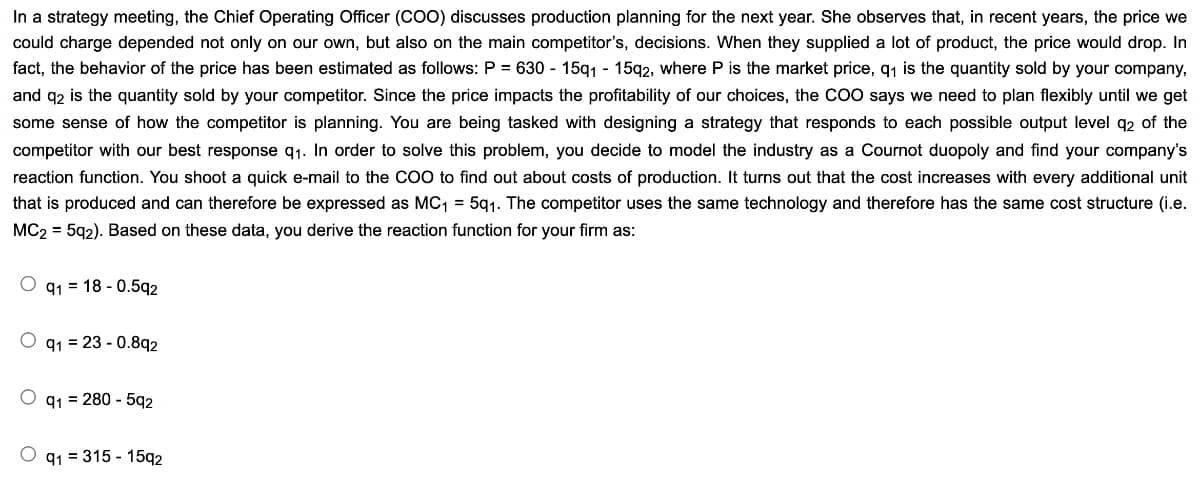
Transcribed Image Text:In a strategy meeting, the Chief Operating Officer (COO) discusses production planning for the next year. She observes that, in recent years, the price we
could charge depended not only on our own, but also on the main competitor's, decisions. When they supplied a lot of product, the price would drop. In
fact, the behavior of the price has been estimated as follows: P = 630-15q1 - 15q2, where P is the market price, q₁ is the quantity sold by your company,
and q2 is the quantity sold by your competitor. Since the price impacts the profitability of our choices, the COO says we need to plan flexibly until we get
some sense of how the competitor is planning. You are being tasked with designing a strategy that responds to each possible output level q2 of the
competitor with our best response q₁. In order to solve this problem, you decide to model the industry as a Cournot duopoly and find your company's
reaction function. You shoot a quick e-mail to the COO to find out about costs of production. It turns out that the cost increases with every additional unit
that is produced and can therefore be expressed as MC₁ = 5q1. The competitor uses the same technology and therefore has the same cost structure (i.e.
MC2 = 5q2). Based on these data, you derive the reaction function for your firm as:
Oq118 -0.592
O q1 23-0.892
Oq1= 280 - 592
91 = 315 - 1592
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-…
Economics
ISBN:
9781259290619
Author:
Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education