In a three-phase separator, gas, oil, and water are separated into layers of different depths. The graph on the right shows the cross-section of this separator. The height of the separator is 2 m. The distance from the oil surface to the top of the separator is 0.6 m, and the distance from the water surface to the bottom of the separator is 0.6 m. Gravity g = 9.81 m/s² .
In a three-phase separator, gas, oil, and water are separated into layers of different depths. The graph on the right shows the cross-section of this separator. The height of the separator is 2 m. The distance from the oil surface to the top of the separator is 0.6 m, and the distance from the water surface to the bottom of the separator is 0.6 m. Gravity g = 9.81 m/s² .
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305578296
Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Chapter1: Heat, Temperature, And Pressure
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6RQ: One British thermal unit will raise the temperature of _____ 1b of water _____F.
Related questions
Question
100%
kindly Solve it with detail . Graph of Cross section is also given below the question this is complete question . Thanks
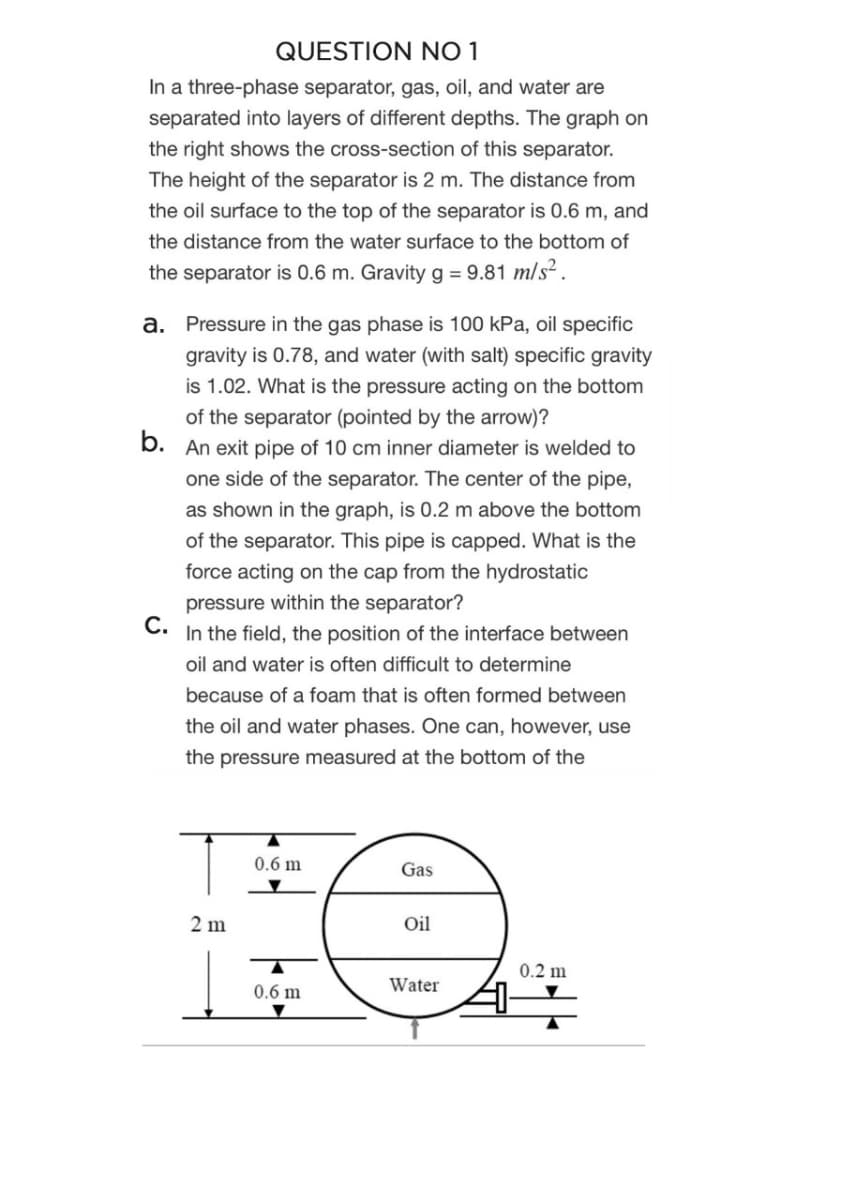
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION NO 1
In a three-phase separator, gas, oil, and water are
separated into layers of different depths. The graph on
the right shows the cross-section of this separator.
The height of the separator is 2 m. The distance from
the oil surface to the top of the separator is 0.6 m, and
the distance from the water surface to the bottom of
the separator is 0.6 m. Gravity g = 9.81 m/s² .
a. Pressure in the gas phase is 100 kPa, oil specific
gravity is 0.78, and water (with salt) specific gravity
is 1.02. What is the pressure acting on the bottom
of the separator (pointed by the arrow)?
b. An exit pipe of 10 cm inner diameter is welded to
one side of the separator. The center of the pipe,
as shown in the graph, is 0.2 m above the bottom
of the separator. This pipe is capped. What is the
force acting on the cap from the hydrostatic
pressure within the separator?
C.
In the field, the position of the interface between
oil and water is often difficult to determine
because of a foam that is often formed between
the oil and water phases. One can, however, use
the pressure measured at the bottom of the
0.6 m
Gas
2 m
Oil
0.2 m
0.6 m
Water
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781133612315
Author:
Jack Erjavec, Rob Thompson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781133612315
Author:
Jack Erjavec, Rob Thompson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning